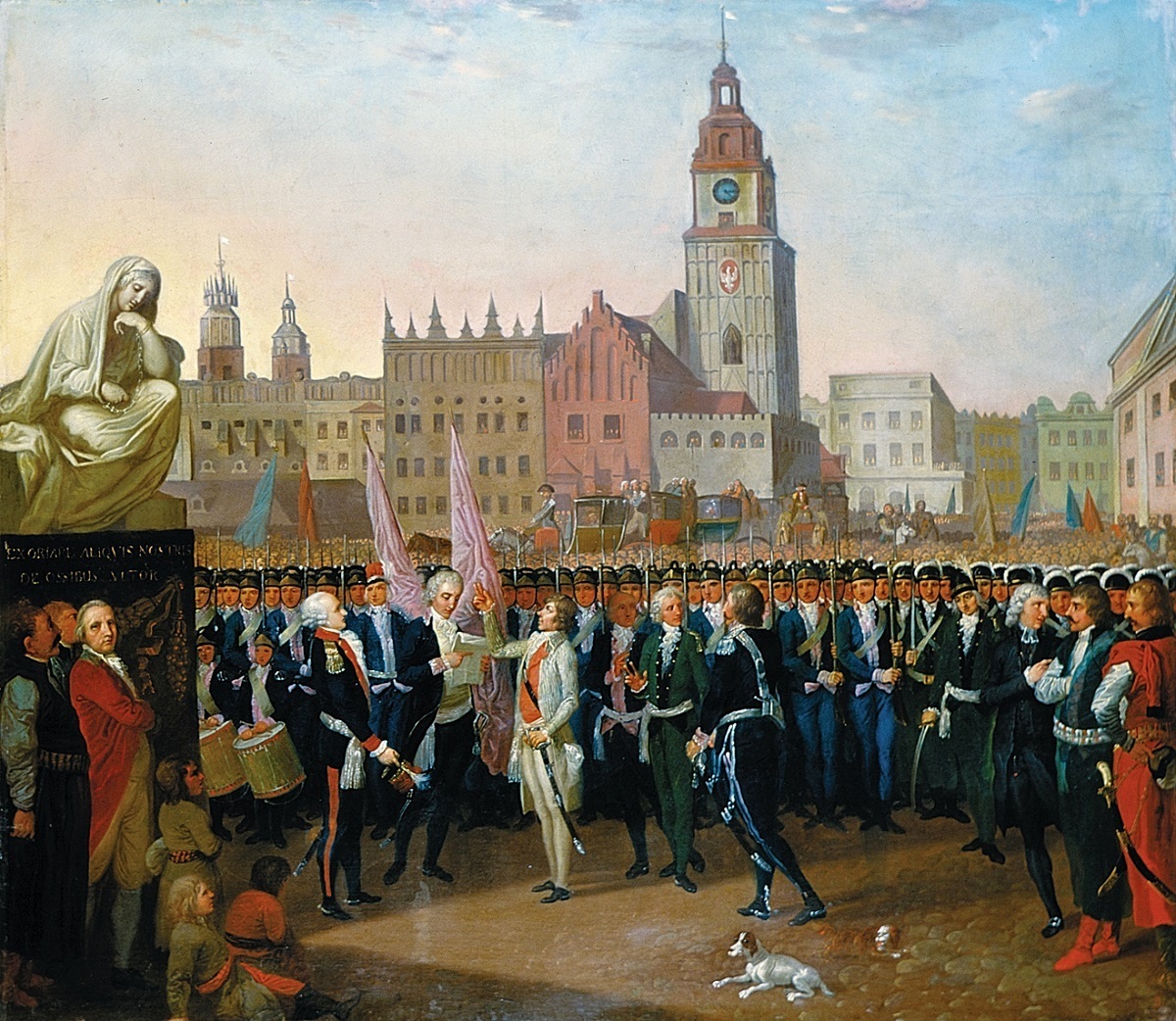|
Lida Castle
Lida Castle ( be, Лідскі замак, lt, Lydos pilis, pl, Zamek w Lidzie) is a historic, medieval castle in Lida, Grodno Region, western Belarus. History It was one of several citadels erected by Grand Duke Gediminas of Lithuania in the early 14th century to defend his lands against the expansion of the Teutonic Knights. Other links in this chain of defense included Hrodna, Navahrudak, Kreva, Medininkai, and Trakai. The modern town of Lida, Belarus grew up around this castle. Lida Castle is above sea level. The site selected for the castle is naturally defended by the Kamenka and Lida rivers to east and west. Construction of boulder walls was carried out in 1323, 1324, and 1325. Later they were faced with red brick. The castle had two angle towers and a church, which was moved outside the walls in 1533. The upper storeys of both towers were lived in. Despite its strong fortifications, Lida was taken by the Teutonic Knights on several occasions (1384, 1392). Lithuani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
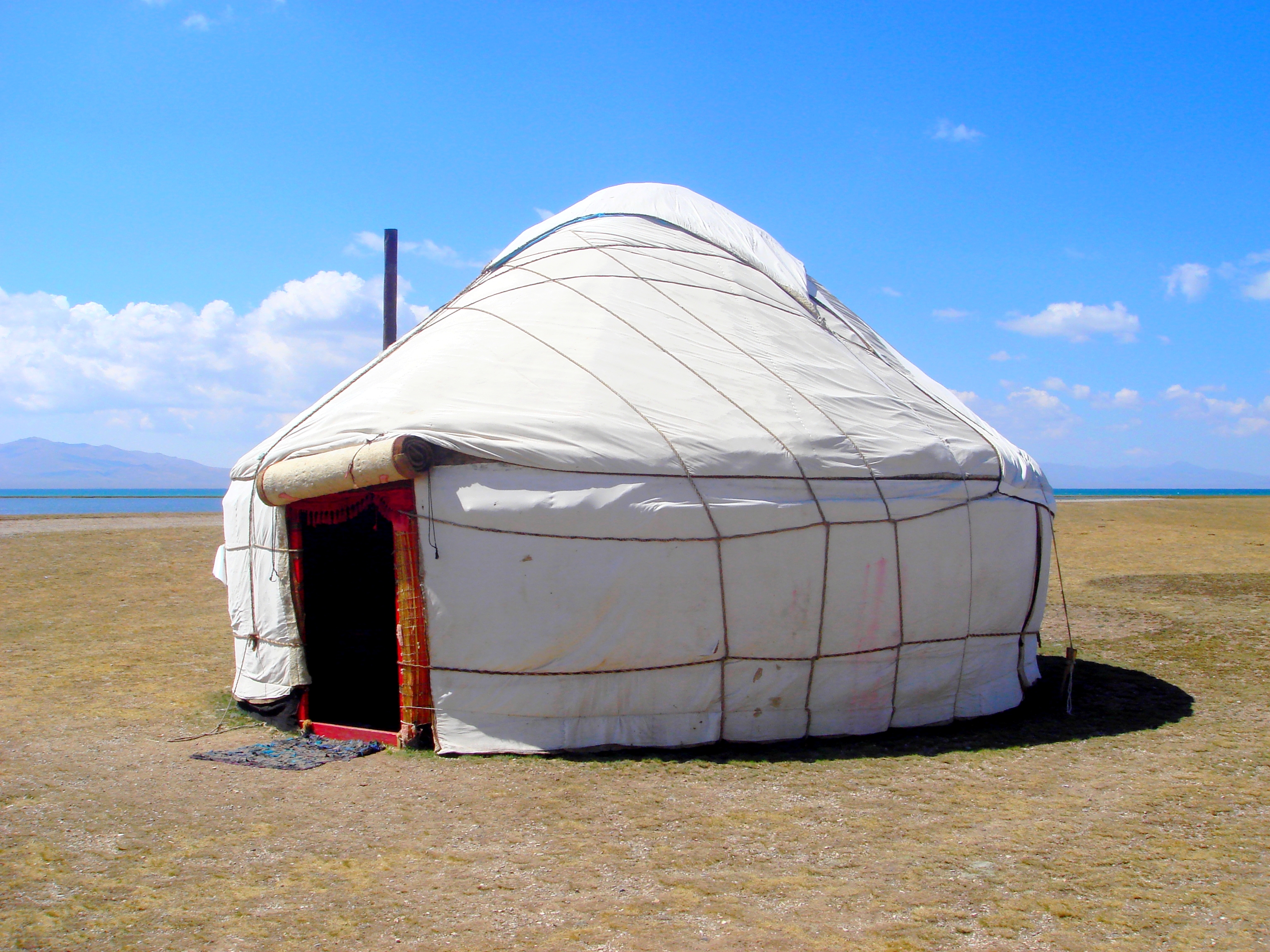
Yurt
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger ( Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and insulated with skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct nomadic groups in the steppes and mountains of Central Asia. The structure consists of a flexible angled assembly or latticework of wood or bamboo for walls, a door frame, ribs (poles, rafters), and a wheel (crown, compression ring) possibly steam-bent as a roof. The roof structure is sometimes self-supporting, but large yurts may have interior posts supporting the crown. The top of the wall of self-supporting yurts is prevented from spreading by means of a tension band which opposes the force of the roof ribs. Yurts take between 30 minutes and 3 hours to set up or take down, and are generally used by between five and 15 people. Nomadic farming with yurts as housing has been the primary life style in Central Asia, particularly Mongolia, for thousands of years. Modern yurts may be permanently built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Belarus ...
This is a list of castles in Belarus. B * Belaya Vezha, a common misnomer for the Tower of Kamyenyets * Babruysk fortress * Brest Fortress, also known as Brest-Litovsk fortress H * Hajciunishki *Halshany Castle * Hieraniony Castle * Hrodna Old Castle * Hrodna New Castle K *Tower of Kamyanyets * Kletsk Castle * Kobryn castles *Kopys * Kosava castle *Kreva Castle L * Liahavichy *Lida Castle * Lubcha Castle M *Mir Castle Complex *Muravanka Church N *Navahrudak Castle * Niasvizh Castle P * Pischalauski R *Ruzhany Palace S * Smalyany Castle * Slutsk Castle * Shklow Castle * Synkavichy Church * Svislach Castle Z *Zaslawye {{Castles in Belarus Castles Belarus Belarus Castles A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Grodno Region
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
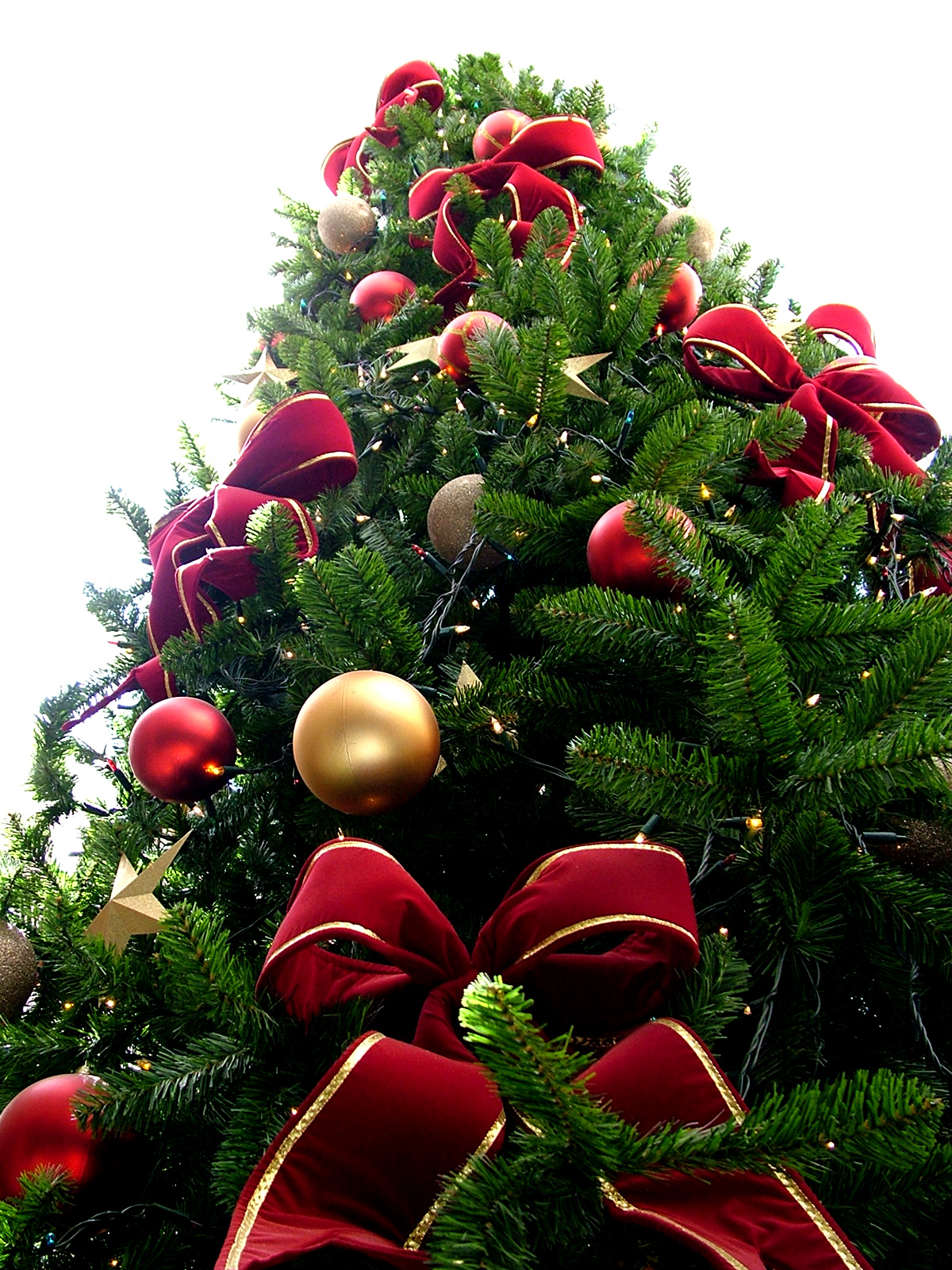
Christmas Tree
A Christmas tree is a decorated tree, usually an evergreen conifer, such as a spruce, pine or fir, or an artificial tree of similar appearance, associated with the celebration of Christmas. The custom was further developed in early modern Germany where German Protestant Christians brought decorated trees into their homes. It acquired popularity beyond the Lutheran areas of Germany and the Baltic governorates during the second half of the 19th century, at first among the upper classes. The tree was traditionally decorated with "roses made of colored paper, apples, wafers, tinsel, ndsweetmeats". Moravian Christians began to illuminate Christmas trees with candles, which were often replaced by Christmas lights after the advent of electrification. Today, there is a wide variety of traditional and modern ornaments, such as garlands, baubles, tinsel, and candy canes. An angel or star might be placed at the top of the tree to represent the Angel Gabriel or the Star of Bethle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circus
A circus is a company of performers who put on diverse entertainment shows that may include clowns, acrobats, trained animals, trapeze acts, musicians, dancers, hoopers, tightrope walkers, jugglers, magicians, ventriloquists, and unicyclists as well as other object manipulation and stunt-oriented artists. The term ''circus'' also describes the performance which has followed various formats through its 250-year modern history. Although not the inventor of the medium, Philip Astley is credited as the father of the modern circus. In 1768, Astley, a skilled equestrian, began performing exhibitions of trick horse riding in an open field called Ha'Penny Hatch on the south side of the Thames River, England. In 1770, he hired acrobats, tightrope walkers, jugglers and a clown to fill in the pauses between the equestrian demonstrations and thus chanced on the format which was later named a "circus". Performances developed significantly over the next fifty years, with large-scale theat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandalism
Vandalism is the action involving deliberate destruction of or damage to public or private property. The term includes property damage, such as graffiti and defacement directed towards any property without permission of the owner. The term finds its roots in an Enlightenment view that the Germanic Vandals were a uniquely destructive people. Etymology The Vandals, an ancient Germanic people, are associated with senseless destruction as a result of their sack of Rome under King Genseric in 455. During the Enlightenment, Rome was idealized, while the Goths and Vandals were blamed for its destruction. The Vandals may not have been any more destructive than other invaders of ancient times, but they did inspire English poet John Dryden to write, ''Till Goths, and Vandals, a rude Northern race, Did all the matchless Monuments deface'' (1694). However, the Vandals did intentionally damage statues, which may be why their name is associated with the vandalism of art. The term ''Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the "Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those simply content to believe they were living in an unprecedented "Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony– Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715. Charles XII led the Swedish army. Swedish allies included Holstein-Gottorp, several Polish magnates under Stanislaus I Leszczyński (1704–1710) and Cossacks under the Ukrainian Hetman Ivan Mazepa (1708–17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually taken as the reign of Gustavus Adolphus, who ascended the throne in 1611, and its end as the loss of territories in 1721 following the Great Northern War. After the death of Gustavus Adolphus in 1632, the empire was controlled for lengthy periods by part of the high nobility, such as the Oxenstierna family, acting as regents for minor monarchs. The interests of the high nobility contrasted with the uniformity policy (i.e., upholding the traditional equality in status of the Swedish estates favoured by the kings and peasantry). In territories acquired during the periods of ''de facto'' noble rule, serfdom was not abolished, and there was also a trend to set up respective estates in Sweden proper. The Great Reduction of 1680 put an end to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
Armed conflicts between Poland (including the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) and Russia (including the Soviet Union) include: Originally a Polish civil war that Russia, among others, became involved in. Originally a Hungarian revolution but was joined with Polish force on Hungarian side against Austria and Russia. Part of the broader Russian Revolution of 1905. See also * * * * * – in most of which Kingdom of Poland was allied with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ... * * * * * * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Polish-Russian War Lists of military conflicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
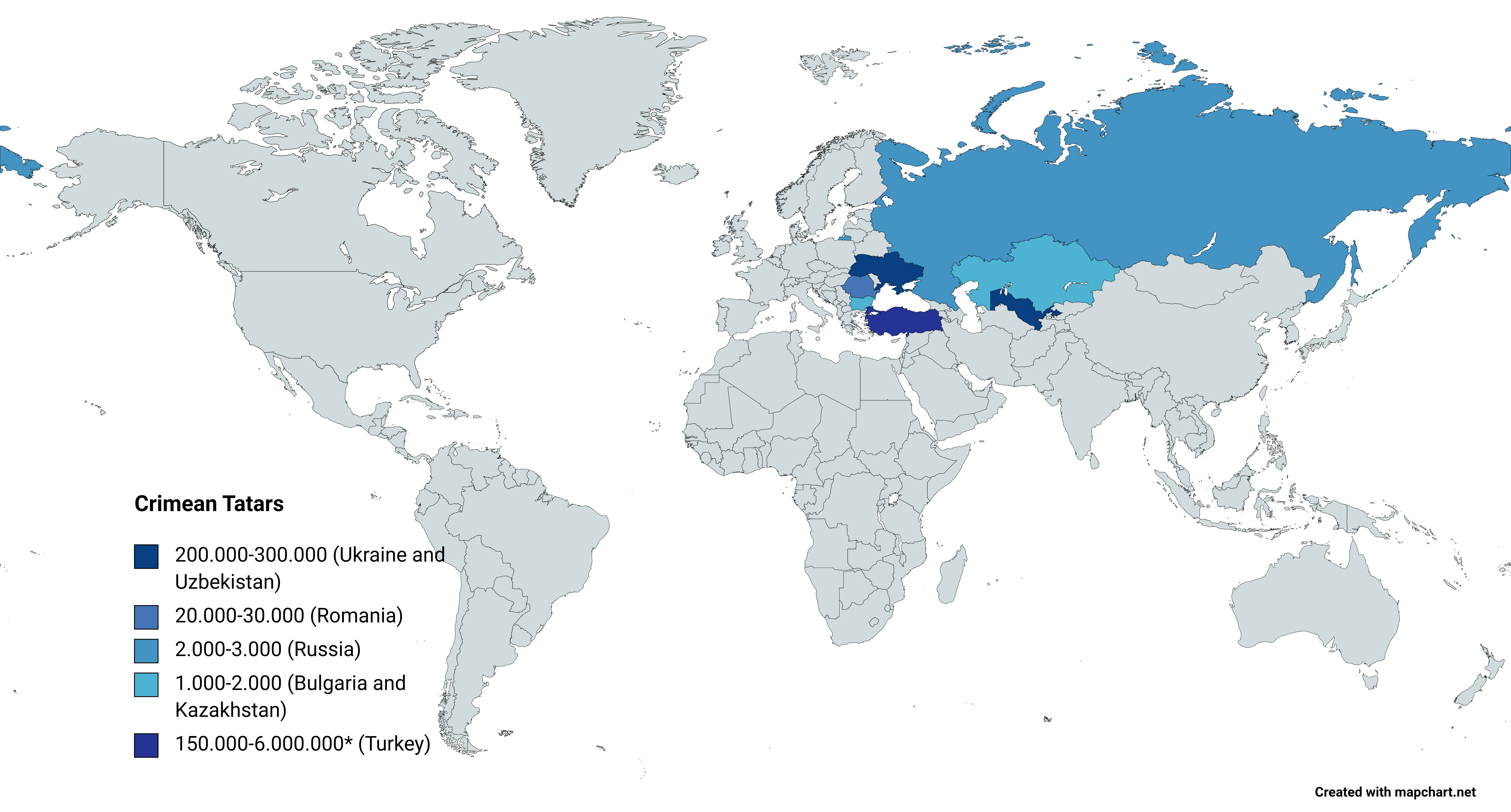
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg , flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars , image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg , caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace , poptime = , popplace = , region1 = , pop1 = 3,500,000 6,000,000 , ref1 = , region2 = * , pop2 = 248,193 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 239,000 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 24,137 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 2,449 , ref5 = , region7 = , pop7 = 1,803 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 1,532 , ref8 = , region9 = *() , pop9 = 7,000(500–1,000) , ref9 = , region10 = Total , pop10 = 4.024.114 (or 6.524.11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |