|
Leucia Violacea
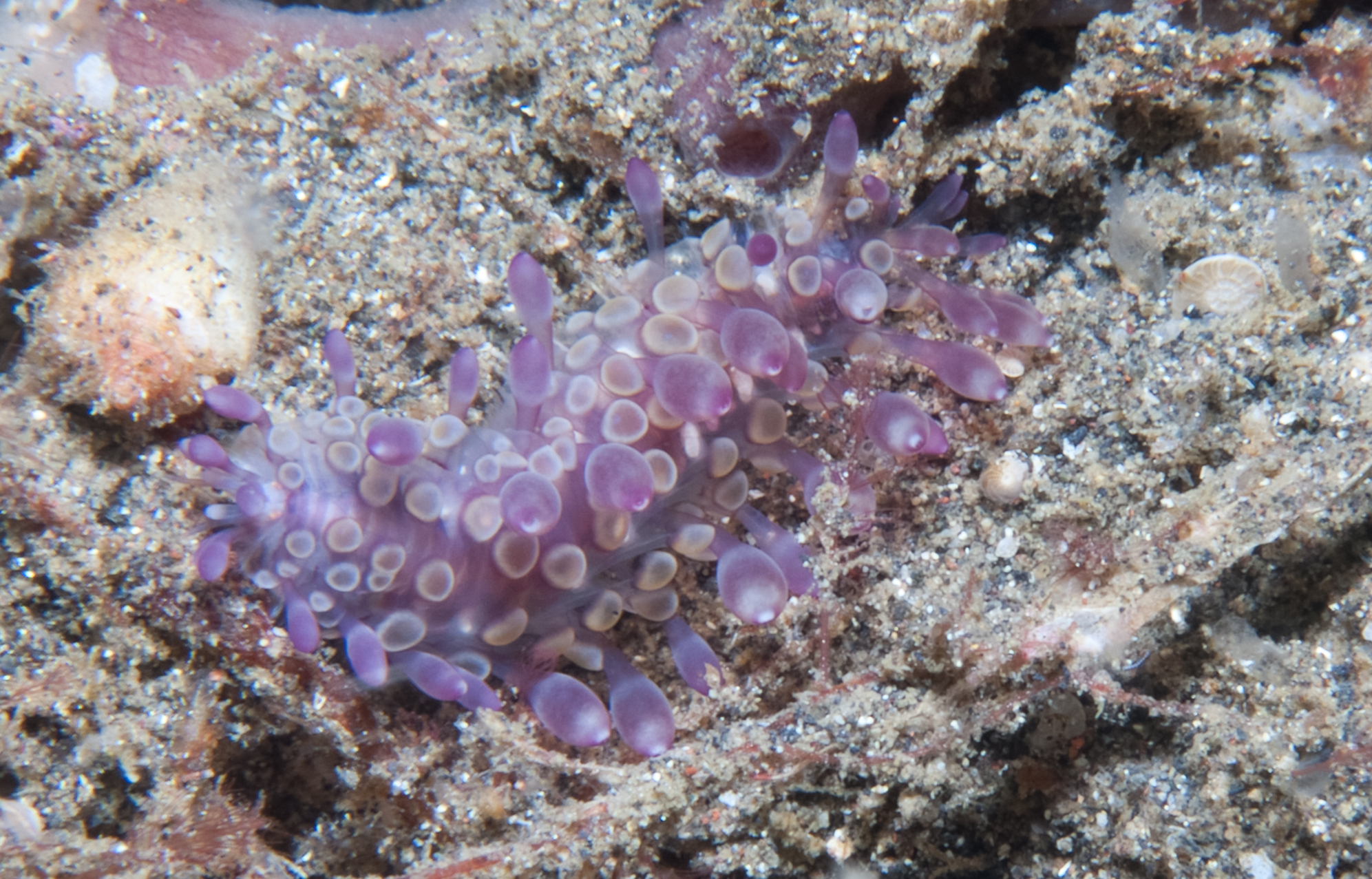
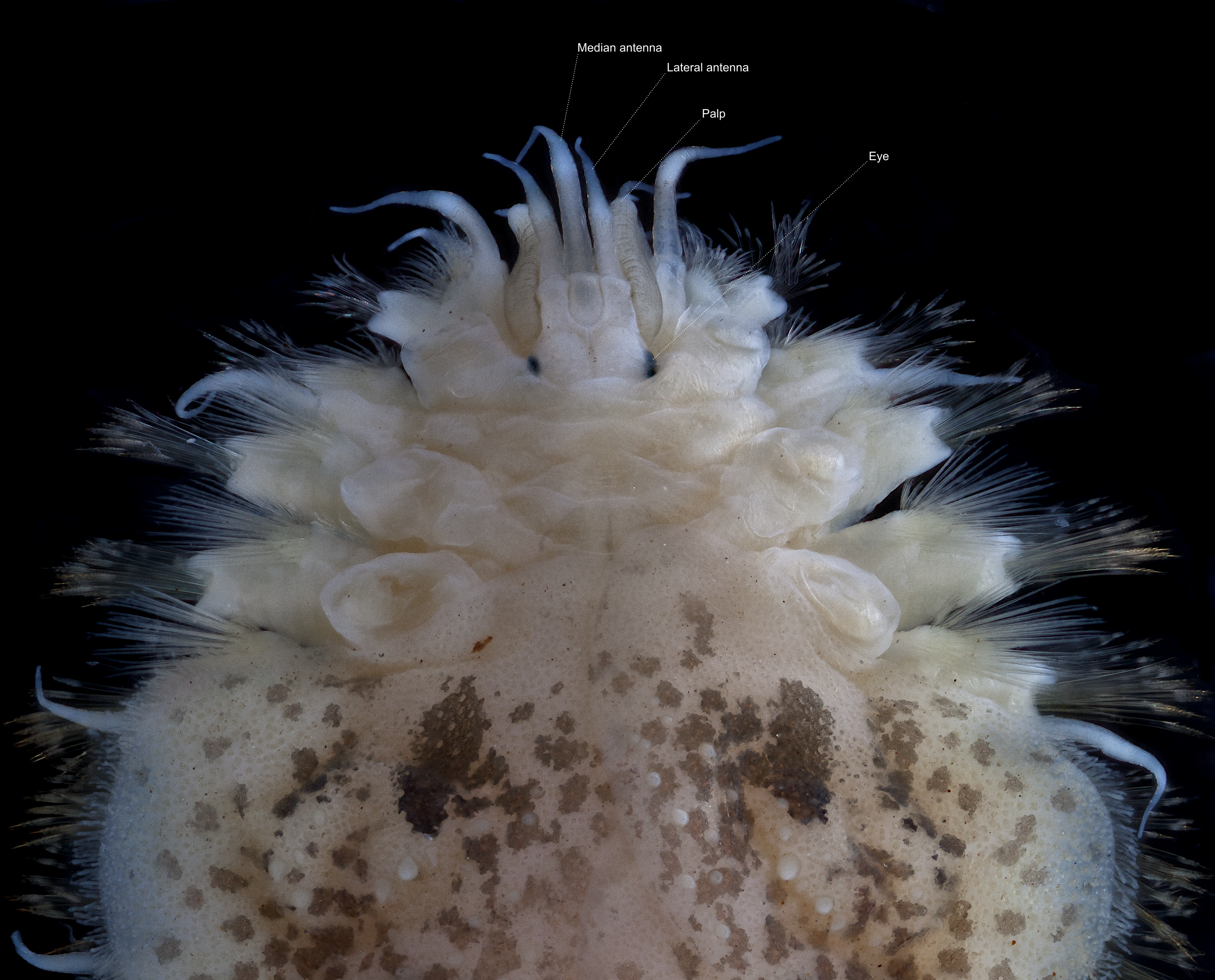
''Leucia violacea'' is a species of polychaete worm, commonly known as a "scale worm", in the family Polynoidae. This species occurs in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Description The body has 42 segments which are concealed by sixteen pairs of elytra in two rows. The length of this worm is about and the width . The prostomium has two lobes with a pair of acute anterior projections, a median antenna and a pair of lateral antennae inserted ventrally (beneath prostomium and median antenna), a pair of smooth palps and two pairs of eyes. The body is red to brown above and white beneath, and the scales are pink to violet. It can be distinguished from '' Leucia nivea '', the only other member of the genus, by the microtubercles on the scales being all conical while the macrotubercles are scattered and indistinct. Notochaetae distinctly thicker than neurochaetae. Unidentate and bidentate neurochaetae are present.Fiege, Dieter; Barnich, Ruth. (2009). Polynoidae (Annelida: Polycha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilhelm Storm
Vilhelm Storm (28 September 1835 – 19 May 1913) was a Norwegian zoologist. He was born in Arendal to priest Frederik Elias Storm and Emilie Fredrikke Cathrine Rønne. He was a brother of Martin Luther Storm and Thora Storm, and a cousin of Johan Storm and Gustav Storm. He was appointed as conservator-restorer at the Royal Norwegian Society of Sciences and Letters in Trondheim for more than fifty years. He is particularly known for his study of marine animals in Trondheimsfjorden The Trondheim Fjord or Trondheimsfjorden (), an inlet of the Norwegian Sea, is Norway's third-longest fjord at long. It is located in the west-central part of the country in Trøndelag county, and it stretches from the municipality of Ørland .... Selected works *'' Veiledning i Throndhjems Omegns Flora '' (1870) *'' Trondhjems Omegns Fugle '' (1881) *'' Throndhjemsfjordens Fiske '' (1884) References 1835 births 1913 deaths People from Arendal 19th-century Norwegian zoologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class (biology), class of generally marine invertebrate, marine annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in ''Eulagisca gigantea'' and ''Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those preda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elytron (Annelida)
In annelids, elytra (; from Greek ἔλυτρον "sheath, cover"; singular: elytron ) are shield-like scales that are attached dorsally, one pair on each of a number of alternating segments and entirely or partly cover the dorsum. Elytra are modified dorsal cirri, and their number, size, location, and ornamentation are important taxonomic characters. The basal part of the elytra is known as the elytrophore; if (as is often the case) elytra are lost their presence is indicated by the elytrophore which is still present and visible. Annelids possessing elytra are also known as "scale worms". Possession of elytra is characteristic of the annelid suborder Aphroditiformia. Gallery File:Eunoe leiotentaculata lower res.jpg, A ''Eunoe leiotentaculata'' specimen showing its 15 pairs of elytra. File:Euphione sp. dorsal.jpg, ''Euphione ''Euphione'' is a genus of polychaetes belonging to the family Polynoidae. The species of this genus are found in Australia, Malesia Malesia is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete prostomia have a posterior extension or ridge with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucia Nivea
''Leucia nivea'' is a species of polychaete worm, commonly known as a "scale worm", in the family Polynoidae. This species occurs in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. Description This worm is yellowish with white scales and about long with 41 segments and 16 pairs of elytra. The prostomium bears 3 antennae, with a pair of lateral antennae inserted ventrally (beneath prostomium and the median antenna). The anterior margin of the prostomium has a pair of an acute anterior projections, a pair of palps and two pairs of eyes. The first segment bears one or two chaetae and a pair of tentacular cirri on both the dorsal and ventral surfaces. The notochaetae are distinctly thicker than the neurochaetae. Unidentate and bidentate neurochaetae are present.Chambers SJ (1989) Leucia nivea: a polynoid (Polychaeta) new to the British Isles. Irish Naturalists Journal 23: 145–147. Taxonomy This species was first described by the Norwegian zoologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods). Polychaete annelids, ('polychaeta' literally meaning "many bristles") are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals. Use in taxonomy and identification The ultrastructure of chaetae is fundamentally similar for all taxa but there is vast diversity in chaetal morphology. Moreover, chaetae bear precise characters for determination of species and taxonomic assessment. The shape, absolute and relative size, number, position, ornamentation and type are important taxonomic characters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmothoe
''Harmothoe'' is a genus of marine Polychaete worms belonging to the family ''Polynoidae'' (scale worms). Species of ''Harmothoe'' are found world-wide to depths of at least 5,000 m but are more common in shallower water. Description Body dorsoventrally flattened, short, with 15 pairs of elytron (Annelida), elytra and up to 50 segments; the body is more or less covered by elytra, although long specimens may have a short posterior region uncovered. The prostomium is rounded anteriorly and has distinct cephalic peaks on the dorsal surface. There are three antennae, a pair of lateral antennae inserted ventrally, directly beneath the median antenna ceratophore. The Parapodia, neuropodia are elongate and tapering. The Chaeta, notoochaetae are stout with transverse rows of spines and blunt tips. The Chaeta, neurochaetae also have transverse rows of spines and both unindentate and bidentate neurochaetae are present.Barnich R, Fiege D (2000) Revision of the Mediterranean specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay ( ) is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean located south of the Celtic Sea. It lies along the western coast of France from Point Penmarc'h to the Spanish border, and along the northern coast of Spain, extending westward to Cape Ortegal. The southern area of the Bay of Biscay that washes over the northern coast of Spain is known locally as the Cantabrian Sea. The average depth is and the greatest depth is . Name The Bay of Biscay is known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya; eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne ; oc, Golf de Gasconha; br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn). Its English name comes from Biscay on the northern Spanish coast, probably standing for the western Basque districts (''Biscay'' up to the early 19th century). Geography Parts of the continental shelf extend far into the bay, resulting in fairly shallow waters in many areas and thus the rough seas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biology)
In biology, a substrate is the surface on which an organism (such as a plant, fungus, or animal) lives. A substrate can include biotic or abiotic materials and animals. For example, encrusting algae that lives on a rock (its substrate) can be itself a substrate for an animal that lives on top of the algae. Inert substrates are used as growing support materials in the hydroponic cultivation of plants. In biology substrates are often activated by the nanoscopic process of substrate presentation. In agriculture and horticulture * Cellulose substrate * Expanded clay aggregate (LECA) * Rock wool * Potting soil * Soil In animal biotechnology Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture Requirements for animal cell and tissue culture are the same as described for plant cell, tissue and organ culture (In Vitro Culture Techniques: The Biotechnological Principles). Desirable requirements are (i) air conditioning of a room, (ii) hot room with temperature recorder, (iii) microscope r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |