|
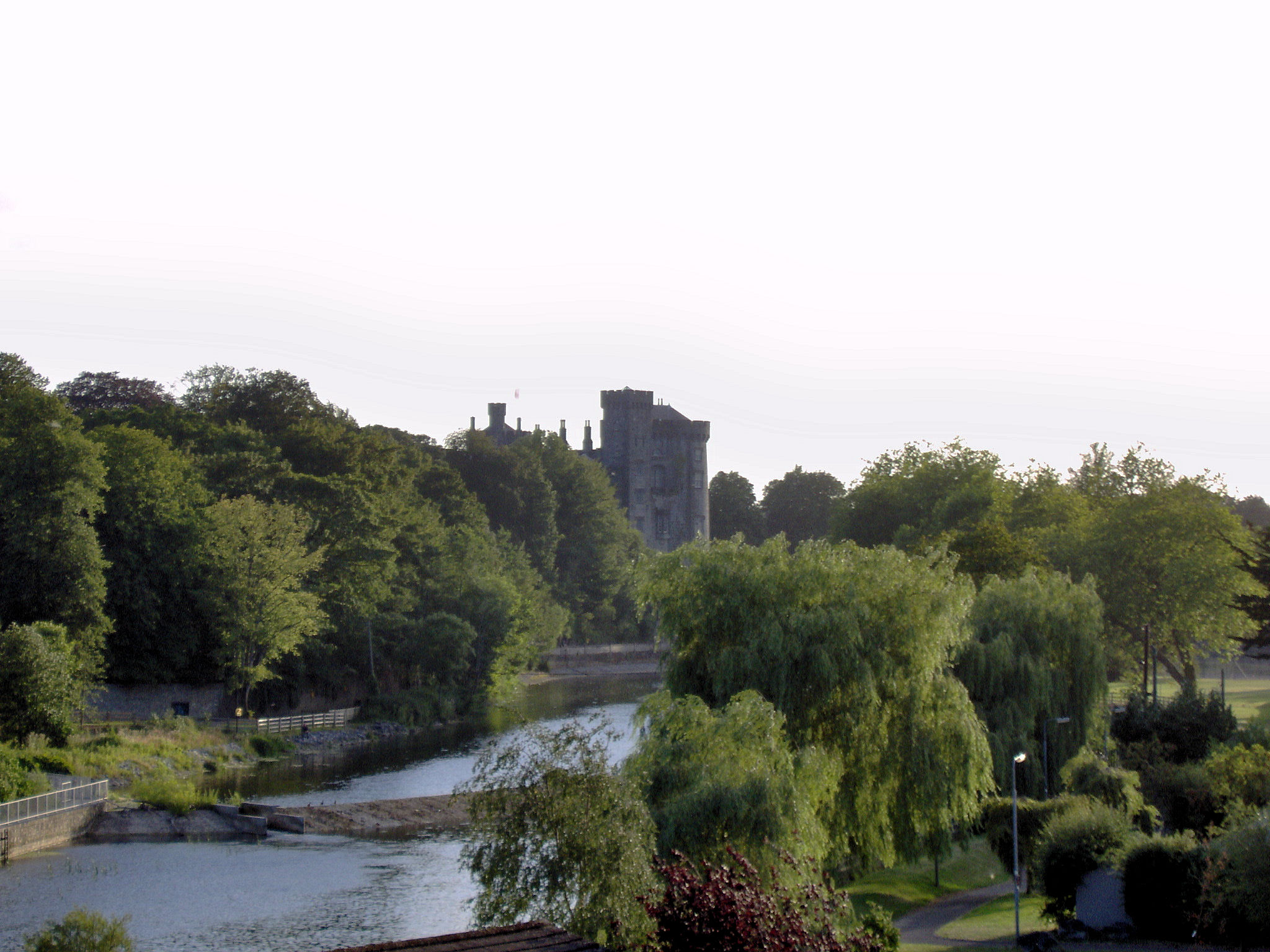
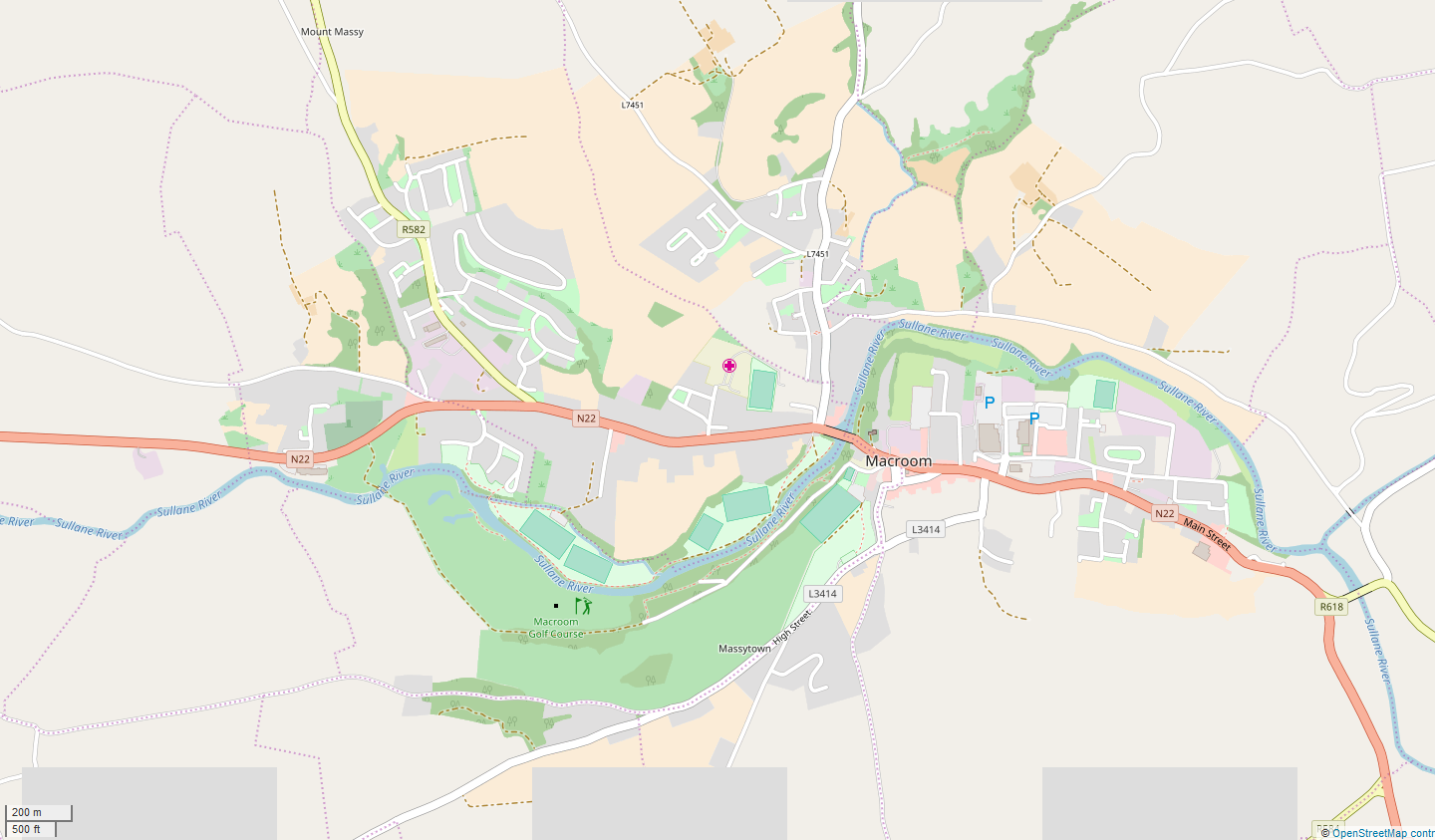
Macroom
Macroom (; ga, Maigh Chromtha) is a market town in County Cork, Ireland, located in the valley of the River Sullane, halfway between Cork city and Killarney. Its population has grown and receded over the centuries as it went through periods of war, famine and workhouses, forced emigration and intermittent prosperity. The 2011 census gave an urban population of 3,879 people, while the 2016 census recorded 3,765 people. Macroom began as a meeting place for the druids of Munster. It is first mentioned is in 6th-century records, and the immediate area hosted a major battle involving the Irish king Brian Boru. During the middle ages, the town was invaded by a succession of warring clans, including the Murcheatach Uí Briain and Richard de Cogan families. In the early modern period the MacCarthy's took control and later the area found prosperity via milling. The MacCarthys built a series of tower houses, some of which survive. The family lost influence during the Williami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destruction Of Irish Country Houses (1919–1923)
The destruction of country houses in Ireland was a phenomenon of the Irish revolutionary period (1919–1923), which saw at least 275 country houses deliberately burned down, blown up, or otherwise destroyed by the Irish Republican Army (IRA). The vast majority of the houses, known in Ireland as big houses, belonged to the Anglo-Irish upper class known as the Protestant Ascendancy. The houses of some Roman Catholic unionists, suspected informers, and members or supporters of the new Irish Free State government were also targeted. Although the practice by the IRA of destroying country houses began in the Irish War of Independence, most of the buildings were destroyed during the Irish Civil War (1922–23). Today, most of the targeted buildings are in ruins or have been demolished. Some were restored by their owners, albeit often smaller in size, or were later rebuilt and re-purposed. The Big House as a target By the start of the Irish revolutionary period in 1919, the Big House ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrigaphooca Castle
Carrigaphooca Castle ( ga, Caisleán Carraig a' Phúca, meaning Castle on the Rock of the Fairy; the word ''Púca'' translates as ghost or fairy), is a ruined five storey rectangular tower house situated on a steep-sided rock overlooking the River Sullane. It is located 6 km west of Macroom, County Cork, Ireland, in an area once known as Gleann na n-Dearg (''Valley of the Reds'').O'Brien (1990), 31 The tower dominates the landscape of Lissacresig (''Fairyland'') in Clondrohid, and Lower Shanballyshane, in Kilnamartyra.O'Brien (1990), 30 Carrigaphooca is made of sandstone and limestone and was built as a defensive tower by MacCarthy clan member Donal MacCarthy of Drishane c. 1336-51. Carrigaphooca is positioned in an area rich with neolithic monuments; a stone circle lies two fields to the east. The tower is located on private property, and is no longer accessible to the public, although it is owned by the state and maintained by the Office of Public Works.Heritage Unit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Sullane
