|
Virtual Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Virtual LACP (VLACP) is an Avaya extension of the Link Aggregation Control Protocol to provide a Layer 2 handshaking protocol which can detect end-to-end failure between two physical Ethernet interfaces. It allows the switch to detect unidirectional or bi-directional link failures irrespective of intermediary devices and enables link recovery in less than one second. With VLACP, far-end failures can be detected, which allows a Link aggregation trunk to fail over properly when end-to-end connectivity is not guaranteed for certain links through the internet in an aggregation group. When a remote link failure is detected, the change is propagated to the partner port. See also * MLT * SMLT * RSMLT Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, a ... External links Virtual Link Aggregatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avaya
Avaya Holdings Corp., often shortened to Avaya (), is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Durham, North Carolina, that provides cloud communications and workstream collaboration services. The company's platform includes unified communications (UCaaS), contact center other services. The company provides services to 220,000 customer locations in 190 countries. History In 1995, Lucent Technologies was spun off from AT&T, and Lucent subsequently spun off units of its own in an attempt to restructure its struggling operations. ">/sup> Avaya was then spun off from Lucent as its own company in 2000 (Lucent merged with Alcatel SA in 2006, becoming Alcatel-Lucent, which was purchased in turn by Nokia in 2016). It remained a public company from 2000 to 2007. In October 2007, Avaya was acquired by two private-equity firms, TPG Capital and Silver Lake Partners, for $8.2 billion. On January 19, 2017, Avaya filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy. On December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining (wikt:aggregation, aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods, in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, to provide redundancy (engineering), redundancy in case one of the links should fail, or both. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports. Other umbrella terms used to describe the concept include trunking, bundling, bonding, channeling or teaming. Implementation may follow vendor-independent standards such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet, defined in #802.1AX, IEEE 802.1AX or the previous #802.3ad, IEEE 802.3ad, but also proprietary protocols. Motivation Link aggregation increases the bandwidth and resilience of Ethernet connections. Bandwidth requirements do not scale linearly. Ethernet bandwidths historically have increased tenfold each generation: 10 megabit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Aggregation
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods, in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, to provide redundancy in case one of the links should fail, or both. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports. Other umbrella terms used to describe the concept include trunking, bundling, bonding, channeling or teaming. Implementation may follow vendor-independent standards such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet, defined in IEEE 802.1AX or the previous IEEE 802.3ad, but also proprietary protocols. Motivation Link aggregation increases the bandwidth and resilience of Ethernet connections. Bandwidth requirements do not scale linearly. Ethernet bandwidths historically have increased tenfold each generation: 10 megabit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1000 Mbit/s, 10,000 Mbit/s. If one started to bum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
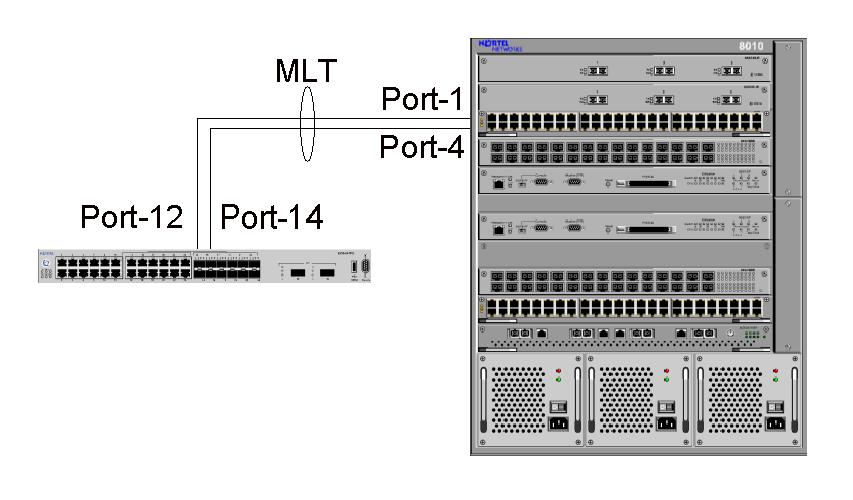
Multi-link Trunking
Multi-link trunking (MLT) is a link aggregation technology developed at Nortel in 1999. It allows grouping several physical Ethernet links into one logical Ethernet link to provide fault-tolerance and high-speed links between routers, switches, and servers. MLT allows the use of several links (from 2 up to 8) and combines them to create a single fault-tolerant link with increased bandwidth. This produces server-to-switch or switch-to-switch connections that are up to 8 times faster. Prior to MLT and other aggregation techniques, parallel links were underutilized due to Spanning Tree Protocol’s loop protection. Fault-tolerant design is an important aspect of Multi-Link Trunking technology. Should any one or more than one link fail, the MLT technology will automatically redistribute traffic across the remaining links. This automatic redistribution is accomplished in less than half a second (typically less than 100 millisecond) so no outage is noticed by end users. This high speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses coaxial cable as a shared medium, while the newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. The Ethernet standards include several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer. Systems communicating over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Protocols
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses pre-determined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Topology
Network topology is the arrangement of the elements ( links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network. Network topology can be used to define or describe the arrangement of various types of telecommunication networks, including command and control radio networks, industrial fieldbusses and computer networks. Network topology is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically. It is an application of graph theory wherein communicating devices are modeled as nodes and the connections between the devices are modeled as links or lines between the nodes. Physical topology is the placement of the various components of a network (e.g., device location and cable installation), while logical topology illustrates how data flows within a network. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, or signal types may differ between two different networks, yet their logical topologies may be identical. A network’s physical topology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |