Çanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
as the Hellespont (; grc-x-classical, Ἑλλήσποντος, translit=Hellēspontos, lit=Sea of Helle), is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe
Determining the boundaries between the continents of Earth is generally a matter of geographical convention. Several slightly different conventions are in use. The number of continents is most commonly considered seven (in English-speaking cou ...
and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace ( tr, Doğu Trakya or simply ''Trakya''; el, Ανατολική Θράκη, ''Anatoliki Thraki''; bg, Източна Тракия, ''Iztochna Trakiya''), also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the pa ...
. Together with the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern T ...
, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits.
One of the world's narrowest straits used for international navigation, the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the ...
with the Aegean and Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
seas while also allowing passage to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
by extension via the Bosporus. The Dardanelles is long and wide. It has an average depth of with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point abreast the city of Çanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
. The first fixed crossing across the Dardanelles opened in 2022 with the completion of the 1915 Çanakkale Bridge
The 1915 Çanakkale Bridge ( tr, 1915 Çanakkale Köprüsü), is a road suspension bridge in the province of Çanakkale Province, Çanakkale in northwestern Turkey. Situated just south of the coastal towns of Lapseki and Gelibolu, the bridge spa ...
.
Most of the northern shores of the strait along the Gallipoli peninsula ( tr, Gelibolu) are sparsely settled, while the southern shores along the Troad
The Troad ( or ; el, Τρωάδα, ''Troáda'') or Troas (; grc, Τρῳάς, ''Trōiás'' or , ''Trōïás'') is a historical region in northwestern Anatolia. It corresponds with the Biga Peninsula (Turkish: ''Biga Yarımadası'') in the Ça ...
peninsula ( tr, Biga) are inhabited by the city of Çanakkale's urban population of 110,000.
Names
The contemporary Turkish name , meaning ' Strait', is derived from the eponymous midsize city that adjoins the strait, itself meaning 'pottery fort'—from (, 'pottery') + (, 'fortress')—in reference to the area's famous pottery and ceramic wares, and the landmark Ottoman fortress of Sultaniye. The English name ''Dardanelles'' is an abbreviation of ''Strait of the Dardanelles''. During Ottoman times there was a castle on each side of the strait. These castles together were called the ''Dardanelles'', probably named after Dardanus, an ancient city on the Asian shore of the strait which in turn was said to take its name from Dardanus, the mythical son ofZeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion, ...
and Electra
Electra (; grc, Ήλέκτρα) is one of the most popular mythological characters in tragedies.Evans (1970), p. 79 She is the main character in two Greek tragedies, '' Electra'' by Sophocles and '' Electra'' by Euripides. She is also the centr ...
.
The ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
name () means "Sea of Helle", and was the ancient name of the narrow strait. It was variously named in classical literature , , and . It was so called from Helle, the daughter of Athamas, who was drowned here in the mythology of the Golden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece ( el, Χρυσόμαλλον δέρας, ''Chrysómallon déras'') is the fleece of the golden-woolled,, ''Khrusómallos''. winged ram, Chrysomallos, that rescued Phrixus and brought him to Colchis, wh ...
.
Geography
As amaritime
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Pr ...
waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
, the Dardanelles connects various seas along the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to comm ...
, the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, the Near East, and Western Eurasia, and specifically connects the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans an ...
to the Sea of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara,; grc, Προποντίς, Προποντίδα, Propontís, Propontída also known as the Marmara Sea, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea via the ...
. The Marmara further connects to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
via the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern T ...
, while the Aegean further links to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
. Thus, the Dardanelles allows maritime connections from the Black Sea all the way to the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean via Gibraltar, and the Indian Ocean through the Suez Canal, making it a crucial international waterway, in particular for the passage of goods coming in from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
.
The strait is located at approximately .
Present morphology
The strait is long, and wide, averaging deep with a maximum depth of at its narrowest point at Nara Burnu, abreastÇanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
. There are two major currents through the strait: a surface current flows from the Black Sea towards the Aegean Sea, and a more saline undercurrent flows in the opposite direction.
The Dardanelles is unique in many respects. The very narrow and winding shape of the strait is more akin to that of a river. It is considered one of the most hazardous, crowded, difficult and potentially dangerous waterways in the world. The currents produced by the tidal action in the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara are such that ships under sail must wait at anchorage for the right conditions before entering the Dardanelles.
History
As part of the only passage between the Black Sea and the Mediterranean, the Dardanelles has always been of great importance from a commercial and military point of view, and remains strategically important today. It is a major sea access route for numerous countries, includingRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
. Control over it has been an objective of a number of hostilities in modern history, notably the attack of the Allied Powers on the Dardanelles during the 1915 Battle of Gallipoli in the course of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
.
Ancient Greek, Persian, Roman, and Byzantine eras (pre-1454)
Greek and Persian history
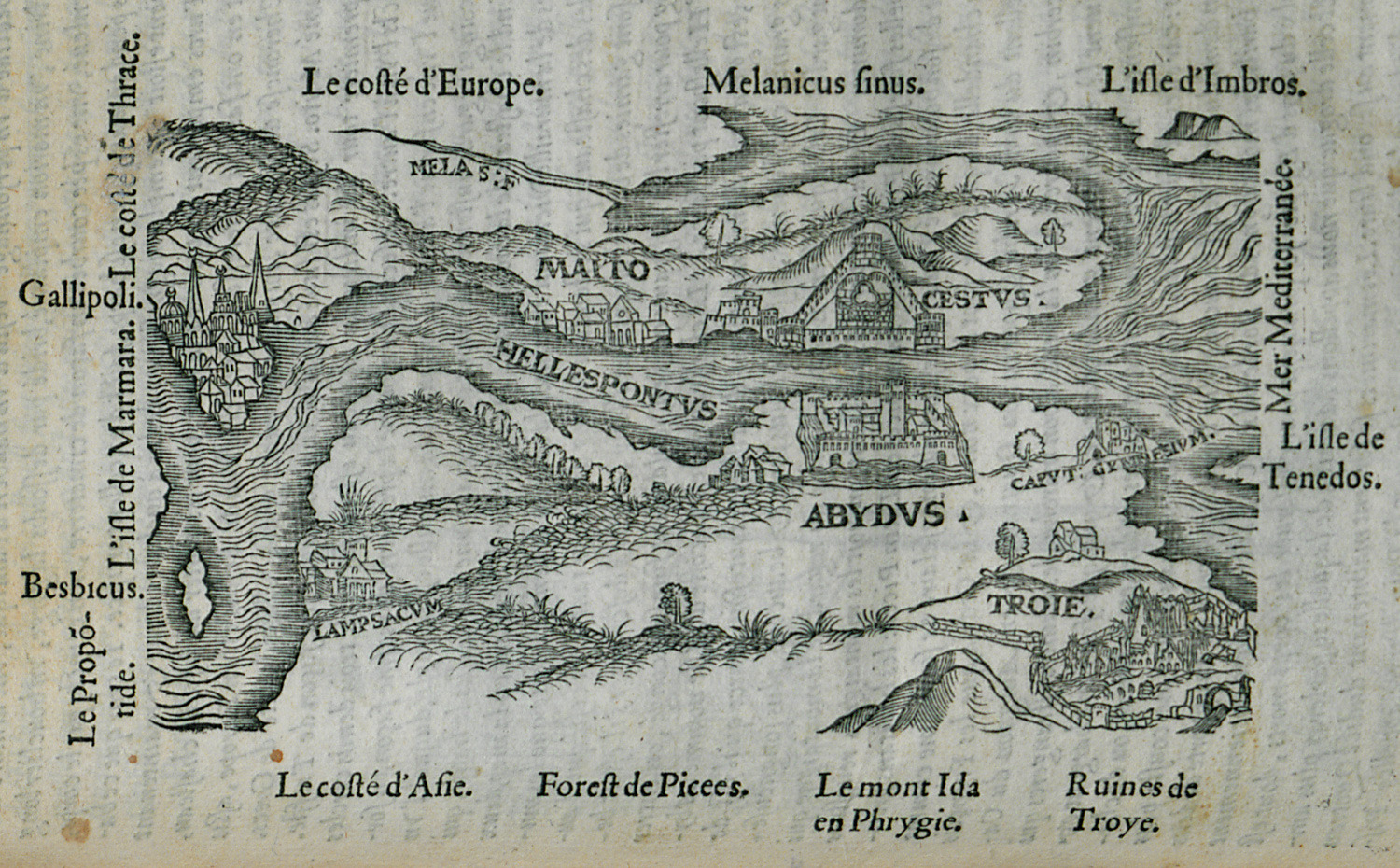
Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Çan ...
was located near the western entrance of the strait, and the strait's Asiatic shore was the focus of the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ha ...
. Troy was able to control the marine traffic entering this vital waterway. The Persian army of Xerxes I of Persia
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of ...
and later the Macedonian army of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
crossed the Dardanelles in opposite directions to invade each other's lands, in 480 BC and 334 BC respectively.
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for ...
says that, circa 482 BC, Xerxes I (the son of Darius
Darius may refer to:
Persian royalty
;Kings of the Achaemenid Empire
* Darius I (the Great, 550 to 487 BC)
* Darius II (423 to 404 BC)
* Darius III (Codomannus, 380 to 330 BC)
;Crown princes
* Darius (son of Xerxes I), crown prince of Persia, ma ...
) had two pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge (or ponton bridge), also known as a floating bridge, uses floats or shallow- draft boats to support a continuous deck for pedestrian and vehicle travel. The buoyancy of the supports limits the maximum load that they can carry. ...
s built across the width of the Hellespont at Abydos Abydos may refer to:
*Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz
* Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor
* Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the '' Stargate'' science fiction universe ...
, in order that his huge army could cross from Persia into Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
. This crossing was named by Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; grc-gre, Αἰσχύλος ; c. 525/524 – c. 456/455 BC) was an ancient Greek tragedian, and is often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Gree ...
in his tragedy ''The Persians
''The Persians'' ( grc, Πέρσαι, ''Persai'', Latinised as ''Persae'') is an ancient Greek tragedy written during the Classical period of Ancient Greece by the Greek tragedian Aeschylus. It is the second and only surviving part of a now other ...
'' as the cause of divine intervention against Xerxes.
According to Herodotus (vv.34), both bridges were destroyed by a storm and Xerxes had those responsible for building the bridges beheaded and the strait itself whipped. The Histories of Herodotus
The ''Histories'' ( el, Ἱστορίαι, ; also known as ''The History'') of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Written around 430 BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, ''The Histories'' serve ...
vii.33–37 and vii.54–58 give details of building and crossing of Xerxes' Pontoon Bridges. Xerxes is then said to have thrown fetters into the strait, given it three hundred lashes and branded it with red-hot irons as the soldiers shouted at the water.
Herodotus commented that this was a "highly presumptuous way to address the Hellespont" but in no way atypical of Xerxes. (vii.35)
Harpalus the engineer is said to have eventually helped the invading armies to cross by lashing the ships together with their bows facing the current and adding two additional anchors to each ship.
From the perspective of ancient Greek mythology Helle, the daughter of Athamas, supposedly was drowned at the Dardanelles in the legend of the Golden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece ( el, Χρυσόμαλλον δέρας, ''Chrysómallon déras'') is the fleece of the golden-woolled,, ''Khrusómallos''. winged ram, Chrysomallos, that rescued Phrixus and brought him to Colchis, wh ...
. Likewise, the strait was the scene of the legend of Hero and Leander
Hero and Leander is the Greek myth relating the story of Hero ( grc, Ἡρώ, ''Hērṓ''; ), a priestess of Aphrodite ( Venus in Roman mythology) who dwelt in a tower in Sestos on the European side of the Hellespont, and Leander ( grc, Λέ ...
, wherein the lovesick Leander swam the strait nightly in order to tryst with his beloved, the priestess Hero, but was ultimately drowned in a storm.
Byzantine history
The Dardanelles were vital to the defence ofConstantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
during the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
period.
Also, the Dardanelles was an important source of income for the ruler of the region. At the Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
Archaeological Museum a marble plate contains a law by the Byzantine Emperor Anastasius I (491–518 AD), that regulated fees for passage through the customs office of the Dardanelles. Translation:
... Whoever dares to violate these regulations shall no longer be regarded as a friend, and he shall be punished. Besides, the administrator of the Dardanelles must have the right to receive 50 golden Litrons, so that these rules, which we make out of piety, shall never ever be violated... ... The distinguished governor and major of the capital, who already has both hands full of things to do, has turned to our lofty piety in order to reorganize the entry and exit of all ships through the Dardanelles... ... Starting from our day and also in the future, anybody who wants to pass through the Dardanelles must pay the following:Since the 14th century the Dardanelles have almost continuously been controlled by the Turks.
– All wine merchants who bring wine to the capital (Constantinopolis), exceptCilicia Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian language, Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from th ...ns, have to pay the Dardanelles officials 6follis The follis (plural ''folles''; it, follaro, ar, فلس, Fels) was a type of coin in the Roman and Byzantine traditions. Roman coin In the past, the term ''follis'' was used to describe a large bronze Roman coin introduced in about 294 (the ...and 2 sextarius of wine.
– In the same manner, all merchants of olive-oil, vegetables and lard must pay the Dardanelles officials 6 follis. Cilician sea-merchants have to pay 3 follis and in addition to that, 1 keration (12 follis) to enter, and 2 keration to exit.
– All wheat merchants have to pay the officials 3 follis per modius, and a further sum of 3 follis when leaving.
Ottoman era (1354–1922)
 The Dardanelles continued to constitute an important waterway during the period of the
The Dardanelles continued to constitute an important waterway during the period of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, which conquered Gallipoli in 1354.
Ottoman control of the strait continued largely without interruption or challenges until the 19th century, when the Empire started its decline.
Nineteenth century
Gaining control of, or guaranteed access to, the strait became a key foreign-policy goal of theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
during the 19th century. During the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, Russia—supported by Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
in the Dardanelles Operation— blockaded the straits in 1807.
In 1833, following the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
's defeat in the Russo-Turkish War of 1828–1829, Russia pressured the Ottomans to sign the Treaty of Hunkiar Iskelesi—which required the closing of the straits to warships of non-Black Sea powers at Russia's request. That would have effectively given Russia a free hand in the Black Sea.
This treaty alarmed the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, who were concerned that the consequences of potential Russian expansionism in the Black Sea and Mediterranean regions could conflict with their own possessions and economic interest in the region. At the London Straits Convention
In the London Straits Convention concluded on 13 July 1841 between the Great Powers of Europe at the time—Russia, the United Kingdom, France, Austria and Prussia—the "ancient rule" of the Ottoman Empire was re-established by closing the Tur ...
in July 1841, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
pressured Russia to agree that only Turkish warships could traverse the Dardanelles in peacetime. The United Kingdom and France subsequently sent their fleets through the straits to defend the Danube front and to attack the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
during the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included t ...
of 1853–1856 – but they did so as allies of the Ottoman Empire. Following the defeat of Russia in the Crimean War, the Congress of Paris
The Congress of Paris is the name for a series of diplomatic meetings held in 1856 in Paris, France, to negotiate peace between the warring powers in the Crimean War that had started almost three years earlier."Paris, Treaty of (1856)". The New E ...
in 1856 formally reaffirmed the London Straits Convention. It remained technically in force into the 20th and 21st centuries.
World War I
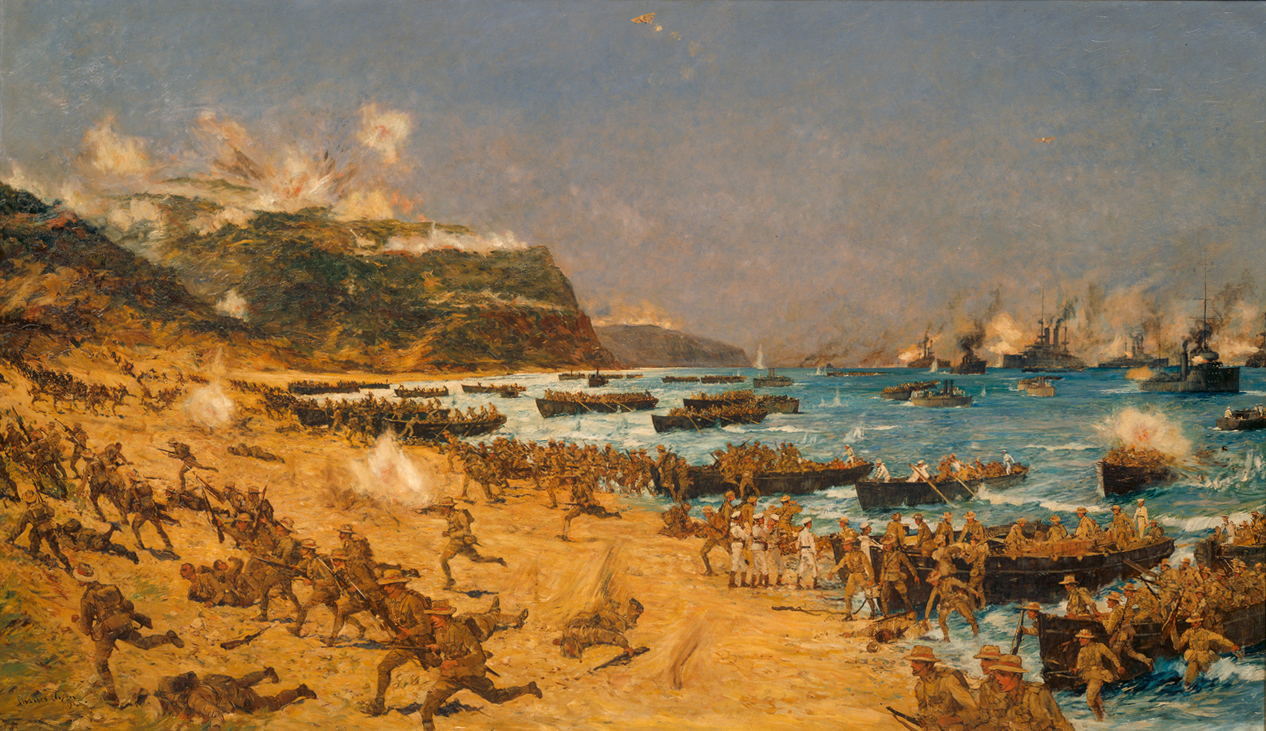
 In 1915 the Allies sent a substantial invasion force of British, Indian, Australian, New Zealand, French and Newfoundland troops to attempt to open up the straits. In the Gallipoli campaign, Turkish troops trapped the Allies on the coasts of the Gallipoli peninsula. The campaign damaged the career of Winston Churchill, then
In 1915 the Allies sent a substantial invasion force of British, Indian, Australian, New Zealand, French and Newfoundland troops to attempt to open up the straits. In the Gallipoli campaign, Turkish troops trapped the Allies on the coasts of the Gallipoli peninsula. The campaign damaged the career of Winston Churchill, then First Lord of the Admiralty
The First Lord of the Admiralty, or formally the Office of the First Lord of the Admiralty, was the political head of the English and later British Royal Navy. He was the government's senior adviser on all naval affairs, responsible for the di ...
(in office 1911–1915), who had eagerly promoted the (unsuccessful) use of Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
sea-power
The Navy League of the United States, commonly referred to as the Navy League, is a national association with nearly 50,000 members who advocate for a strong, credible United States Navy, United States Marine Corps, United States Coast Guard and ...
to force open the straits. Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, or Mustafa Kemal Pasha until 1921, and Ghazi Mustafa Kemal from 1921 until 1934 ( 1881 – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish field marshal, revolutionary statesman, author, and the founding father of the Rep ...
, subsequent founder of the Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula i ...
, served as an Ottoman commander during the land campaign.
The Turks mined the straits to prevent Allied ships from penetrating them but, in minor actions two submarines, one British and one Australian, did succeed in penetrating the minefields. The British submarine sank an obsolete Turkish pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, prot ...
off the Golden Horn
The Golden Horn ( tr, Altın Boynuz or ''Haliç''; grc, Χρυσόκερας, ''Chrysókeras''; la, Sinus Ceratinus) is a major urban waterway and the primary inlet of the Bosphorus in Istanbul, Turkey. As a natural estuary that connects with t ...
of Istanbul. Sir Ian Hamilton's Mediterranean Expeditionary Force failed in its attempt to capture the Gallipoli peninsula, and the British cabinet ordered its withdrawal in December 1915, after eight months' fighting. Total Allied deaths included 43,000 British, 15,000 French, 8,700 Australians, 2,700 New Zealanders, 1,370 Indians and 49 Newfoundlanders. Total Turkish deaths were around 60,000.
Following the war, the 1920 Treaty of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well ...
demilitarized the strait and made it an international territory under the control of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by ...
. The Ottoman Empire's non-ethnically Turkish territories were broken up and partitioned among the Allied Powers, and Turkish jurisdiction over the straits
A strait is an Ocean, oceanic landform connecting two Sea, seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ...
curbed.
Turkish republican and modern eras (1923–present)
After the dissolution of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
following a lengthy campaign by Turks as part of the Turkish War of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by th ...
against both the Allied Powers and the Ottoman court, the Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula i ...
was created in 1923 by the Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conf ...
, which established most of the modern sovereign territory of Turkey and restored the straits
A strait is an Ocean, oceanic landform connecting two Sea, seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ...
to Turkish territory, with the condition that Turkey keep them demilitarized and allow all foreign warships and commercial shipping to traverse the straits freely.
As part of its national security strategy, Turkey eventually rejected the terms of the treaty, and subsequently remilitarized the straits area over the following decade. Following extensive diplomatic negotiations, the reversion was formalized under the Montreux Convention Regarding the Regime of the Turkish Straits
The (Montreux) Convention regarding the Regime of the Straits, often known simply as the Montreux Convention, is an international agreement governing the Bosporus and Dardanelles Straits in Turkey. Signed on 20 July 1936 at the Montreux Palac ...
on 20 July 1936. That convention, which is still in force today, treats the straits as an international shipping lane while allowing Turkey to retain the right to restrict the naval traffic of non-Black Sea states.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, through February 1945, when Turkey was neutral for most of the length of the conflict, the Dardanelles were closed to the ships of the belligerent nations. Turkey declared war on Germany in February 1945, but it did not employ any offensive forces during the war.
In July 1946, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
sent a note to Turkey proposing a new régime for the Dardanelles that would have excluded all nations except the Black Sea powers. The second proposal was that the straits should be put under joint Turkish-Soviet defence. This meant that Turkey, the Soviet Union, Bulgaria and Romania would be the only states having access to the Black Sea through the Dardanelles. The Turkish government however, under pressure from the United States, rejected these proposals.
Turkey joined NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in 1952, thus affording its straits even more strategic importance as a commercial and military waterway.
In more recent years, the Turkish Straits have become particularly important for the oil industry. Russian oil, from ports such as Novorossyisk
Novorossiysk ( rus, Новоросси́йск, p=nəvərɐˈsʲijsk; ady, ЦIэмэз, translit=Chəməz, p=t͡sʼɜmɜz) is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is one of the largest ports on the Black Sea. It is one of the few cities hono ...
, is exported by tankers primarily to western Europe and the U.S. via the Bosporus and the Dardanelles straits.
Crossings

Maritime
The waters of the Dardanelles are traversed by numerous passenger and vehicular ferries daily, as well as recreational and fishing boats ranging from dinghies to yachts owned by both public and private entities. The strait also experiences significant amounts of commercial shipping traffic.Land
The Çanakkale 1915 Bridge joins Lapseki, a district of Çanakkale, on the Asian side and Sütlüce, a village of theGelibolu
Gelibolu, also known as Gallipoli (from el, Καλλίπολις, ''Kallipolis'', "Beautiful City"), is the name of a town and a district in Çanakkale Province of the Marmara Region, located in Eastern Thrace in the European part of Turkey on th ...
district, on the European side. It is part of planned expansions to the Turkish National Highway Network. Work on the bridge began in March 2017, and it was opened on March 18, 2022.
Subsea
2 submarine cable systems transmitting electric power at 400 kV bridge the Dardanelles to feed west and east of Istanbul. They have their own landing stations in Lapseki and Sütlüce. The first, situated in the northeast quarter portion of the strait, was energised in April 2015 and provides 2 GW via 6 phases 400 kV AC 3.9 km far through the sea. The second, somewhat in the middle of the strait, was still under construction in June 2016 and will provide similar capabilities to the first line. Both subsea power lines cross 4 optical fibre data lines laid earlier along the strait. A published map shows communication lines leading from Istanbul into the Mediterranean, named MedNautilus and landing atAthens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
, Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and elsewhere.
Image gallery
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
law regulating payment of customs in the Dardanelles
File:Dardanelles and Gulf of Saros by Piri Reis.jpg, Historic map of the Dardanelles by Piri Reis
Ahmet Muhiddin Piri ( 1465 – 1553), better known as Piri Reis ( tr, Pîrî Reis or '' Hacı Ahmet Muhittin Pîrî Bey''), was a navigator, geographer and cartographer. He is primarily known today for his maps and charts collected in his ''K ...
File:Anzac Beach 1915.jpg, The ANZAC
The Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (ANZAC) was a First World War army corps of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force. It was formed in Egypt in December 1914, and operated during the Gallipoli campaign. General William Birdwood comm ...
s at Gallipoli in 1915
File:Graphic map of the Dardanelles.JPG, Map of the Dardanelles drawn by G. F. Morrell, 1915, showing the Gallipoli peninsula and the west coast of Turkey, as well as the location of front line troops and landings during the Gallipoli Campaign
File:Dardanellen 1.JPG, A view of the Dardanelles from Gallipoli peninsula
File:Chanakkale Turkey.jpg, A view of Çanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
from the Dardanelles
File:ChanakkaleFerry.jpg, Ferry line across the Dardanelles in Çanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
File:Havadan cnk.jpg, Aerial view of the city of Çanakkale
Çanakkale (pronounced ), ancient ''Dardanellia'' (), is a city and seaport in Turkey in Çanakkale province on the southern shore of the Dardanelles at their narrowest point. The population of the city is 195,439 (2021 estimate).
Çanakkale is ...
File:Dardanelles 2021.jpg, Dardanelles in 2021
See also
* Action of 26 June 1656 *Battle of the Dardanelles (disambiguation) Battle of the Dardanelles may refer to:
During the Ottoman–Venetian War of 1645–1669:
* Battle of the Dardanelles (1654)
* Battle of the Dardanelles (1655)
* Battle of the Dardanelles (1656)
* Battle of the Dardanelles (1657)
During other c ...
* Dardanelles Commission
The Dardanelles Commission was an investigation into the disastrous 1915 Dardanelles Campaign. It was set up under the Special Commissions (Dardanelles and Mesopotamia) Act 1916. The final report of the commission, issued in 1919, found major p ...
* List of maritime incidents in the Turkish Straits
References
External links
Pictures of the city of Çanakkale
Canakkale Onsekiz Mart University
* [http://merhav.nli.org.il/primo-explore/search?query=any,contains,dardanelles%20maps&tab=default_tab&search_scope=Local&sortby=lso01&vid=NLI&mfacet=rtype,include,maps,1&mfacet=tlevel,include,online_resources,2&lang=en_US Old Maps of the Dardanelles], Eran Laor Cartographic collection, The National Library of Israel {{DEFAULTSORT:Dardanelles Dardanelles, Landforms of Çanakkale Province Straits of the Mediterranean Sea Trojans World Heritage Tentative List for Turkey Straits of Turkey Turkish Straits Important Bird Areas of Turkey