The River Sullane ( ga, An Sulán) runs from the mountains between County Cork and County Kerry in southern Ireland, near the village of Cúil Aodha. After passing Ballyvourney, it runs through the centre of Macroom, to which it provides drinking water (and occasionally floods). The Sullane is joined by the River Bohill at Ballyvourney, the River Foherish at Clondrohid, about 5 kilometres west of Macroom and the River Launa locally known as "The Launey" one kilometre east of the town. The Sullane joins the River Lee a further kilometre east. It is well stocked with trout, and also contains European perch (200 g average), minnow and a small number of pike Pike, Pikes or The Pike may refer to: Fish * Blue pike or blue walleye, an extinct color morph of the yellow walleye ''Sander vitreus'' * Ctenoluciidae, the "pike characins", some species of which are commonly known as pikes * ''Esox'', genus o .... References Sullane {{Ireland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clondrohid
Clondrohid () is a village and civil parish in County Cork, Ireland, four miles (6 km) north of Macroom. As of the 2016 census, the population of the village was recorded as 179, down from 188 people as of the 2011 census. Geography Parishes adjoining Clondrohid include Aghabulloge, Ballyvourney, Drishane, Kilcorney, Kilnamartry, and Macroom. The townlands of Clondrohid were part of the barony of West Muskerry. Clondrohid lies within the Cork North-West Dáil constituency. Amenities Local amenities include Clondrohid National School and community hall and a number of shops, pubs and services. A childcare facility is next to the GAA pitch which is also a preschool and an afterschool. Carrigaphooca Castle is in one of the neighbouring townlands. Carrigaphooca stone circle, about 3,000 years old, stands next to it. Much of the western side of the village is a part of the Irish-speaking area or ''Gaeltacht''. Some pupils of the national school go to the second l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Cork
County Cork ( ga, Contae Chorcaí) is the largest and the southernmost county of Ireland, named after the city of Cork, the state's second-largest city. It is in the province of Munster and the Southern Region. Its largest market towns are Mallow, Macroom, Midleton, and Skibbereen. the county had a population of 581,231, making it the third- most populous county in Ireland. Cork County Council is the local authority for the