|
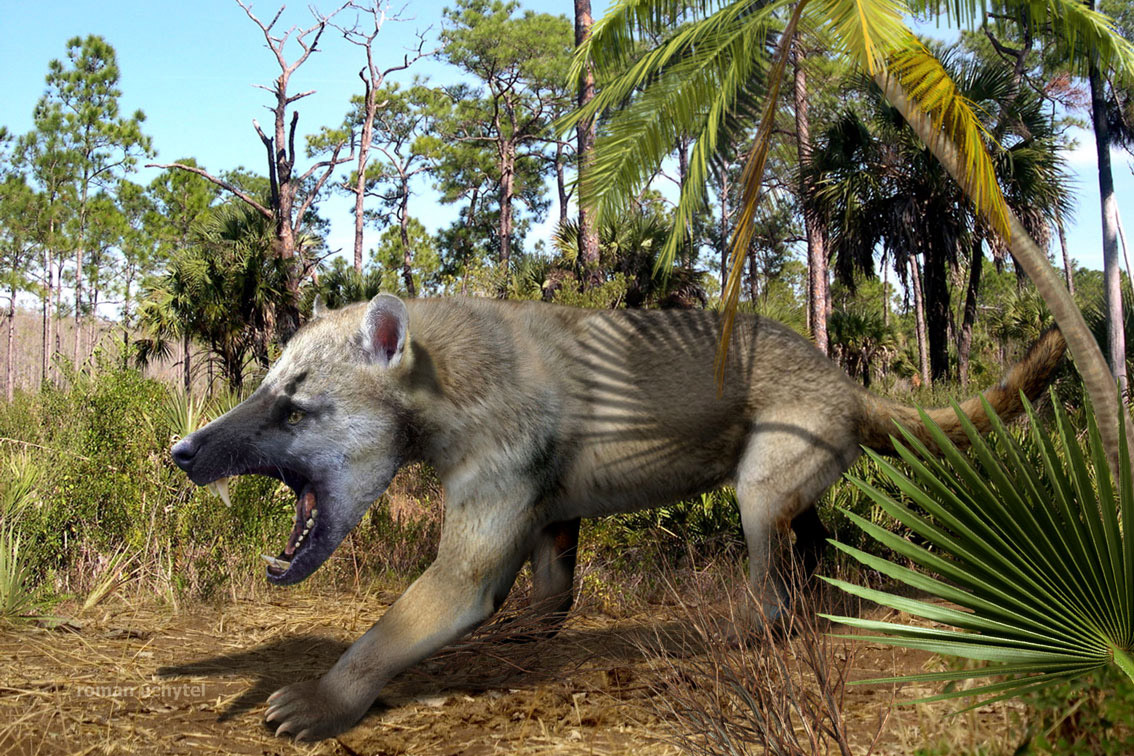
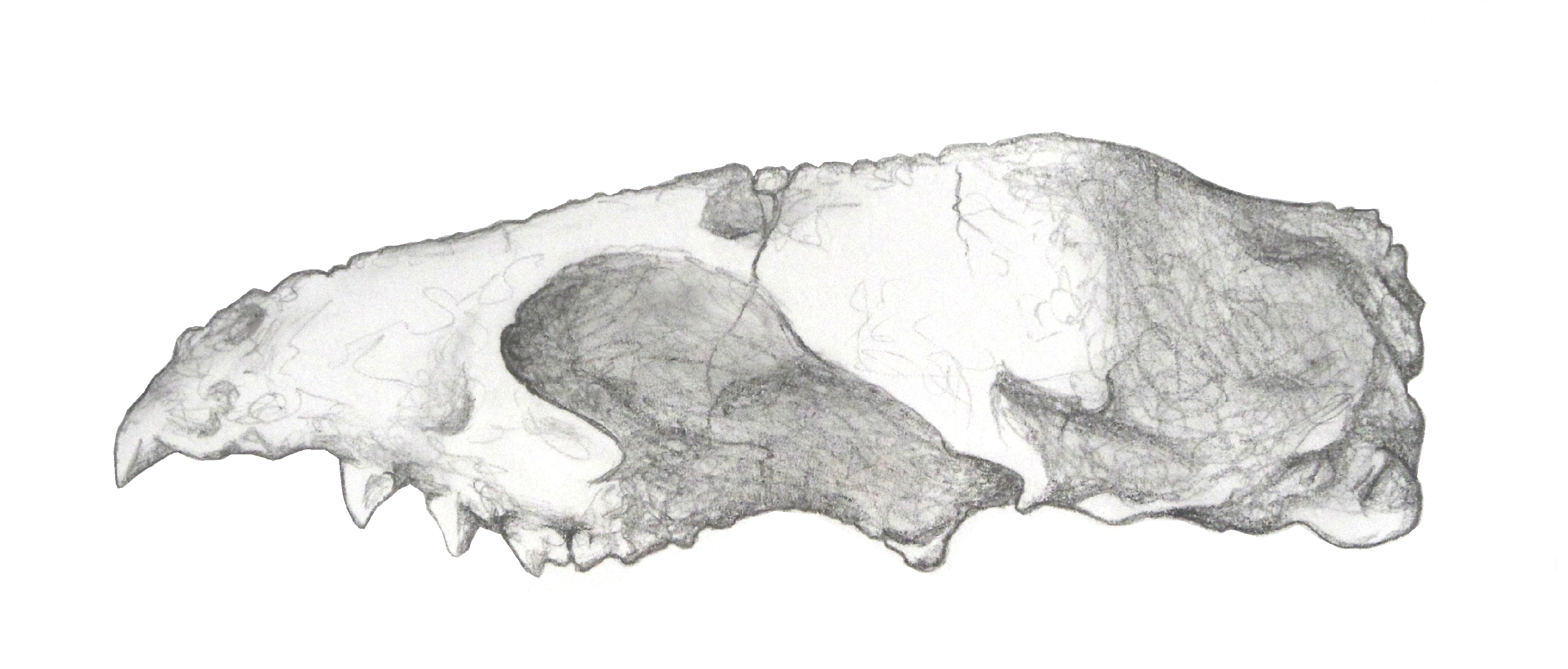
Lycophocyon Skull Lateral
''Lycophocyon'' is an extinct genus of caniformian carnivoran from Middle Eocene (early Duchesnean and possibly late Uintan NALMA) deposits of San Diego County, California. ''Lycophocyon'' is known from the holotype UCMP 85202, a partial left and right dentary. Paratypes include UCMP 170713, SDSNH 107658, SDSNH 107659, SDSNH 107442, SDSNH 107443 and SDSNH 107444, partial dentaries, mandibles and other cranial remains, and SDSNH 107446 and SDSNH 107447, cranial and postcranial fragments. Many additional specimens are also known. All specimens were collected from numerous localities, all of them from the upper portions of "member C" of the Santiago Formation. It was first named by Susumu Tomiya in 2011 and the type species is ''Lycophocyon hutchisoni''. The generic name means "twilight dog" in Greek, in references to its occurrence on the west coast of North America, and its affinity to the Caniformia. The specific name honours the paleontologist J. Howard Hutchison. Phylog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Of A Biological Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctoidea
Arctoidea is a clade of mostly carnivorous mammals which include the extinct Hemicyonidae (dog-bears), and the extant Musteloidea (weasels, raccoons, skunks, red pandas), Pinnipedia (seals, sea lions), and Ursidae (bears), found in all continents from the Eocene, , to the present. The oldest group of the clade is the bears, as their CMAH gene is still intact. The gene became non-functional in the common ancestor of the Mustelida (the musteloids and pinnipeds). Arctoids are caniforms, along with dogs (canids) and extinct bear dogs (Amphicyonidae). The earliest caniforms were superficially similar to martens, which are tree-dwelling mustelids. Together with feliforms, caniforms comprise the order Carnivora; sometimes Arctoidea can be considered a separate suborder from Caniformia and a sister taxon to Feliformia. Systematics Arctoidea was named by Flower (1869). It was reranked as the unranked clade Arctoidea by Hunt (2001), Hunt (2002) and Hunt (2002); it was reranked as the infrao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otarocyon
''Otarocyon'' ("large eared dog") is an extinct genus of the Borophaginae subfamily of canids native to North America. It lived during the Oligocene epoch, about 34—30 Ma (million years ago). Fossils have been found only in Montana, Wyoming, and South Dakota. ''Otarocyon'' was a small borophagine characterized by a short, broad skull, a specialized middle ear, simple, tall premolar teeth, and molars that are incipiently adapted to a hypocarnivorous diet. Despite its Oligocene age, the skull of ''Otarocyon'' shows several striking similarities to the living fennec fox, particularly in the structure of its middle ear. The similarities are probably convergent, but they suggest that ''Otarocyon'' may have been similar in its appearance and habits. Species *''O. macdonaldi'' Wang ''et al.'' 1999, Early Oligocene *''O. cooki'' Macdonald 1963, Late Oligocene In addition to its earlier age, ''O. macdonaldi'' differs from ''O. cooki'' in being smaller and in showing lesser devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperocyon
''Hesperocyon'' is an extinct genus of canids (subfamily Hesperocyoninae, family Canidae) that was endemic to North America, ranging from southern Canada to Colorado. It appeared during the Uintan age, – Bridgerian age (NALMA) of the Mid-Eocene– 42.5 Ma to 31.0 Ma. ( AEO). ''Hesperocyon'' existed for approximately . Taxonomy ''Hesperocyon'' was assigned to Borophagini by Wang et al. in 1999 and was the earliest of the canids to evolve after the Caniformia-Feliformia split some 42 million years ago. Fossil evidence dates ''Hesperocyon gregarius'' to at least 37 mya, but the oldest ''Hesperocyon'' has been dated at 39.74 mya from the Duchesnean North American land mammal age. The Canidae subfamily Hesperocyoninae probably arose out of ''Hesperocyon'' to become the first of the three great dogs groups: Hesperocyoninae (~40–30 Ma), Borophaginae (~36–2 Ma), and the Caninae lineage that led to the present-day canids (including grey wolves, foxes, coyotes, jackals and dogs). A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canidae
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found within the canid family, which are the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae, and the extant Caninae. The Caninae are known as canines, and include domestic dogs, wolves, coyotes, foxes, jackals and other extant and extinct species. Canids are found on all continents except Antarctica, having arrived independently or accompanied human beings over extended periods of time. Canids vary in size from the gray wolf to the fennec fox. The body forms of canids are similar, typically having long muzzles, upright ears, teeth adapted for cracking bones and slicing flesh, long legs, and bushy tails. They are mostly social animals, living together in family units or small groups and behaving cooperatively. Typically, only the dominant pair in a group bree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canoidea
Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs (wolves, foxes, etc.), bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia (seals, walruses and sea lions) are also assigned to this group. The center of diversification for the Caniformia is North America and northern Eurasia. Caniformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, the Feliformia ("cat-like" carnivorans), the center of diversification of which was in Africa and United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, southern Asia. Description Most members of this group have nonretractile claws (the Fisher (animal), fisher, marten, sea otter (Forepaw, forepaws only), red panda, and Bassariscus astutus, ringtail, and some foxes have retractile or semi-retractile claws) and tend to be plantigrade (with the exception of the Canidae). Other traits that separate the Caniformia from the Feliformia is that caniforms have longer jaws and more teeth, with less speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphoenus
''Daphoenus'' is an extinct genus of bear dogs. ''Daphoenus'' inhabited North America from the Middle Eocene to the Middle Miocene, 37.2—16.0 Mya, existing for approximately . Species ''D. hartshornianus'' fossils found in Oligocene Orellan rocks in the Lower Nodular Zone, Pennington County, South Dakota are dated at ~33.4 Ma. Other sites include the Prairie Dog Creek Site and Warbonnet Creek Site, Sioux County, Nebraska ~33.4 Ma., Bartlett High Site, Dawes County, Nebraska ~33.2 Ma., Babby Butte Site, Oglala Lakota County, South Dakota ~33.4 Ma—33.2 Ma. ''D. lambei'' fossils found in Eocene Duchesnean rocks at the Big Red Horizon Site, Presidio County, Texas are dated at ~38.4—38.3 Ma. Other sites include the Badwater Locality 20 Site and Wood Locality Site, Natrona County, Wyoming ~41.8 Ma., Lac Pelletier Lower Fauna Site, Saskatchewan ~42.3 Ma. ''D. ruber'' fossils were found in Oligocene Arikareean rocks in the Tecuya Canyon Formation of Kern County, California wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustafsonia
''Gustafsonia'' is an extinct genus of carnivoran belonging to the family Amphicyonidae (a bear dog). The type species, ''Gustafsonia cognita'', was described in 1986 by Eric Paul Gustafson, who originally interpreted it as a miacid and named it ''Miacis cognitus''. It was subsequently considered to be the only species of the diverse genus ''Miacis'' that belonged to the crown-group Carnivora, within the Caniformia, and it was ultimately assigned to the family Amphicyonidae. The type specimen or holotype was discovered in Reeve's bonebed, western Texas, in the Chambers Tuff Formation in 1986. The University of Texas holds this specimen. It is the only confirmed fossil of this species. Morphology Fossil The holotype is missing the mandible, upper canines, and zygomatic arch. The remainder of the skull is damaged, but relatively intact. Teeth It preserves the old style of many teeth, probably having forty-two, as compared to most modern carnivorans in the low thirties. With the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphicyonidae
Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestrial carnivorans belonging to the suborder Caniformia. They first appeared in North America in the middle Eocene (around 45 mya), spread to Europe by the late Eocene (35 mya), and appear in Asia, and Africa by the early Miocene (23 mya). They had largely disappeared worldwide by the late Miocene (8 mya), with the latest recorded species at the end of the Miocene in Pakistan. They were among the first carnivorans to evolve large body size. Later in their history, they came into competition with hesperocyonine and borophagine canids. As dogs evolved similar body sizes and cranial and dental adaptations, the rise of these groups may have led to their extinction. Amphicyonids are often colloquially referred to as "bear-dogs". Taxonomy The family was erected by Haeckel (1886) lso attributed to Trouessart (1885) Their exact position has long been disputed. Some early paleontologists defined them as members of the family Canidae, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |