|
Lissacresig
Lissacresig is a ringfort (rath) and National Monument (#571) located in County Cork, Ireland. Location Lissacresig is located 6.7 km west-northwest of Macroom, in the hills between the River Sullane and River Foherish. History and description Lissacresig is a circular ''lios'', in diameter with entrances in the southwest and northeast corners. The name means "ringfort of the glutton." Ringforts of this type were mostly built c. AD 550–900. Internally people were housed in wooden huts. Another fort lies 900 m to the northwest; this may have served as a livestock enclosure. There are three monoliths (gallauns) and an axial stone circle An axial stone circle is a megalithic ring of stones of a particular design found in County Cork and County Kerry in southwest Ireland. Archaeologists have found it convenient to consider the axial five-stone circle and axial multiple-stone circ ... in the area as well. The stone circle is formed of five large boulders; unusually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
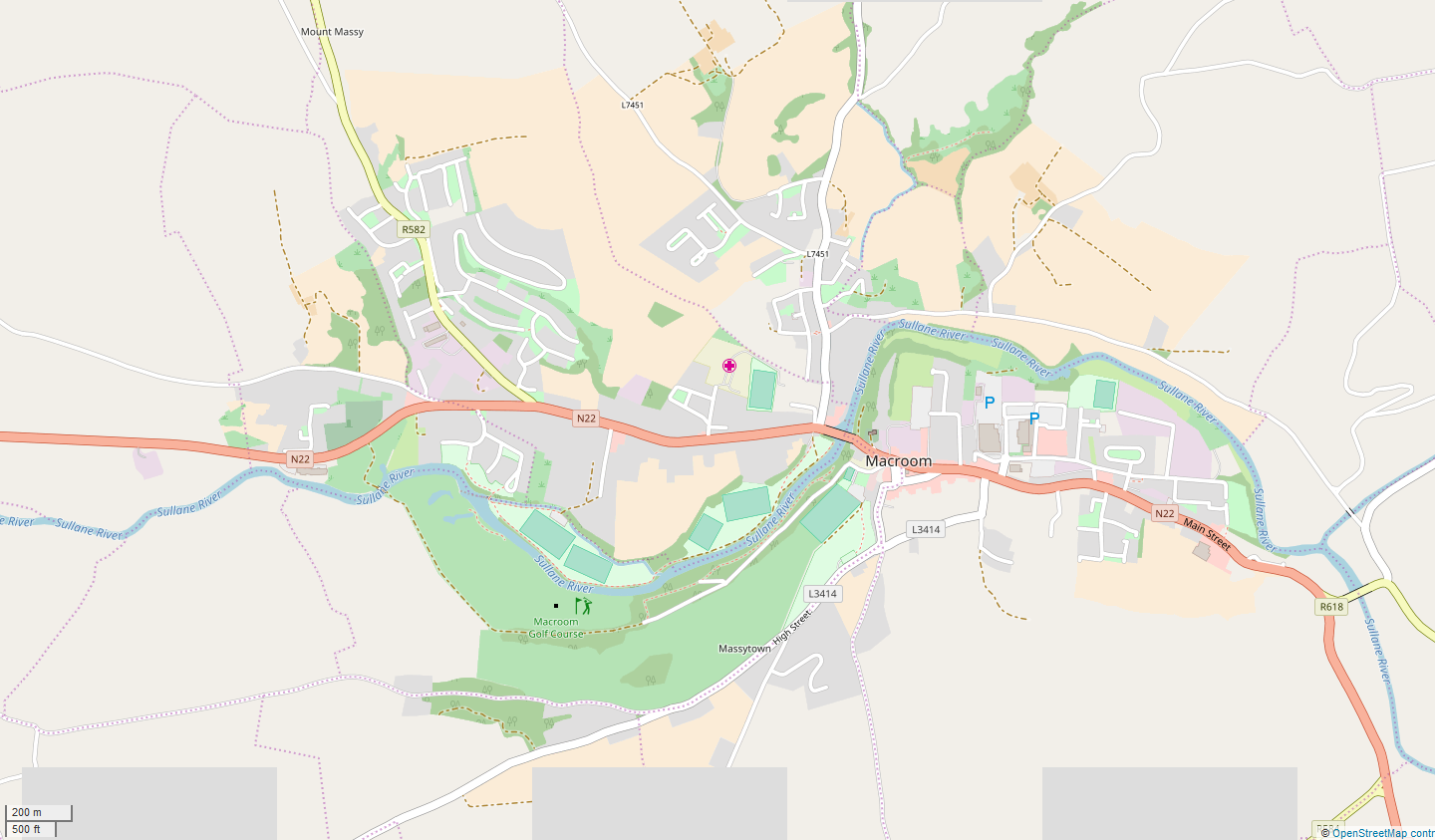
Macroom
Macroom (; ga, Maigh Chromtha) is a market town in County Cork, Ireland, located in the valley of the River Sullane, halfway between Cork city and Killarney. Its population has grown and receded over the centuries as it went through periods of war, famine and workhouses, forced emigration and intermittent prosperity. The 2011 census gave an urban population of 3,879 people, while the 2016 census recorded 3,765 people. Macroom began as a meeting place for the druids of Munster. It is first mentioned is in 6th-century records, and the immediate area hosted a major battle involving the Irish king Brian Boru. During the middle ages, the town was invaded by a succession of warring clans, including the Murcheatach Uí Briain and Richard de Cogan families. In the early modern period the MacCarthy's took control and later the area found prosperity via milling. The MacCarthys built a series of tower houses, some of which survive. The family lost influence during the Williamite wars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are Mallow, Macroom, Midleton, and Skibbereen. the county had a population of 581,231, making it the third- most populous county in Ireland. Cork County Council is the local authority for the county, while Cork City Council governs the city of Cork and its environs. Notable Corkonians include Michael Collins, Jack Lynch, Roy Keane, Sonia O'Sullivan and Cillian Murphy. Cork borders four other counties: Kerry to the west, Limerick to the north, Tipperary to the north-east and Waterford to the east. The county contains a section of the Golden Vale pastureland that stretches from Kanturk in the north to Allihies in the south. The south-west region, including West Cork, is one of Ireland's main tourist destinations, known for its rugged coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringfort
Ringforts, ring forts or ring fortresses are circular fortified settlements that were mostly built during the Bronze Age up to about the year 1000. They are found in Northern Europe, especially in Ireland. There are also many in South Wales and in Cornwall, where they are called rounds. Ringforts come in many sizes and may be made of stone or earth. Earthen ringforts would have been marked by a circular rampart (a bank and ditch), often with a stakewall. Both stone and earthen ringforts would generally have had at least one building inside. Distribution Ireland In Irish language sources they are known by a number of names: ' (anglicised ''rath'', also Welsh ''rath''), ' (anglicised ''lis''; cognate with Cornish '), ' (anglicised ''cashel''), ' (anglicised ''caher'' or ''cahir''; cognate with Welsh ', Cornish and Breton ') and ' (anglicised ''dun'' or ''doon''; cognate with Welsh and Cornish ').Edwards, Nancy. ''The Archaeology of Early Medieval Ireland''. Routledge, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Stone Circle
An axial stone circle is a megalithic ring of stones of a particular design found in County Cork and County Kerry in southwest Ireland. Archaeologists have found it convenient to consider the axial five-stone circle and axial multiple-stone circle separately. The circle has an approximate axis of symmetry aligned in a generally northeast–southwest direction. The stone at the southwest side of the circle, rather than being an upright orthostat like all the rest, is a slab lying horizontally with its long thin edge along the circumference of the ring. Because it marks the axis of the circle it is called the axial stone. Constructed in the Bronze Age, axial stone circles have an odd number of stones with two stones placed on either side of where the axis crosses the northeast side of the ring. The pair of uprights is generally taller that any of the others and they frame what is sometimes regarded as the entrance, or portal, to the ring. For this reason these two stones are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland ( ga, Éire Ghaelach) was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the early 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans conquered parts of Ireland in the 1170s. Thereafter, it comprised that part of the country not under foreign dominion at a given time (i.e. the part beyond The Pale). For most of its history, Gaelic Ireland was a "patchwork" hierarchy of territories ruled by a hierarchy of kings or chiefs, who were chosen or elected through tanistry. Warfare between these territories was common. Occasionally, a powerful ruler was acknowledged as High King of Ireland. Society was made up of clans and, like the rest of Europe, was structured hierarchically according to class. Throughout this period, the economy was mainly pastoral and money was generally not used. A Gaelic Irish style of dress, music, dance, sport and art can be identified, with Irish art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest on Earth. Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Sullane
The River Sullane ( ga, An Sulán) runs from the mountains between County Cork and County Kerry in southern Ireland, near the village of Cúil Aodha. After passing Ballyvourney, it runs through the centre of Macroom, to which it provides drinking water (and occasionally floods). The Sullane is joined by the River Bohill at Ballyvourney, the River Foherish at Clondrohid, about 5 kilometres west of Macroom and the River Launa locally known as "The Launey" one kilometre east of the town. The Sullane joins the River Lee a further kilometre east. It is well stocked with trout, and also contains European perch (200 g average), minnow and a small number of pike Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to: Fish * Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus'' * Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes * ''Esox'', genus of .... References Sullane {{Ireland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Foherish
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, " burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringfort
Ringforts, ring forts or ring fortresses are circular fortified settlements that were mostly built during the Bronze Age up to about the year 1000. They are found in Northern Europe, especially in Ireland. There are also many in South Wales and in Cornwall, where they are called rounds. Ringforts come in many sizes and may be made of stone or earth. Earthen ringforts would have been marked by a circular rampart (a bank and ditch), often with a stakewall. Both stone and earthen ringforts would generally have had at least one building inside. Distribution Ireland In Irish language sources they are known by a number of names: ' (anglicised ''rath'', also Welsh ''rath''), ' (anglicised ''lis''; cognate with Cornish '), ' (anglicised ''cashel''), ' (anglicised ''caher'' or ''cahir''; cognate with Welsh ', Cornish and Breton ') and ' (anglicised ''dun'' or ''doon''; cognate with Welsh and Cornish ').Edwards, Nancy. ''The Archaeology of Early Medieval Ireland''. Routledge, 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluttony
Gluttony ( la, gula, derived from the Latin ''gluttire'' meaning "to gulp down or swallow") means over-indulgence and over-consumption of food, drink, or wealth items, particularly as status symbols. In Christianity, it is considered a sin if the excessive desire for food causes it to be withheld from the needy.Okholm, Dennis"Rx for Gluttony" ''Christianity Today'', Vol. 44, No. 10, September 11, 2000, p.62 Some Christian denominations consider gluttony one of the seven deadly sins. Etymology In Deut 21:20 and Proverbs 23:21, it is זלל. The Gesenius Entry (lower left word) has indications of "squandering" and "profligacy" (waste). In Matthew 11:19 and Luke 7:34, it is φαγος ("" transliterated character for character), The LSJ Entry is tiny, and only refers to one external source, Zenobius Paroemiographus 1.73. The word could mean merely "an eater", since φαγω means "eat" In religion Judaism Rambam, for example, prohibits excessive eating and drinking in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In County Cork
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Co_Roscommon%2C_Ireland.jpg)





.jpg)