county, while Cork City Council governs the city of Cork and its environs. Notable Corkonians include Michael Collins, Jack Lynch, Roy Keane, Sonia O'Sullivan and Cillian Murphy. Cork borders four other counties: Kerry to the west, Limerick to the north, Tipperary to the north-east and Waterford to the east. The county contains a section of the Golden Vale pastureland that stretches from Kanturk in the north to Allihies in the south. The south-west region, including West Cork, is one of Ireland's main tourist destinations, known for it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromwellian Conquest Of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland or Cromwellian war in Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the forces of the English Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Cromwell invaded Ireland with the New Model Army on behalf of England's Rump Parliament in August 1649. Following the Irish Rebellion of 1641, most of Ireland came under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation. In early 1649, the Confederates allied with the English Royalists, who had been defeated by the Parliamentarians in the English Civil War. By May 1652, Cromwell's Parliamentarian army had defeated the Confederate and Royalist coalition in Ireland and occupied the country, ending the Irish Confederate Wars (or Eleven Years' War). However, guerrilla warfare continued for a further year. Cromwell passed a series of Penal Laws against Roman Catholics (the vast majority of the population) and confiscated large amounts of their land. As punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In The Republic Of Ireland
Numbers on the Irish telephone numbering plan are regulated and assigned to operators by ComReg. Overview Telephone numbers in Ireland are part of an open numbering plan that allows variations in number length. The Irish format is similar to systems used in many parts of Europe, notably the Netherlands, Sweden, Germany, Belgium and France, where geographical numbers are organised using a logic of large regional prefixes, which are then further subdivided into smaller regions. It differs from UK numbering, which originated as alphanumeric codes based on town names. Irish Mobile and non–geographic numbers are fixed length and do not support local dialling. The trunk prefix 0 is used to access numbers outside the local area and for all mobile calls. This is followed by an area code, referred to as a National Dialling Code (NDC), the first digit of which indicates the geographical area or type of service (e.g. mobile). Calls made from mobile phones and some VoIP systems always ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eircode
