|
Latina (genus)
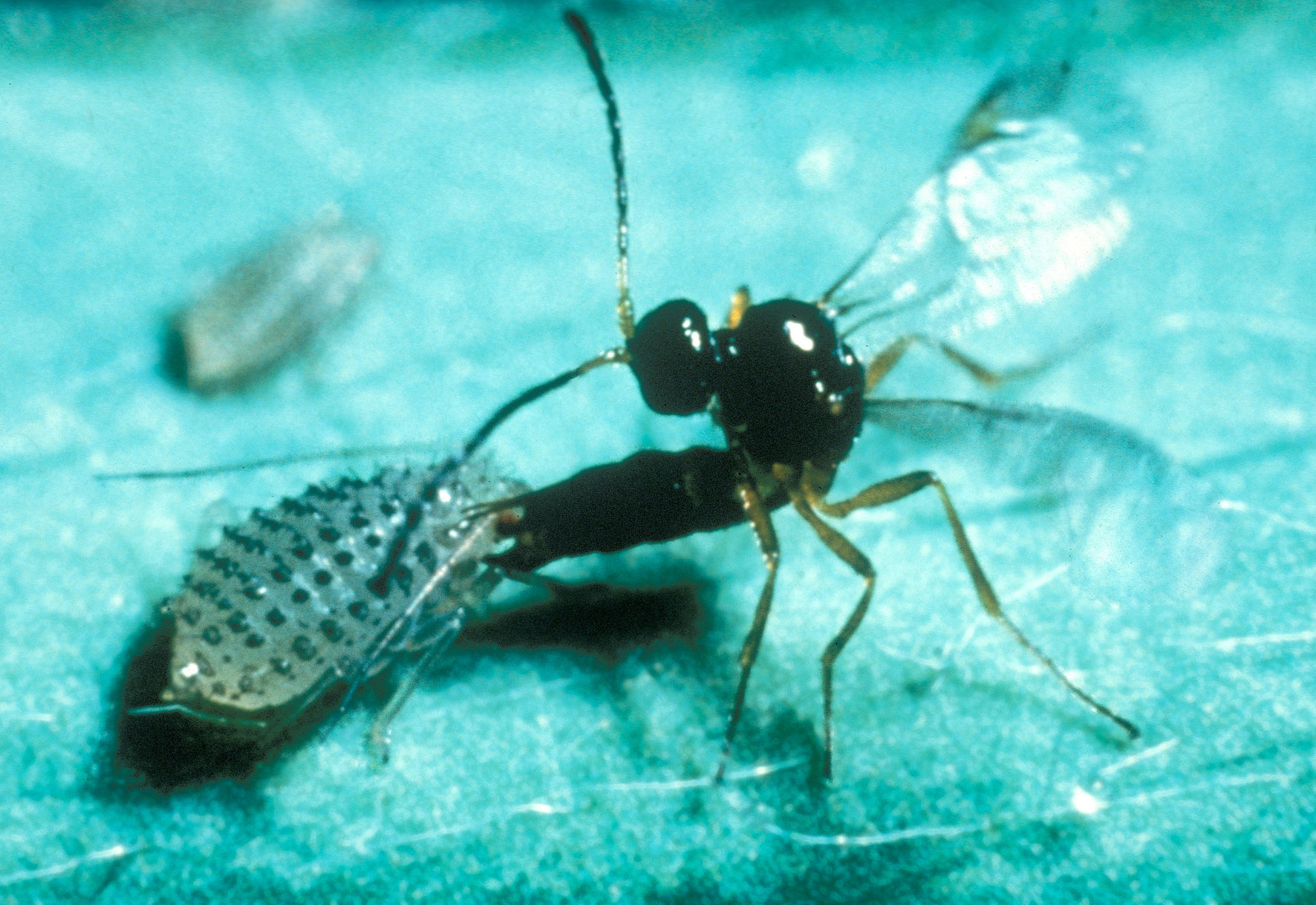
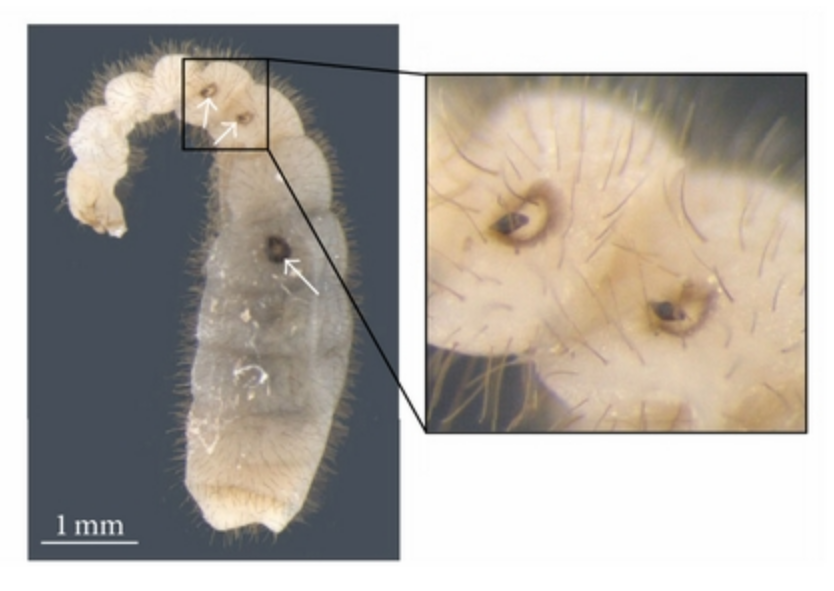
''Latina'' is a genus of South American chalcid wasps in the family Eucharitidae. There are four known species of ''Latina'' with three known in Argentina and one from Venezuela. Originally the genus was named ''Laurella'' in 2002, but it turned out that the name had already been assigned to a genus of bee flies 30 years prior, and so the name ''Latina'' was adopted as a replacement, in honor of Latin America where the genus occurs. Biology Like all members of the Euchratidae, ''Latina'' wasps are ant parasitoids. The wasp lays eggs on the undersides of leaves near the nests of Ponerine Ponerinae is a subfamily of ants in the Poneromorph subfamilies group, with about 1,600 species in 47 extant genera, including ''Dinoponera gigantea'' - one of the world's largest species of ant. Mated workers have replaced the queen as the ... ants. Within a few days the eggs hatch into planidial larvae that are mobile and can leap. They enter the ant colony, most likely being carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order (biology), order of insects, comprising the sawfly, sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are Parasitoid wasp, parasitic. Females typically have a special ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or places that are otherwise inaccessible. This ovipositor is often modified into a stinger. The young develop through holometabolism (complete metamorphosis (biology), metamorphosis)—that is, they have a wormlike larval stage and an inactive pupal stage before they mature. Etymology The name Hymenoptera refers to the wings of the insects, but the original derivation is ambiguous. All references agree that the derivation involves the Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek wikt:πτερόν, πτερόν (''pteron'') for wing. The Ancient Greek wikt:ὑμήν, ὑμήν (''hymen'') for membrane provides a plausible etymology for the term bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucharitidae
The Eucharitidae are a family of parasitic wasps.Ayre, G.L. Pseudometagea schwarzii (Ashm.) (Eucharitidae: Hymenoptera), a parasite of Lasius neoniger Emery (Formicidae: Hymenoptera). Canadian Journal of Zoology 40 (1962) : 157-164. Eucharitid wasps are members of the superfamily Chalcidoidea and consist of three subfamilies: Oraseminae, Eucharitinae, and Gollumiellinae. Most of the 55 genera and 417 species of Eucharitidae are members of the subfamilies Oraseminae and Eucharitinae,Heraty, John. Eucharitidae. Hymenopteran Systematics, University of California, Riverside (2002): Web. 16 Sep. 2011. and are found in tropical regions of the world. Eucharitids are specialized parasitoids of ants, meaning each species is usually only parasitic of one genus of ant. Furthermore, they are one of the few parasitoids that have been able to use ants as hosts, despite ants’ effective defense systems against most parasitoids.Lachaud, Jean-Paul and Perez-Lachaud, Gavriela. Impact of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcid Wasp
Chalcid wasps (, , for their metallic colour) are insects within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, part of the order Hymenoptera. The superfamily contains some 22,500 known species, and an estimated total diversity of more than 500,000 species, meaning the vast majority have yet to be discovered and described. The name "chalcid" is often confused with the name "chalcidid", though the latter refers strictly to one constituent family, the Chalcididae, rather than the superfamily as a whole; accordingly, most recent publications (e.g.,) use the name "chalcidoid" when referring to members of the superfamily. Most chalcid wasps are parasitoids of other insects, though other life styles are known, with the herbivorous fig wasps acting as pollinators. Various species are used as biological pest control agents or in scientific research. Description Chalcidoids are generally small wasps, averaging 1.5 mm in length and usually being less than 3 mm. The body is often metallic in colour. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombyliidae
The Bombyliidae are a family of flies, commonly known as bee flies. Adults generally feed on nectar and pollen, some being important pollinators. Larvae are mostly parasitoids of other insects. Overview The Bombyliidae are a large family of flies comprising hundreds of genera, but the life cycles of most species are known poorly, or not at all. They range in size from very small (2 mm in length) to very large for flies (wingspan of some 40 mm).Hull, Frank Montgomery, Bee flies of the world: the genera of the family Bombyliidae Washington, Smithsonian Institution Press 1973 . Downloadable from: https://archive.org/details/beefliesofworl2861973hull When at rest, many species hold their wings at a characteristic "swept back" angle. Adults generally feed on nectar and pollen, some being important pollinators, often with spectacularly long proboscises adapted to plants such as ''Lapeirousia'' species with very long, narrow floral tubes. Unlike butterflies, bee flies hold t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation. Among parasitoids, strategies range from living inside the host (''endoparasitism''), allowing it to continue growing before emerging as an adult, to Paralysis, paralysing the host and living outside it (''ectoparasitism''). Hosts can include other parasitoids, resulting in hyperparasitism; in the case of oak galls, up to five levels of parasitism are possible. Some parasitoids Behavior-altering parasite, influence their host's behaviour in ways that favour the propagation of the parasitoid. Parasitoids are found in a variety of Taxon, taxa across the insect superorder Endopterygota, whose compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponerinae
Ponerinae is a subfamily of ants in the Poneromorph subfamilies group, with about 1,600 species in 47 extant genera, including ''Dinoponera gigantea'' - one of the world's largest species of ant. Mated workers have replaced the queen as the functional egg-layers in several species of ponerine ants. In such queenless species, the reproductive status of workers can only be determined through ovarian dissections. Description and identification They are most easily identified from other subfamilies by possessing a single-node petiole with a constriction before the second gastral segment. They are rare examples of stinging ants. In addition to the sting, they can also be characterized by a single segmented petiole and the constriction of the first and second segment of the gaster. They can also be identified by the shape of their head. Female workers have twelve segmented antennae, whereas male workers have 13 segmented antennae. Behavior These ants typically nest in soil, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planidium
A planidium is a specialized form of insect larva seen in the first-instar of a few families of insects that have parasitoidal ways of life. They are usually flattened, highly sclerotized (hardened), and quite mobile. The function of the planidial stage is to find a host on which the later larval instars may feed, generally until the insect pupates. Etymology The term "planidium" is derived from the Greek language ''πλανής'' (planis) meaning "wanderer". The term planula was similarly derived in reference to the wandering larvae of certain Cnidaria. Accordingly, "planidium" is the general term for such an adaptation, and it is not limited to any particular species or morphology. Planidia of different species differ variously from each other in form. The first instar larva in the beetle family Meloidae has three claws on each foot, and is therefore called a triungulin (plural ''triungula''). The term is derived from the Latin ''tri'' meaning "three" and ''ungula'' meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoptera Genera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic. Females typically have a special ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or places that are otherwise inaccessible. This ovipositor is often modified into a stinger. The young develop through holometabolism (complete metamorphosis)—that is, they have a wormlike larval stage and an inactive pupal stage before they mature. Etymology The name Hymenoptera refers to the wings of the insects, but the original derivation is ambiguous. All references agree that the derivation involves the Ancient Greek πτερόν (''pteron'') for wing. The Ancient Greek ὑμήν (''hymen'') for membrane provides a plausible etymology for the term because species in this order have membranous wings. However, a key characteristic of this order is that the hindwings are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |