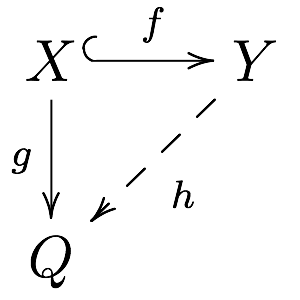|
Leray Spectral Sequence
In mathematics, the Leray spectral sequence was a pioneering example in homological algebra, introduced in 1946 by Jean Leray. It is usually seen nowadays as a special case of the Grothendieck spectral sequence. Definition Let f:X\to Y be a continuous map of topological spaces, which in particular gives a functor f_* from Sheaf (mathematics), sheaves of abelian groups on X to sheaves of abelian groups on Y. Composing this with the functor \Gamma of taking sections on \text_\text(Y) is the same as taking sections on \text_\text(X), by the definition of the direct image functor f_*: :\mathrm (X) \xrightarrow \mathrm(Y) \xrightarrow \mathrm. Thus the Derived functor, derived functors of \Gamma \circ f_* compute the sheaf cohomology for X: : R^i (\Gamma \cdot f_*)(\mathcal)=H^i(X,\mathcal). But because f_* and \Gamma send Injective object, injective objects in \text_\text(X) to \Gamma-Acyclic object, acyclic objects in \text_\text(Y), there is a spectral sequencepg 33,19 whose second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enough Injectives
In mathematics, especially in the field of category theory, the concept of injective object is a generalization of the concept of injective module. This concept is important in cohomology, in homotopy theory and in the theory of model categories. The dual notion is that of a projective object. Definition An object Q in a category \mathbf is said to be injective if for every monomorphism f: X \to Y and every morphism g: X \to Q there exists a morphism h: Y \to Q extending g to Y, i.e. such that h \circ f = g. That is, every morphism X \to Q factors through every monomorphism X \hookrightarrow Y. The morphism h in the above definition is not required to be uniquely determined by f and g. In a locally small category, it is equivalent to require that the hom functor \operatorname_(-,Q) carries monomorphisms in \mathbf to surjective set maps. In Abelian categories The notion of injectivity was first formulated for abelian categories, and this is still one of its primary areas of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Deligne
Pierre René, Viscount Deligne (; born 3 October 1944) is a Belgian mathematician. He is best known for work on the Weil conjectures, leading to a complete proof in 1973. He is the winner of the 2013 Abel Prize, 2008 Wolf Prize, 1988 Crafoord Prize, and 1978 Fields Medal. Early life and education Deligne was born in Etterbeek, attended school at Athénée Adolphe Max and studied at the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), writing a dissertation titled ''Théorème de Lefschetz et critères de dégénérescence de suites spectrales'' (Theorem of Lefschetz and criteria of degeneration of spectral sequences). He completed his doctorate at the University of Paris-Sud in Orsay 1972 under the supervision of Alexander Grothendieck, with a thesis titled ''Théorie de Hodge''. Career Starting in 1965, Deligne worked with Grothendieck at the Institut des Hautes Études Scientifiques (IHÉS) near Paris, initially on the generalization within scheme theory of Zariski's main theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serre Spectral Sequence
In mathematics, the Serre spectral sequence (sometimes Leray–Serre spectral sequence to acknowledge earlier work of Jean Leray in the Leray spectral sequence) is an important tool in algebraic topology. It expresses, in the language of homological algebra, the singular (co)homology of the total space ''X'' of a (Serre) fibration in terms of the (co)homology of the base space ''B'' and the fiber ''F''. The result is due to Jean-Pierre Serre in his doctoral dissertation. Cohomology spectral sequence Let f\colon X\to B be a Serre fibration of topological spaces, and let ''F'' be the (path-connected) fiber. The Serre cohomology spectral sequence is the following: : E_2^ = H^p(B, H^q(F)) \Rightarrow H^(X). Here, at least under standard simplifying conditions, the coefficient group in the E_2-term is the ''q''-th integral cohomology group of ''F'', and the outer group is the singular cohomology of ''B'' with coefficients in that group. The differential on the ''k''th page is d_k:E_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bundle
In mathematics, and particularly topology, a fiber bundle ( ''Commonwealth English'': fibre bundle) is a space that is a product space, but may have a different topological structure. Specifically, the similarity between a space E and a product space B \times F is defined using a continuous surjective map, \pi : E \to B, that in small regions of E behaves just like a projection from corresponding regions of B \times F to B. The map \pi, called the projection or submersion of the bundle, is regarded as part of the structure of the bundle. The space E is known as the total space of the fiber bundle, B as the base space, and F the fiber. In the '' trivial'' case, E is just B \times F, and the map \pi is just the projection from the product space to the first factor. This is called a trivial bundle. Examples of non-trivial fiber bundles include the Möbius strip and Klein bottle, as well as nontrivial covering spaces. Fiber bundles, such as the tangent bundle of a manifol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Künneth Theorem
In mathematics, especially in homological algebra and algebraic topology, a Künneth theorem, also called a Künneth formula, is a statement relating the homology of two objects to the homology of their product. The classical statement of the Künneth theorem relates the singular homology of two topological spaces ''X'' and ''Y'' and their product space X \times Y. In the simplest possible case the relationship is that of a tensor product, but for applications it is very often necessary to apply certain tools of homological algebra to express the answer. A Künneth theorem or Künneth formula is true in many different homology and cohomology theories, and the name has become generic. These many results are named for the German mathematician Hermann Künneth. Singular homology with coefficients in a field Let ''X'' and ''Y'' be two topological spaces. In general one uses singular homology; but if ''X'' and ''Y'' happen to be CW complexes, then this can be replaced by cellular ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Form
In mathematics, differential forms provide a unified approach to define integrands over curves, surfaces, solids, and higher-dimensional manifolds. The modern notion of differential forms was pioneered by Élie Cartan. It has many applications, especially in geometry, topology and physics. For instance, the expression f(x) \, dx is an example of a -form, and can be integrated over an interval ,b/math> contained in the domain of f: \int_a^b f(x)\,dx. Similarly, the expression f(x,y,z) \, dx \wedge dy + g(x,y,z) \, dz \wedge dx + h(x,y,z) \, dy \wedge dz is a -form that can be integrated over a surface S: \int_S \left(f(x,y,z) \, dx \wedge dy + g(x,y,z) \, dz \wedge dx + h(x,y,z) \, dy \wedge dz\right). The symbol \wedge denotes the exterior product, sometimes called the ''wedge product'', of two differential forms. Likewise, a -form f(x,y,z) \, dx \wedge dy \wedge dz represents a volume element that can be integrated over a region of space. In general, a -form is an object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simply Connected Space
In topology, a topological space is called simply connected (or 1-connected, or 1-simply connected) if it is path-connected and every path between two points can be continuously transformed into any other such path while preserving the two endpoints in question. Intuitively, this corresponds to a space that has no disjoint parts and no holes that go completely through it, because two paths going around different sides of such a hole cannot be continuously transformed into each other. The fundamental group of a topological space is an indicator of the failure for the space to be simply connected: a path-connected topological space is simply connected if and only if its fundamental group is trivial. Definition and equivalent formulations A topological space X is called if it is path-connected and any loop in X defined by f : S^1 \to X can be contracted to a point: there exists a continuous map F : D^2 \to X such that F restricted to S^1 is f. Here, S^1 and D^2 denotes the unit c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiable Manifold
In mathematics, a differentiable manifold (also differential manifold) is a type of manifold that is locally similar enough to a vector space to allow one to apply calculus. Any manifold can be described by a collection of charts (atlas). One may then apply ideas from calculus while working within the individual charts, since each chart lies within a vector space to which the usual rules of calculus apply. If the charts are suitably compatible (namely, the transition from one chart to another is differentiable), then computations done in one chart are valid in any other differentiable chart. In formal terms, a differentiable manifold is a topological manifold with a globally defined differential structure. Any topological manifold can be given a differential structure locally by using the homeomorphisms in its atlas and the standard differential structure on a vector space. To induce a global differential structure on the local coordinate systems induced by the homeomorphism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiley (publisher)
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduate Texts In Mathematics
Graduate Texts in Mathematics (GTM) () is a series of graduate-level textbooks in mathematics published by Springer-Verlag. The books in this series, like the other Springer-Verlag mathematics series, are yellow books of a standard size (with variable numbers of pages). The GTM series is easily identified by a white band at the top of the book. The books in this series tend to be written at a more advanced level than the similar Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics series, although there is a fair amount of overlap between the two series in terms of material covered and difficulty level. List of books #''Introduction to Axiomatic Set Theory'', Gaisi Takeuti, Wilson M. Zaring (1982, 2nd ed., ) #''Measure and Category – A Survey of the Analogies between Topological and Measure Spaces'', John C. Oxtoby (1980, 2nd ed., ) #''Topological Vector Spaces'', H. H. Schaefer, M. P. Wolff (1999, 2nd ed., ) #''A Course in Homological Algebra'', Peter Hilton, Urs Stammbach (1997, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Rham Cohomology
In mathematics, de Rham cohomology (named after Georges de Rham) is a tool belonging both to algebraic topology and to differential topology, capable of expressing basic topological information about smooth manifolds in a form particularly adapted to computation and the concrete representation of cohomology classes. It is a cohomology theory based on the existence of differential forms with prescribed properties. On any smooth manifold, every Closed and exact differential forms, exact form is closed, but the converse may fail to hold. Roughly speaking, this failure is related to the possible existence of Hole#In mathematics, "holes" in the manifold, and the de Rham cohomology groups comprise a set of Topological invariant, topological invariants of smooth manifolds that precisely quantify this relationship. Definition The de Rham complex is the cochain complex of differential forms on some smooth manifold , with the exterior derivative as the differential: :0 \to \Omega^0(M)\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |