|
List Of Nortel Protocols ...
* Nortel Simple Loop Prevention Protocol * Distributed Multi-Link Trunking * Distributed Split Multi-Link Trunking * InterSwitch Trunk * Metro Ethernet Routing Switch 8600 * Multi-link trunking * Nortel Discovery Protocol * Provider Backbone Bridge Traffic Engineering * R-SMLT * Split multi-link trunking * UNIStim * Virtual Link Aggregation Control Protocol protocols * Nortel Nortel Networks Corporation (Nortel), formerly Northern Telecom Limited, was a Canadian Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications and data networking equipment manufacturer headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. It was foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nortel Simple Loop Prevention Protocol
Simple Loop Prevention Protocol (SLPP) in computer networking is a data link layer protocol developed by Nortel (previously acquired by Avaya, now a part of by Extreme Networks) to protect against Layer 2 network loops. SLPP uses a small hello packet to detect network loops. The SLPP protocol checks packets from the originating switch and the peer switch in a SMLT configuration. Sending hello packets on a per VLAN basis allows SLPP to detect VLAN based network loops for un-tagged as well as tagged IEEE 802.1Q VLAN link configurations. If a loop is detected, the associated port is shut down. Compatible equipment * Avaya VSP 9000 Series - Software version 3.0 or above * Avaya VSP 7000 Series - Software version 10.0 or above * Avaya ERS 8600 The Avaya Ethernet Routing Switch 8600 or ERS 8600, previously known as the ''Passport 8600'' or the ''Accelar 8000'', is a modular chassis combination hardware router and switch used in computer networking. The system, originally designed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
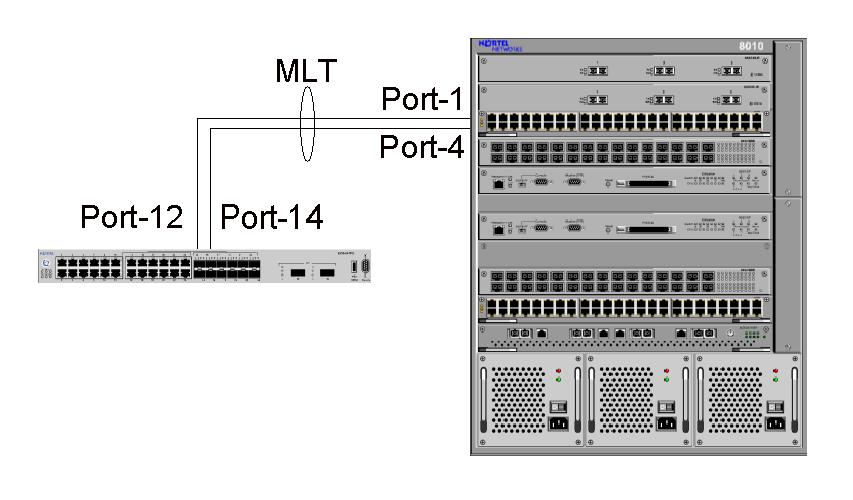
Distributed Multi-Link Trunking
Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers. MLT allows the use of several links (from 2 up to 8) and combines them to create a single fault-tolerant link with increased bandwidth. This produces server-to-switch or switch-to-switch connections that are up to 8 times faster. Prior to MLT and other aggregation techniques, parallel links were underutilized due to Spanning Tree Protocol’s loop protection. Fault-tolerant design is an important aspect of Multi-Link Trunking technology. Should any one or more than one link fail, the MLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. This automatic redistribution is accomplished in less than half a second (typically less than 100 millisecond) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterSwitch Trunk
InterSwitch Trunk (IST) is one or more parallel point-to-point links ( Link aggregation) that connect two switches together to create a single logical switch. The IST allows the two switches to share addressing information, forwarding tables, and state information, permitting rapid (less than one second) fault detection and forwarding path modification. The link may have different names depending on the vendor. For example, Brocade calls this an Inter-Chassis Link (ICL). Cisco calls this a VSL (Virtual Switch Link). Edge switches, servers or PCs see the two aggregate switches as one large switch. This allows any vendor's equipment configured to use the IEEE 802.3ad static link aggregation protocol to connect to both switches and take advantage of load balancing, redundant connections. The IST protocol was developed by Nortel (now acquired by Avaya, which is now acquired by Extreme Networks) to enhance the capabilities of Link aggregation, and is required to be configured prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metro Ethernet Routing Switch 8600
Metro Ethernet Routing Switch 8600 or MERS 8600 is a modular chassis router and/or switch manufactured by Nortel now acquired by Ciena. The MERS 8600 supports the Provider Backbone Bridges (PBB), Provider Backbone Transport (PBT) technologies and carrier class Operations Administration & Maintenance (OAM) tools. Configurable as a 1.440 Terabit Switch cluster using SMLT and RSMLT protocols, cluster failover (normally less than 100 millisecond). BT uses the MERS 8600 PBB/PBT technologies in its 21st Century Network (21CN) and India has selected this platform for the most extensive IP network ever deployed by an international airport in India. The MERS 8600 has 3 chassis options * 8006, 6-slot chassis for backbones of low density or high space premium * 8010, 10-slot chassis for high availability and high scalability * 8010CO, 10-slot NEBS-compliant chassis. The chassis can be configured with one or two CPU modules (8692SF), and is normally configured with two or three load b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-link Trunking
Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers. MLT allows the use of several links (from 2 up to 8) and combines them to create a single fault-tolerant link with increased bandwidth. This produces server-to-switch or switch-to-switch connections that are up to 8 times faster. Prior to MLT and other aggregation techniques, parallel links were underutilized due to Spanning Tree Protocol’s loop protection. Fault-tolerant design is an important aspect of Multi-Link Trunking technology. Should any one or more than one link fail, the MLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. This automatic redistribution is accomplished in less than half a second (typically less than 100 millisecond) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nortel Discovery Protocol
The Nortel Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a data link layer (OSI Layer 2) network protocol for discovery of Nortel networking devices and certain products from Avaya and Ciena. The device and topology information may be graphically displayed network management software. The Nortel Discovery Protocol had its origin in the SynOptics Network Management Protocol (SONMP), developed before the SynOptics and Wellfleet Communications merger in 1994. The protocol was rebranded as the Bay Network Management Protocol (BNMP) and some protocol analyzers referenced it as the ''Bay Discovery Protocol'' (BDP). Four years later, in 1998, Bay Networks was acquired by Nortel and renamed it to Nortel Discovery Protocol. The IEEE 802.1AB or Link Layer Discovery Protocol The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on a local area network based on IEEE 802 technology, principally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provider Backbone Bridge Traffic Engineering
Provider Backbone Bridge Traffic Engineering (PBB-TE) is an approved telecommunications networking standard, IEEE 802.1Qay-2009. PBB-TE adapts Ethernet technology to carrier class transport networks. It is based on the layered VLAN tags and MAC-in-MAC encapsulation defined in IEEE 802.1ah (Provider Backbone Bridges (PBB)), but it differs from PBB in eliminating flooding, dynamically created forwarding tables, and spanning tree protocols. Compared to PBB and its predecessors, PBB-TE behaves more predictably and its behavior can be more easily controlled by the network operator, at the expense of requiring up-front connection configuration at each bridge along a forwarding path. PBB-TE Operations, Administration, and Management (OAM) is usually based on IEEE 802.1ag. It was initially based on Nortel's Provider Backbone Transport (PBT). PBB-TE's connection-oriented features and behaviors, as well as its OAM approach, are inspired by SDH/SONET. PBB-TE can also provide path protecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-SMLT
Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers. MLT allows the use of several links (from 2 up to 8) and combines them to create a single fault-tolerant link with increased bandwidth. This produces server-to-switch or switch-to-switch connections that are up to 8 times faster. Prior to MLT and other aggregation techniques, parallel links were underutilized due to Spanning Tree Protocol’s loop protection. Fault-tolerant design is an important aspect of Multi-Link Trunking technology. Should any one or more than one link fail, the MLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. This automatic redistribution is accomplished in less than half a second (typically less than 100 millisecond) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIStim
UNIStim (or Unified Networks IP Stimulus) is a deprecated Telecommunications protocol developed by Nortel (now acquired by Avaya) for IP Phone (terminals and soft phones) and IP PBX communications. Most manufacturers of IP PBX equipment (Aastra, Alcatel, Avaya...) have followed the same path, developing their own proprietary protocols. These protocols are being gradually replaced or complemented by standardized protocols, including H.323, especially SIP. Operating principle The protocols works through a "master" / "slave" mode of operations. They simply reflect the basic actions a user can perform on his terminal (such as press a button) and the commands that can be sent to the display through the network to the terminal (such as turn a light on or display a message ). The "stimulus" can implement easily any new facility telephone without having to modify the software embedded in the terminals, which simplifies the procedures for maintenance and upgrade of the installed base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Virtual LACP (VLACP) is an Avaya extension of the Link Aggregation Control Protocol to provide a Layer 2 handshaking protocol which can detect end-to-end failure between two physical Ethernet interfaces. It allows the switch to detect unidirectional or bi-directional link failures irrespective of intermediary devices and enables link recovery in less than one second. With VLACP, far-end failures can be detected, which allows a Link aggregation trunk to fail over properly when end-to-end connectivity is not guaranteed for certain links through the internet in an aggregation group. When a remote link failure is detected, the change is propagated to the partner port. See also * MLT * SMLT * RSMLT Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, a ... External links Virtual Link Aggregatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |