|
Lipoprotein-associated Phospholipase A2
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) also known as platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) is a phospholipase A2 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLA2G7'' gene. Lp-PLA2 is a 45-kDa protein of 441 amino acids. It is one of several PAF acetylhydrolases. Function In the blood Lp-PLA2 travels mainly with low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Less than 20% is associated with high-density lipoprotein HDL. Several lines of evidence suggest that HDL-associated Lp-PLA2 may substantially contribute to the HDL antiatherogenic activities. It is an enzyme produced by inflammatory cells and hydrolyzes oxidized phospholipids in LDL. Lp-PLA2 is platelet-activating factor ( PAF) acetylhydrolase (EC 3.1.1.47), a secreted enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of PAF to inactive products by hydrolysis of the acetyl group at the sn-2 position, producing the biologically inactive products LYSO-PAF and acetate. Clinical significance Lp-PLA2 is involved in the developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyse the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid “tail” and the glycerol molecule: :phosphatidylcholine + H2O = 1-acylglycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate This particular phospholipase specifically recognizes the ''sn''2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. Upon downstream modification by cyclooxygenases or lipoxygenases, arachidonic acid is modified into active compounds called eicosanoids. Eicosanoids include prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which are categorized as anti-inflammatory and inflammatory mediators. PLA2 enzymes are commonly found in mammalian tissues as well as arachnid, insect, and snake venom. Venom from bees is largely composed of melittin, which is a stimulant of PLA2. Due to the increased presenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
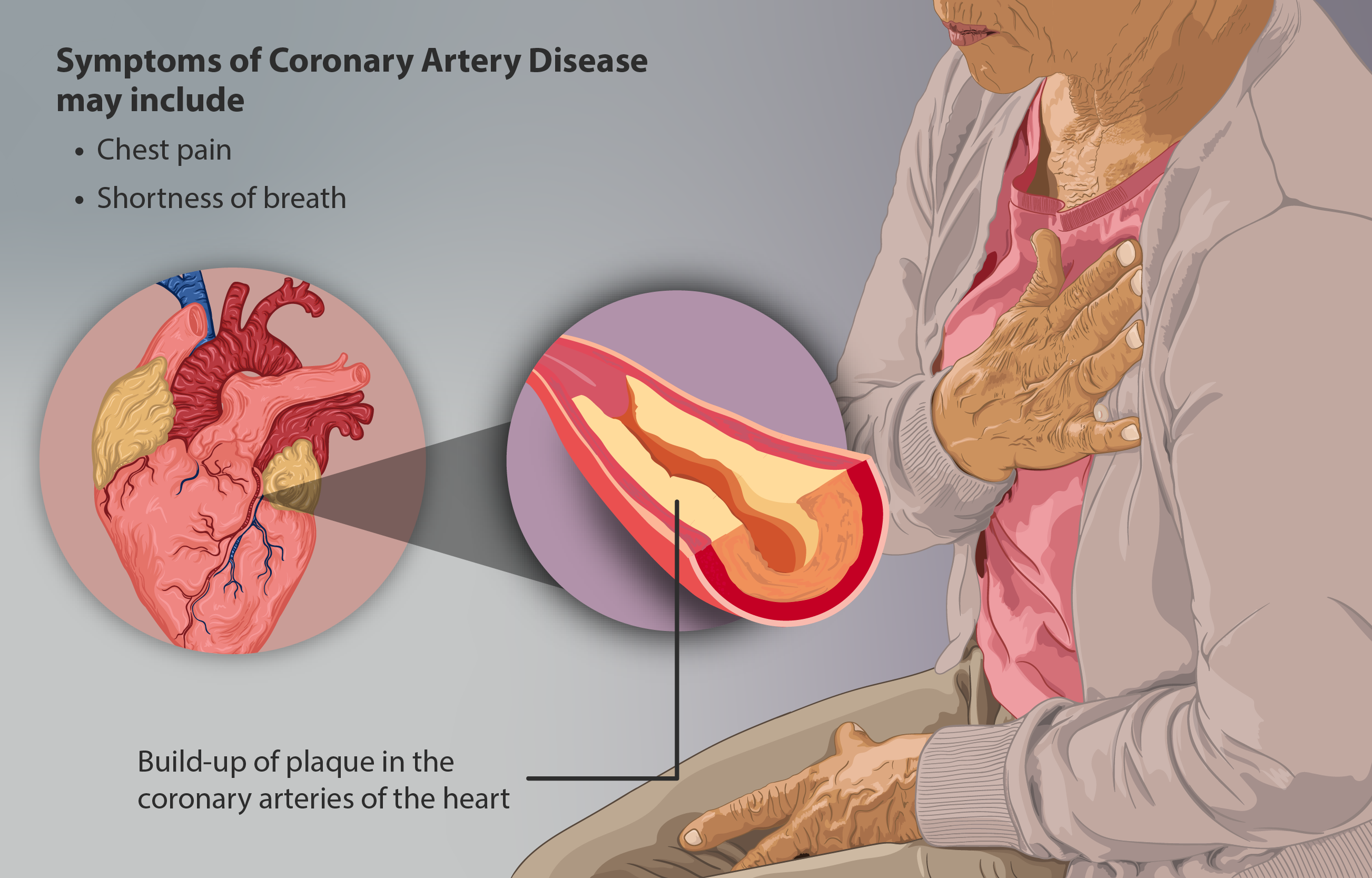
Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. Types include stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting measurements that are expected to have some degree of error. The aim then is to use approaches from statistics to derive a pooled estimate closest to the unknown common truth based on how this error is perceived. Meta-analytic results are considered the most trustworthy source of evidence by the evidence-based medicine literature.Herrera Ortiz AF., Cadavid Camacho E, Cubillos Rojas J, Cadavid Camacho T, Zoe Guevara S, Tatiana Rincón Cuenca N, Vásquez Perdomo A, Del Castillo Herazo V, & Giraldo Malo R. A Practical Guide to Perform a Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 2022;7(4):47–57. https://doi.org/10.21801/ppcrj.2021.74.6 Not only can meta-analyses provide an estimate of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intima
The tunica intima (New Latin "inner coat"), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow. The three layers of a blood vessel are an inner layer (the tunica intima), a middle layer (the tunica media), and an outer layer (the tunica externa). In dissection, the inner coat (tunica intima) can be separated from the middle (tunica media) by a little maceration, or it may be stripped off in small pieces; but, because of its friability, it cannot be separated as a complete membrane. It is a fine, transparent, colorless structure which is highly elastic, and, after death, is commonly corrugated into longitudinal wrinkles. Structure The structure of the tunica intima depends on the blood vessel type. Elastic arteries – A single layer of Endothelial and a supporting layer of elastin-rich collagen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darapladib
Darapladib is an inhibitor lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) that is in development as a drug for treatment of atherosclerosis. It was discovered by Human Genome Sciences in collaboration with GlaxoSmithKline (GSK). In November 2013, GSK announced that the drug had failed to meet Phase III endpoints in a trial of 16,000 patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). An additional trial of 13,000 patients (SOLID-TIMI 52) finished in May 2014. The study failed to reduce the risk of coronary heart disease death, myocardial infarction, and urgent coronary revascularization In medical and surgical therapy, revascularization is the restoration of perfusion to a body part or organ that has had ischemia. It is typically accomplished by surgical means. Vascular bypass and angioplasty are the two primary means of reva ... compared with placebo in acute coronary syndrome patients treated with standard medical care. References Drugs acting on the cardiovascular s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheroma, atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no symptoms, but if they develop, symptoms generally begin around middle age. When severe, it can result in coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, or kidney problems, depending on which Artery, arteries are affected. The exact cause is not known and is proposed to be multifactorial. Risk factors include dyslipidemia, abnormal cholesterol levels, elevated levels of inflammatory markers, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, obesity, family history, genetic, and an unhealthy diet. Atheroma, Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. The narrowing of Artery, arteries limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to parts of the body. Diagnosis is based upon a physical exam, ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues was lecith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammatory Cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage (myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes (monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells (myelocytes) include neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells, ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules) and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. The lipids carried include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides, amounts of each are variable. Increasing concentrations of HDL particles are associated with decreasing accumulation of atherosclerosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |