|
Leo Of Tripoli
Leo of Tripoli ( el, Λέων ὸ Τριπολίτης), known in Arabic as Rashīq al-Wardāmī (), and Ghulām Zurāfa (), was a Greek renegade and fleet commander for the Abbasid Caliphate in the early tenth century. He is most notable for his sack of Thessalonica, the Byzantine Empire's second city, in 904. Life Nothing is known of Leo's early life except that he was born in or near Attaleia, the capital of the maritime Cibyrrhaeot Theme, and was captured in an Arab raid and brought to Tripoli. In captivity, he converted to Islam, and entered the service of his captors as a seaman and commander. In Arabic sources he is called Lāwī Abū'l-Ḥārith and given the sobriquet ghulām Zurāfa, "servant/page of Zurafa", probably reflecting the name of his first Muslim master. He is also referred to as Rashīq al-Wardāmī. Alexander Vasiliev interpreted the element ''Wardāmī'' in his second Arabic name to mean that Leo was a Mardaite. The details of Leo's early career in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
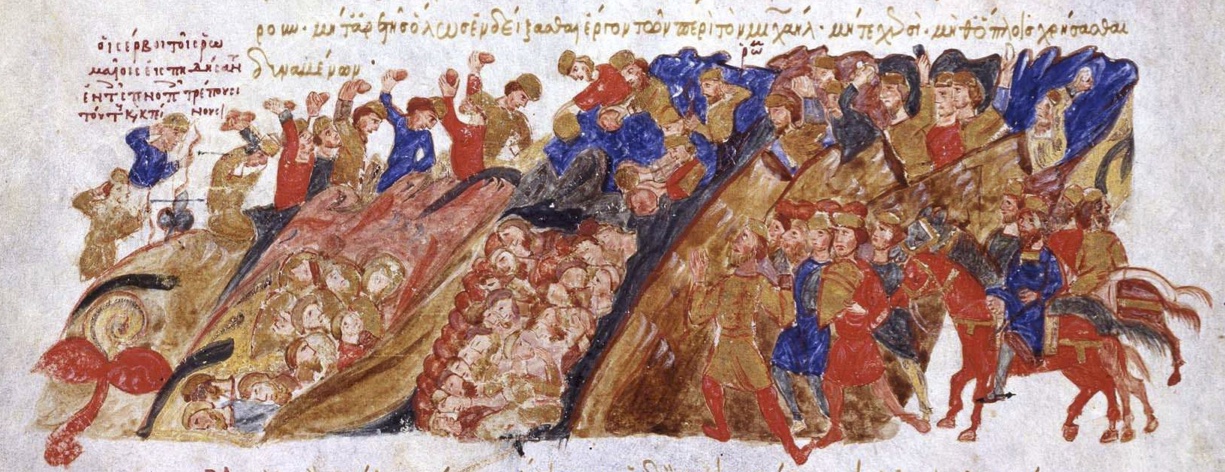
Madrid Skylitzes
The ''Madrid Skylitzes'' is a richly illustrated illuminated manuscript of the ''Synopsis of Histories'' ( el, Σύνοψις Ἱστοριῶν, ), by John Skylitzes, which covers the reigns of the Byzantine emperors from the death of Nicephorus I in 811 to the deposition of Michael VI Bringas, Michael VI in 1057. The manuscript was produced in Sicily in the 12th century, and is now at the Biblioteca Nacional de España in Madrid, with the shelfmark MS Graecus Vitr. 26–2. Other names for it are and . Apart from the very fragmentary 6th-century Alexandrian World Chronicle, it is the only surviving illustrated manuscript of a Greek chronicle, and includes 574 miniatures. It is unclear whether these illustrations are copies of earlier Byzantine images or were newly created specifically for this copy. Bibliography * Color facsimile edition by Militos (Μίλητος) Publishers, . * Vasiliki Tsamakda, The Illustrated Chronicle of Ioannes Skylitzes, Leiden 2002. * Bente Bj� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mas'udi
Al-Mas'udi ( ar, أَبُو ٱلْحَسَن عَلِيّ ٱبْن ٱلْحُسَيْن ٱبْن عَلِيّ ٱلْمَسْعُودِيّ, '; –956) was an Arab historian, geographer and traveler. He is sometimes referred to as the "Herodotus of the Arabs". A polymath and prolific author of over twenty works on theology, history (Islamic and universal), geography, natural science and philosophy, his celebrated magnum opus '' Murūj al-Dhahab wa-Ma'ādin al-Jawhar'' ( ar, مُرُوج ٱلذَّهَب وَمَعَادِن ٱلْجَوْهَر, link=no), combines universal history with scientific geography, social commentary and biography, and is published in English in a multi-volume series as '' The Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems''. Birth, travels and literary output Apart from what Al-Mas'udi writes of himself little is known. Born in Baghdad, he was descended from Abdullah Ibn Mas'ud, a companion of Muhammad. He mentions many scholar associates met on his travels t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo VI The Wise
Leo VI, called the Wise ( gr, Λέων ὁ Σοφός, Léōn ho Sophós, 19 September 866 – 11 May 912), was Byzantine Emperor from 886 to 912. The second ruler of the Macedonian dynasty (although his parentage is unclear), he was very well read, leading to his epithet. During his reign, the renaissance of letters, begun by his predecessor Basil I, continued; but the Empire also saw several military defeats in the Balkans against Bulgaria and against the Arabs in Sicily and the Aegean. His reign also witnessed the formal discontinuation of several ancient Roman institutions, such as the separate office of Roman consul. Early life Born on 19 September 866 to the empress Eudokia Ingerina, Leo was either the illegitimate son of Emperor Michael III or the second son of Michael's successor, Basil I the Macedonian. Eudokia was both Michael III's mistress and Basil's wife. In 867, Michael was assassinated by Basil, who succeeded him as emperor. As the second-eldest son of the Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustathios Argyros (admiral Under Leo VI)
Eustathios Argyros (Greek: Εύστάθιος Άργυρός) was a Byzantine admiral under Emperor Leo VI the Wise (r. 886–912). Life Eustathios Argyros first appears during the outbreak of the war with Bulgaria in 894, under the overall command of Nikephoros Phokas the Elder. At the time, he was already ''patrikios'' and commander of the imperial fleet (''droungarios tou ploimou''), and he was sent to the Danube to ferry across the allied Magyars and put pressure on Bulgaria from the rear; the strategy worked, and Tsar Simeon asked for peace. As soon as the Byzantines withdrew for negotiations to take place, however, Simeon drove back the Magyars and renewed war with Byzantium. In 902, Emperor Leo VI the Wise had sent a fleet under Eustathios to aid Taormina in Sicily, which was being threatened by the Arabs. The city fell on 1 August 902, and on his return to Constantinople, Eustathios and the city's garrison commander, Constantine Karamallos, were accused by commander Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droungarios Of The Fleet
The ''droungarios'' of the Fleet ( el, δρουγγάριος τοῦ πλοΐμου/τῶν πλοΐμων, ''droungarios tou ploïmou/tōn ploïmōn''; after the 11th century δρουγγάριος τοῦ στόλου, ''droungarios tou stolou''), sometimes anglicized as Drungary of the Fleet, was the commander of the Imperial Fleet (βασιλικὸς στόλος, ''basilikos stolos'', or βασιλικὸν πλόϊμον, ''basilikon ploïmon''), the central division of the Byzantine navy stationed at the capital of Constantinople, as opposed to the provincial ( thematic) fleets. From the late 11th century, when the Byzantine fleets were amalgamated into a single force under the '' megas doux'', the post, now known as the Grand ''droungarios'' of the Fleet (μέγας δρουγγάριος τοῦ στόλου, ''megas droungarios tou stolou''), became the second-in-command of the ''megas doux'' and continued in this role until the end of the Byzantine Empire. Backgroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Navy
The Byzantine navy was the naval force of the East Roman or Byzantine Empire. Like the empire it served, it was a direct continuation from its Imperial Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than its earlier iteration. While the fleets of the unified Roman Empire faced few great naval threats, operating as a policing force vastly inferior in power and prestige to the legions, the sea became vital to the very existence of the Byzantine state, which several historians have called a "maritime empire". The first threat to Roman hegemony in the Mediterranean was posed by the Vandals in the 5th century, but their threat was ended by the wars of Justinian I in the 6th century. The re-establishment of a permanently maintained fleet and the introduction of the dromon galley in the same period also marks the point when the Byzantine navy began departing from its late Roman roots and developing its own characteristic identity. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
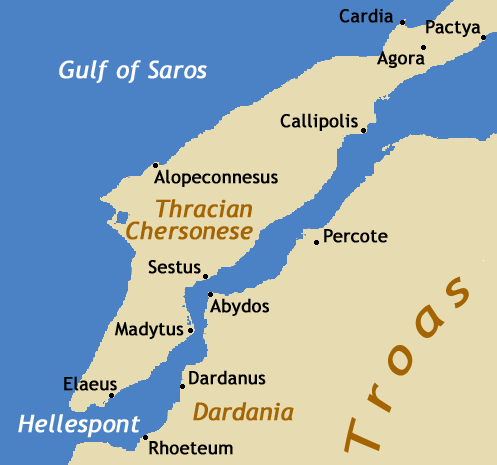
Abydos (Hellespont)
Abydos ( grc, Ἄβυδος, la, Abydus) was an ancient city and bishopric in Mysia. It was located at the Nara Burnu promontory on the Asian coast of the Hellespont (the straits of Dardanelles), opposite the ancient city of Sestos, and near the city of Çanakkale in Turkey. Abydos was founded in c. 670 BC at the most narrow point in the straits, and thus was one of the main crossing points between Europe and Asia, until its replacement by the crossing between Lampsacus and Kallipolis in the 13th century, and the abandonment of Abydos in the early 14th century. In Greek mythology, Abydos is presented in the myth of Hero and Leander as the home of Leander. The city is also mentioned in ''Rodanthe and Dosikles'', a novel written by Theodore Prodromos, a 12th-century writer, in which Dosikles kidnaps Rodanthe at Abydos. Archaeology In 1675, the site of Abydos was first identified, and was subsequently visited by numerous classicists and travellers, such as Robert Wood, Richard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; grc-x-classical, Ἑλλήσποντος, translit=Hellēspontos, lit=Sea of Helle), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosporus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits. One of the world's narrowest straits used for international navigation, the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean and Mediterranean seas while also allowing passage to the Black Sea by extension via the Bosporus. The Dardanelles is long and wide. It has an average depth of with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point abreast the city of Çanakkale. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulunids
The Tulunids (), were a Mamluk dynasty of Turkic origin who were the first independent dynasty to rule Egypt, as well as much of Syria, since the Ptolemaic dynasty. They were independent from 868, when they broke away from the central authority of the Abbasid Caliphate, to 905, when the Abbasids restored the Tulunid domains to their control. In the late 9th century, internal conflict amongst the Abbasids made control of the outlying areas of the empire was increasingly tenuous, and in 868 the Turkic officer Ahmad ibn Tulun established himself as an independent governor of Egypt. He subsequently achieved nominal autonomy from the central Abbasid government. During his reign (868–884) and those of his successors, the Tulunid domains were expanded to include Jordan Rift Valley, as well as Hejaz, Cyprus and Crete. Ahmad was succeeded by his son Khumarawayh, whose military and diplomatic achievements made him a major player in the Middle Eastern political stage. The Abbasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian Empire, Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture and List of inventions in the medieval Islamic world, invention in what became known as the Islamic Golden Age, Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)