|
Lucianovenator
''Lucianovenator'' is an extinct genus of coelophysidae, coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur which lived in Argentina during the Triassic. The genus name ''Lucianovenator'' translates to "Luciano's hunter", in reference to Don Luciano Leyes, who first reported the remains. The species name ''bonoi'' refers to Tulio del Bono, a local scientific authority who collaborated on the describers' research. It is one of the few Neotheropoda, neotheropods known from South America. Discovery The holotype (PVSJ 906) of ''Lucianovenator bonoi'' was found in the "Quebrada del puma" locality of the Quebrada del Barro Formation in Argentina, which is estimated to be from the late Norian to Rhaetian in age, approximately 210 to 202 million years ago. PVSJ 906 represents an articulated vertebral sequence from the third Cervical vertebrae, cervical to fourth dorsal vertebra, as well as a sacrum and a partial pelvis. In addition, three more specimens were referred to ''Lucianovenator''. These in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucianovenator Scale
''Lucianovenator'' is an extinct genus of coelophysidae, coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur which lived in Argentina during the Triassic. The genus name ''Lucianovenator'' translates to "Luciano's hunter", in reference to Don Luciano Leyes, who first reported the remains. The species name ''bonoi'' refers to Tulio del Bono, a local scientific authority who collaborated on the describers' research. It is one of the few Neotheropoda, neotheropods known from South America. Discovery The holotype (PVSJ 906) of ''Lucianovenator bonoi'' was found in the "Quebrada del puma" locality of the Quebrada del Barro Formation in Argentina, which is estimated to be from the late Norian to Rhaetian in age, approximately 210 to 202 million years ago. PVSJ 906 represents an articulated vertebral sequence from the third Cervical vertebrae, cervical to fourth dorsal vertebra, as well as a sacrum and a partial pelvis. In addition, three more specimens were referred to ''Lucianovenator''. These in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
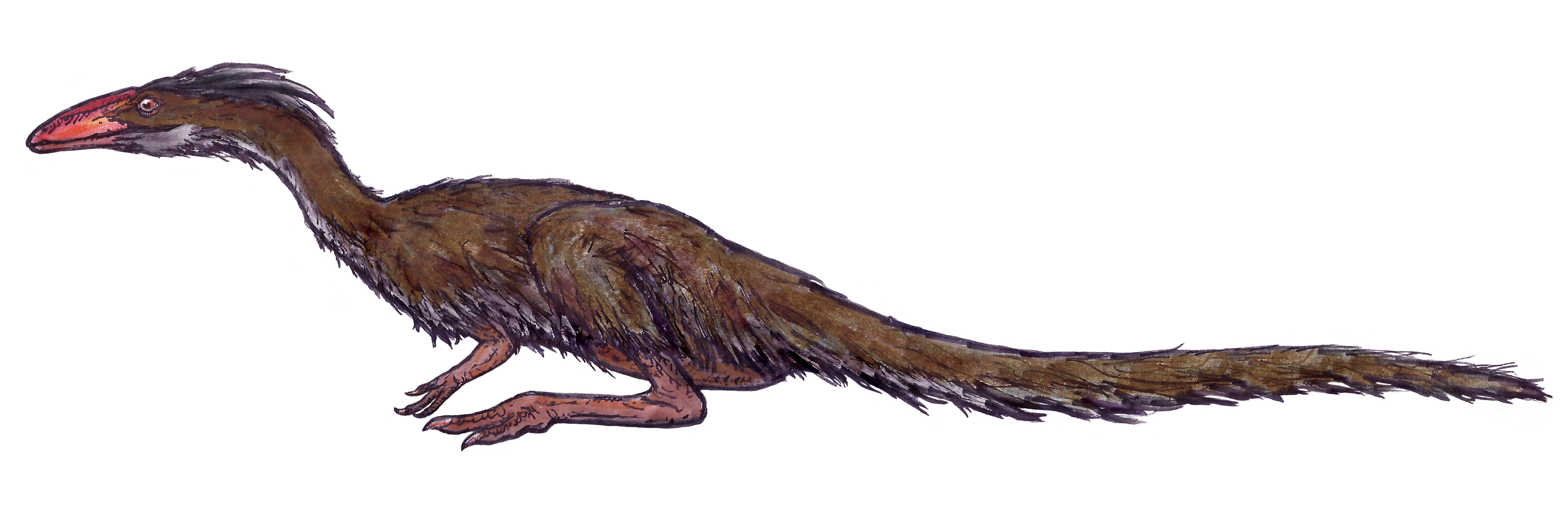
Coelophysidae
Coelophysidae is a family of primitive carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Most species were relatively small in size. The family flourished in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods, and has been found on numerous continents. Many members of Coelophysidae are characterized by long, slender skulls and light skeletons built for speed. One member genus, ''Coelophysis'', displays the earliest known furcula in a dinosaur. Under Cladistics, cladistic analysis, Coelophysidae was first defined by Paul Sereno in 1998 as the most recent common ancestor of ''Coelophysis, Coelophysis bauri'' and ''Procompsognathus, Procompsognathus triassicus'', and all of that common ancestor's descendants. However, Tykoski (2005) has advocated for the definition to change to include the additional taxa of Coelophysis kayentakatae, "Syntarsus" ''kayentakatae'' and ''Segisaurus halli''. Coelophysidae is part of the superfamily Coelophysoidea, which in turn is a subset of the larger Neotheropoda clade. As p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebrada Del Barro Formation
The Quebrada del Barro Formation is a geological formation of the Marayes-El Carrizal Basin in San Juan Province, Argentina. This formation is the most fossiliferous portion of the Triassic Marayes Group, and is also the youngest unit of the group, overlying the El Carrizal Formation. An unconformity at the top of the Quebrada del Barro Formation separates it from the Cretaceous-age Los Riscos Formation of the El Gigante Group.Gardini et al., 2009, p.554 Part of the formation may be made into a provincial park following the discovery of the fossils of ''Ingentia'', a giant sauropodomorph dinosaur which helped elucidate the early evolution of sauropods. Sedimentology The Quebrada del Barro Formation formed within a rift basin during a period of renewed fracturing. It encompasses of red sandstones, fine conglomerates, and diamictites. Early hypotheses on the depositional environment proposed that the sediments formed in an alluvial fan or braided river system, while a newer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysidae
Coelophysidae is a family of primitive carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. Most species were relatively small in size. The family flourished in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods, and has been found on numerous continents. Many members of Coelophysidae are characterized by long, slender skulls and light skeletons built for speed. One member genus, ''Coelophysis'', displays the earliest known furcula in a dinosaur. Under Cladistics, cladistic analysis, Coelophysidae was first defined by Paul Sereno in 1998 as the most recent common ancestor of ''Coelophysis, Coelophysis bauri'' and ''Procompsognathus, Procompsognathus triassicus'', and all of that common ancestor's descendants. However, Tykoski (2005) has advocated for the definition to change to include the additional taxa of Coelophysis kayentakatae, "Syntarsus" ''kayentakatae'' and ''Segisaurus halli''. Coelophysidae is part of the superfamily Coelophysoidea, which in turn is a subset of the larger Neotheropoda clade. As p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Coelophysoid Research
This timeline of coelophysoid research is a chronological listing of events in the History of paleontology, history of paleontology focused on the coelophysoids, a group of primitive theropod dinosaurs that were among Earth's dominant predators during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic epochs. Although formally trained scientists didn't discover coelophysoid fossils until the late : 19th century in paleontology, 19th century, Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans of the modern southwestern United States may have already encountered their fossils. Navajo people, Navajo creation mythology describes the early Earth as being inhabited by a variety of different kinds of monsters who hunted humans for food. These monsters were killed by storms and the heroic Monster Slayers, leaving behind their bones. As these tales were told in New Mexico not far from bonebeds of ''Coelophysis'', this dinosaur's remains may have been among the fossil remains that inspired the story. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis Rhodesiensis
''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μεγα = "big", 'απνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαυρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Africa. The species was a small to medium-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to long and weigh up to . It was originally given the genus name ''Syntarsus'', but that name was later determined to be preoccupied by a beetle. The species was subsequently given a new genus name, ''Megapnosaurus,'' by Ivie, Ślipiński & Węgrzynowicz in 2001. Some studies have classified it as a species within the genus ''Coelophysis,'' but this interpretation has been challenged by more subsequent studies and the genus is now considered valid. Discovery and history The first fossils of ''Megapnosaurus'' were found in 1963 by a group of students from Northlea S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camposaurus
''Camposaurus'' ( ) is a coelophysid dinosaur genus from the Norian stage of the Late Triassic period of North America. The pertinent fossil remains date back to the early to middle Norian stage, and is widely regarded as the oldest known neotheropod. Description ''Camposaurus'' is a small, carnivorous, theropod dinosaur. Its approximate length and weight cannot be reliably estimated because of the sparse material that is known from this genus. ''Camposaurus'' is known from partial lower leg bones, holotype UCMP 34498 (which includes distal tibiae, distal fibulae, and astragalocalcanea), and other fragmentary material. Like other coelophysids, it has fused tibio-tarsals and fibulo-tarsals. Unlike its relatives, the area of the tibia that fits with the fibula has a distinct ridge at the back. Another unique feature is the lack of a large medial condyle on the astragalus. The type species, ''C. arizonensis'', was formally named and described by Adrian Hunt, Spencer G. Lucas, Andre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neotheropoda
Neotheropoda (meaning "new theropods") is a clade that includes coelophysoids and more advanced theropod dinosaurs, and is the only group of theropods that survived the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. All neotheropods became extinct by the end of the Early Jurassic (Pliensbachian) period except for Averostra. Classification Neotheropoda was named by Robert T. Bakker in 1986 as a group including the relatively derived theropod subgroups Ceratosauria and Tetanurae, and excluding coelophysoids. However, most later researchers have used it to denote a broader group. Neotheropoda was first defined as a clade by Paul Sereno in 1998 as ''Coelophysis'' plus modern birds, which includes almost all theropods except the most primitive species.Sereno, 1998. A rationale for phylogenetic definitions, with application to the higher-level taxonomy of Dinosauria. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen. 210, 41-83. Dilophosauridae was formerly considered a small cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 In Archosaur Paleontology
The year 2017 in archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology is the scientific study of those animals, especially as they existed before the Holocene Epoch began about 11,700 years ago. The year 2017 in paleontology included various significant developments regarding archosaurs. This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that have been described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in the year 2017. General research * A study on the evolution of forelimb anatomy, musculature and joint ranges of motion from early archosaurs to sauropodomorph dinosaurs based on data from ''Mussaurus patagonicus'' and extant freshwater crocodile is published by Otero ''et al.'' (2017). Pseudosuchians Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period from the Carnian and Rhaetian faunal stages in what is now the southwestern United States. ''Megapnosaurus'' was once considered a species within this genus,Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Jurassic, Africa)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 535–536. but this interpretation has been challenged since 2017 and the genus ''Megapnosaurus'' is now considered valid. ''Coelophysis'' was a small, slenderly-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore that could grow up to long. It is one of the earliest known dinosaur genera. Scattered material representing similar animals has been found worldwide in some Late Tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysoids
Coelophysoidea were common dinosaurs of the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the coelurosaurs, with which they were formerly classified, and some species had delicate cranial crests. Sizes range from about 1 to 6 m in length. It is unknown what kind of external covering coelophysoids had, and various artists have portrayed them as either scaly or feathered. Some species may have lived in packs, as inferred from sites where numerous individuals have been found together. Examples of coelophysoids include ''Coelophysis'', ''Procompsognathus'' and ''Liliensternus''. Most dinosaurs formerly referred to as being in the dubious taxon "Podokesauridae" are now classified as coelophysoids. Classification Despite their very early occurrence in the fossil record, coelophysoids have a number of derived features that separate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taphonomic Bias
Taphonomy is the study of how organisms decay and become fossilized or preserved in the paleontological record. The term ''taphonomy'' (from Greek , 'burial' and , 'law') was introduced to paleontology in 1940 by Soviet scientist Ivan Efremov to describe the study of the transition of remains, parts, or products of organisms from the biosphere to the lithosphere. The term taphomorph is used to describe fossil structures that represent poorly-preserved, deteriorated remains of a mixture of taxonomic groups, rather than of a single one. Description Taphonomic phenomena are grouped into two phases: biostratinomy, events that occur between death of the organism and the burial; and diagenesis, events that occur after the burial. Since Efremov's definition, taphonomy has expanded to include the fossilization of organic and inorganic materials through both cultural and environmental influences. This is a multidisciplinary concept and is used in slightly different contexts througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