A "postal address" in Ireland is a place of delivery defined by Irish Standard (IS) EN 14142-1:2011 ("Postal services. Address databases") and serviced by the universal service provider, '' An Post''. Its addressing guides comply with the guidelines of the Universal Postal Union (UPU), the United Nations-affiliated body responsible for promoting standards in the postal industry, across the world. In Ireland, 35% of Irish premises (over 600,000) have non-unique addresses due to an absence of house numbers or names. Before the introduction of a national postcode system (Eircode) in 2015, this required postal workers to remember which family names corresponded to which house in smaller towns, and many townlands,. As of 2021, An Post encourages customers to use Eircode because it ensures that their post person can pinpoint the exact location. Ireland was the last country in the OECD to create a postcode system. In July 2015 all 2.2 million residential and business addres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (city)
Cork ( , from , meaning 'marsh') is the second largest city in Ireland and third largest city by population on the island of Ireland. It is located in the south-west of Ireland, in the province of Munster. Following an extension to the city's boundary in 2019, its population is over 222,000. The city centre is an island positioned between two channels of the River Lee which meet downstream at the eastern end of the city centre, where the quays and docks along the river lead outwards towards Lough Mahon and Cork Harbour, one of the largest natural harbours in the world. Originally a monastic settlement, Cork was expanded by Viking invaders around 915. Its charter was granted by Prince John in 1185. Cork city was once fully walled, and the remnants of the old medieval town centre can be found around South and North Main streets. The city's cognomen of "the rebel city" originates in its support for the Yorkist cause in the Wars of the Roses. Corkonians sometimes r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early ..., High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish People
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the established church of Ireland until 1871, or to a lesser extent one of the English dissenting churches, such as the Methodist church, though some were Roman Catholics. They often defined themselves as simply "British", and less frequently "Anglo-Irish", "Irish" or "English". Many became eminent as administrators in the British Empire and as senior army and naval officers since Kingdom of England and Great Britain were in a real union with the Kingdom of Ireland until 1800, before politically uniting into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland) for over a century. The term is not usually applied to Presbyterians in the province of Ulster, whose ancestry is mostly Lowland Scottish, rather than English or Irish, and who are sometimes id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |