|
Lono
In Hawaiian religion, the god Lono is associated with fertility, agriculture, rainfall, music and peace. In one of the many Hawaiian stories of Lono, he is a fertility and music god who descended to Earth on a rainbow to marry Laka. In agricultural and planting traditions, Lono was identified with rain and food plants. He was one of the four gods (with Kū, Kāne, and Kāne's twin brother Kanaloa)The Kumulipō, line 1714 who existed before the world was created. Lono was also the god of peace. In his honor, the great annual festival of the Makahiki was held. During this period (from October through February), war and unnecessary work was kapu (forbidden). In Hawaiian weather terminology, the winter Kona storms that bring rain to leeward areas are associated with Lono. Lono brings on the rains and dispenses fertility, and as such was sometimes referred to as Lono-makua (Lono the Provider). Ceremonies went through a monthly and yearly cycle. For 8 months of the year, the luakini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makahiki
The Makahiki season is the ancient Hawaiian New Year festival, in honor of the god Lono of the Hawaiian religion. It is a holiday covering four consecutive lunar months, approximately from October or November through February or March. The focus of this season was a time for men, women and chiefs to rest, strengthen the body, and have great feasts of commemoration (''ʻahaʻaina hoʻomanaʻo''). During Makahiki season labor was prohibited and there were days for resting and feasting. The Hawaiians gave thanks to the god Lonoikamakahiki for his care. He brought life, blessings, peace and victory to the land. They also prayed to the gods for the death of their enemies. ''Makaʻainana'' (commoners) prayed that lands of their ''aliʻi'' (chief) may be increased, and that their own physical health along with the health of their chiefs be at the fullest. In antiquity, many religious ceremonies occurred during this period. Commoners stopped work, made offerings to the chief or ''alii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Religion
Hawaiian religion refers to the indigenous religious beliefs and practices of native Hawaiians, also known as the kapu system. Hawaiian religion is based largely on the tapu religion common in Polynesia and likely originated among the Tahitians and other Pacific islanders who landed in Hawaii between 500 and 1300 AD. It is polytheistic and animistic, with a belief in many deities and spirits, including the belief that spirits are found in non-human beings and objects such as other animals, the waves, and the sky. It was only during the reign of Kamehameha I that a ruler from Hawaii island attempted to impose a singular "Hawaiian" religion on all the Hawaiian islands that was not Christianity. Today, Hawaiian religious practices are protected by the American Indian Religious Freedom Act. Traditional Hawaiian religion is unrelated to the modern New Age practice known as " Huna".Rothstein, Mikael, in Lewis, James R. and Daren Kemp. ''Handbook of New Age''. Brill Academic Publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
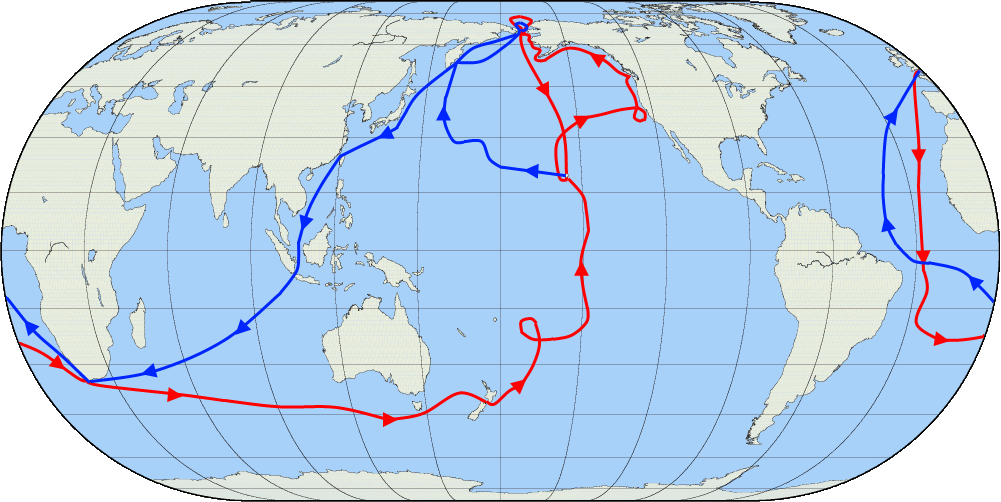
Third Voyage Of James Cook
James Cook's third and final voyage (12 July 1776 – 4 October 1780) took the route from Plymouth via Cape Town and Tenerife to New Zealand and the Hawaiian Islands, and along the North American coast to the Bering Strait. Its ostensible purpose was to return Omai, a young man from Raiatea, to his homeland, but the Admiralty used this as a cover for their plan to send Cook on a voyage to discover the Northwest Passage. HMS ''Resolution'', to be commanded by Cook, and HMS ''Discovery'', commanded by Charles Clerke, were prepared for the voyage which started from Plymouth in 1776. Omai was returned to his homeland and the ships sailed onwards, encountering the Hawaiian Archipelago, before reaching the Pacific coast of North America. The two charted the west coast of the continent and passed through the Bering Strait when they were stopped by ice from sailing either east or west. The vessels returned to the Pacific and called briefly at the Aleutians before retiring towar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand. Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years' War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keaweʻīkekahialiʻiokamoku
Keaweīkekahialiiokamoku (c. 1665 – c. 1725) was the king of Hawaii Island in the late 17th century. He was the great-grandfather of Kamehameha I, the first king of the Kingdom of Hawaii. He was a progenitor of the House of Keawe. Biography He was believed to have lived from 1665 to 1725. He was son of Keakealaniwahine, the ruling Queen of Hawaii and Kanaloakapulehu. He is sometimes referred to as King Keawe II, since prior to him there was already Keawenuiaumi. Keawe was surnamed "īkekahialiiokamoku". Keaweīkekahialiiokamoku, a strong leader, ruled over much of the Big Island. He is said to have been an enterprising and stirring chief, who traveled all over the eight islands, and obtained a reputation for bravery and prudent management of his island. It appears that in some manner he composed the troubles that had disturbed the peace during his mother's time; mainly the conflict between the independent I family of Hilo. It was not by force or by conquest, for in that case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kāne
In Hawaiian mythology, Kāne is considered the highest of the three major Hawaiian deities, along with Kū and Lono. He represented the god of procreation and was worshipped as ancestor of chiefs and commoners. Kāne is the creator and gives life associated with dawn, sun and sky. No human sacrifice or laborious ritual was needed in the worship of Kāne. In the Kumuhonua legend, he created Earth, bestowed upon it sea creatures, animals, plants, and created man and woman. Mythology The 1907 book '' Legends of Hawaii'' has the following account of creation involving Kāne. The author says that there are several versions of this story, probably due to waves of immigration from different areas of Polynesia at different times, but generally they agree on the major points. It says that in the beginning, there was nothing but Po; the endless black chaos. Then Kāne, sensing that he was separate from the Po, pulled himself free of Po by an act of sheer will. Sensing Kāne's presence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
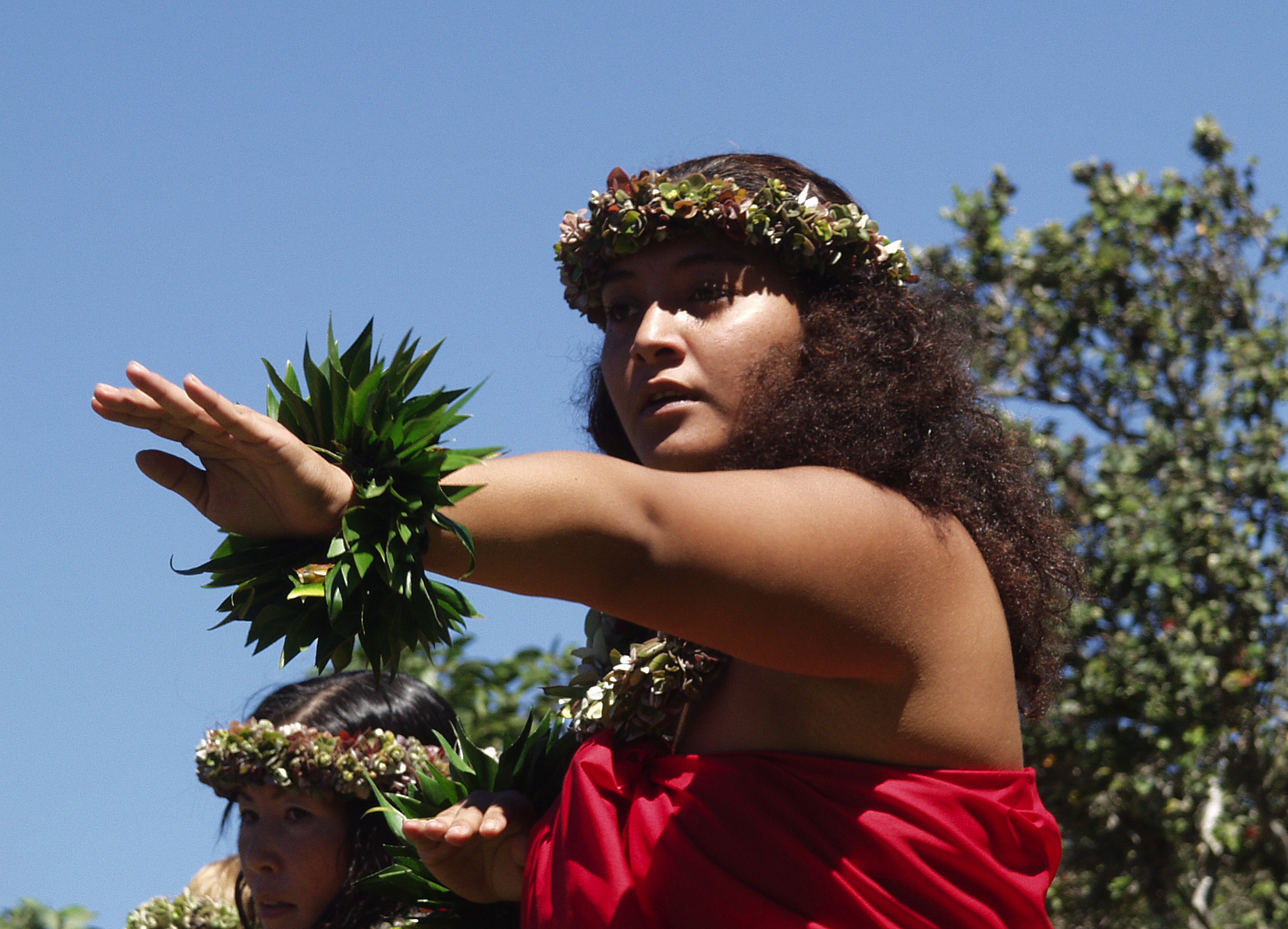
Hula
Hula () is a Hawaiian dance form accompanied by chant (oli) or song (Mele (Hawaiian language), mele). It was developed in the Hawaiian Islands by the Native Hawaiians who originally settled there. The hula dramatizes or portrays the words of the oli or mele in a visual dance form. There are many sub-styles of hula, with the main two categories being Hula ʻAuana and Hula Kahiko. Ancient hula, as performed before Western encounters with Hawaii, is called ''kahiko''. It is accompanied by chant and traditional instruments. Hula, as it evolved under Western influence in the 19th and 20th centuries, is called ''auana'' (a word that means "to wander" or "drift"). It is accompanied by song and Western-influenced musical instruments such as the guitar, the ukulele, ukulele, and the double bass. Terminology for two main additional categories is beginning to enter the hula lexicon: "Monarchy" includes any hula which were composed and choreographed during the 19th century. During that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesticated Plants And Animals Of Austronesia
One of the major Early human migrations, human migration events was the Maritime history, maritime Austronesian expansion, settlement of Austronesia, the islands of the Indo-Pacific by the Austronesian peoples, believed to have started from at least 5,500 to 4,000 Before Present, BP (3500 to 2000 BCE). These migrations were accompanied by a set of domesticated, semi-domesticated, and commensal plants and animals transported via outrigger canoe, outrigger ships and catamarans that enabled early Austronesians to thrive in the islands of Maritime Southeast Asia (also known as 'Island Southeast Asia'. e.g.: Philippines, Indonesia), Near Oceania (Melanesia), Remote Oceania (Micronesia and Polynesia), Madagascar, and the Comoros Islands. They include domesticated plants, crops and domesticated animals, animals believed to have originated from the Hemudu culture, Hemudu and Majiabang cultures in the hypothetical pre-Austronesian homelands in mainland China, as well as other plants and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamapuaʻa
In Hawaiian mythology, Kamapuaa ("hog child") is a hog-man fertility superhuman associated with Lono, the god of agriculture. The son of Hina and Kahikiula, the chief of Oahu, Kamapuaʻa was particularly connected with the island of Maui. A ''kupua'' (demigod), Kamapuaa is best known for his romantic pursuit of the fire goddess Pele, with whom he shared a turbulent relationship. Despite Pele's power, Kamapuaa's persistence allows him to turn her lava rock into fertile soil. He is linked with the '' humuhumunukunukuāpua'a'' (reef triggerfish), the state fish of Hawaiʻi. Lilikalā Kameʻeleihiwa describes him as "defiant of all authority, bold and untamed," and states that he "recalls the pig nature that is dormant in most people . . . . Treacherous and tender, he thirsts after the good things in life—adventure, love, and sensual pleasure . . . . Early life Kamapua’a was born to human parents, Kahikiula and Hina, on Oahu. He is recorded as having one brother, Kahikihonua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapu (Hawaiian Culture)
''Kapu'' is the ancient Hawaiian code of conduct of laws and regulations. The ''kapu'' system was universal in lifestyle, gender roles, politics and religion. An offense that was ''kapu'' was often a capital offense, but also often denoted a threat to spiritual power, or theft of ''mana''. ''Kapus'' were strictly enforced. Breaking one, even unintentionally, often meant immediate death, ''Koʻo kapu''. The concept is related to taboo and the '' tapu'' or ''tabu'' found in other Polynesian cultures. The Hawaiian word ''kapu'' is usually translated to English as "forbidden", though it also carries the meanings of "keep out", "no trespassing", "sacred", "consecrated", or "holy". The opposite of kapu is ''noa'', meaning "common" or "free". Kahili The ''Kahili'' were restrictions placed upon contact with chiefs (kings), but these also apply to all people of known spiritual power. ''Kapu Kū mamao'' means prohibited from a place of the chief, while ''Kalu noho'' was to assemble befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rongo
In Māori mythology, Rongo or Rongo-mā-Tāne (also Rongo-hīrea, Rongo-marae-roa, and Rongo-marae-roa-a-Rangi) is a major god (''atua'') of cultivated plants, especially kumara (spelled ''kūmara'' in Māori), a vital crop. Other crops cultivated by Māori in traditional times included taro, yams (''uwhi''), cordyline (''tī''), and gourds (''hue''). Because of their tropical origin, most of these crops were difficult to grow except in the far north of the North Island, hence the importance of Rongo in New Zealand. He was also an important god of agriculture and god of war in the southern Cook Islands, especially on Mangaia where the Akaoro marae and Orongo marae were centres of his worship; where cooked taro was offered to him cited in to assure success in battle and the fertility of land. A legend concerning Rongo flying the first kite is told in the waiting room of Walt Disney's Enchanted Tiki Room, in which Rongo is voiced by Ernest Tavares. Separation of the primo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliʻi
The aliʻi were the traditional nobility of the Hawaiian islands. They were part of a hereditary line of rulers, the ''noho aliʻi''. The word ''aliʻi'' has a similar meaning in the Samoan language and other Polynesian languages, and in Māori it is pronounced "ariki". Background In ancient Hawaiian society, the ''aliʻi'' were hereditary nobles (a social class or caste). The ''aliʻi'' consisted of the higher and lesser chiefs of the various levels on the islands. The ''noho aliʻi'' were the ruling chiefs. The ''aliʻi'' were believed to be descended from the deities. There were eleven classes of ''aliʻi'', of both men and women. These included the ''kahuna'' (priestesses and priests, experts, craftsmen, and canoe makers) as part of four professions practiced by the nobility. Each island had its own aliʻi nui, who governed their individual systems. ''Aliʻi'' continued to play a role in the governance of the Hawaiian islands until 1893, when Queen Liliʻuokalani was overt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)