|
Langer Lines
Langer's lines, Langer lines of skin tension, or sometimes called cleavage lines, are topological lines drawn on a map of the human body. They are parallel to the natural orientation of collagen fibers in the dermis, and generally perpendicular to the underlying muscle fibers. Langer's lines have relevance to forensic science and the development of surgical techniques. History The lines were first discovered in 1861 by Austrian anatomist Karl Langer (1819–1887), though he cited the surgeon Baron Dupuytren as being the first to recognise the phenomenon. Langer punctured numerous holes at short distances from each other into the skin of a cadaver with a tool that had a circular-shaped tip, similar to an ice pick. He noticed that the resultant punctures in the skin had ellipsoidal shapes. From this testing he observed patterns and was able to determine "line directions" by the longer axes of the ellipsoidal holes and lines. Application Knowing the direction of Langer's lines withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Map
In cartography and geology, a topological map is a type of diagram that has been simplified so that only vital information remains and unnecessary detail has been removed. These maps lack scale, also distance and direction are subject to change and/or variation, but the topological relationship between points is maintained. A good example are the tube maps for the London Underground and the New York City Subway. See also *Outline of cartography The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cartography: Cartography (also called mapmaking) – study and practice of making and using maps or globes. Maps have traditionally been made using pen and paper, but ... References Map types {{Cartography-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stab Wound
A stab wound is a specific form of penetrating trauma to the skin that results from a knife or a similar pointed object. While stab wounds are typically known to be caused by knives, they can also occur from a variety of implements, including broken bottles and ice picks. Most stabbings occur because of intentional violence or through self-infliction. The treatment is dependent on many different variables such as the anatomical location and the severity of the injury. Even though stab wounds are inflicted at a much greater rate than gunshot wounds, they account for less than 10% of all penetrating trauma deaths. Management Stab wounds can cause various internal and external injuries. They are generally caused by low-velocity weapons, meaning the injuries inflicted on a person are typically confined to the path it took internally, instead of causing damage to surrounding tissue, which is common of gunshot wounds. The abdomen is the most commonly injured area from a stab wound. Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
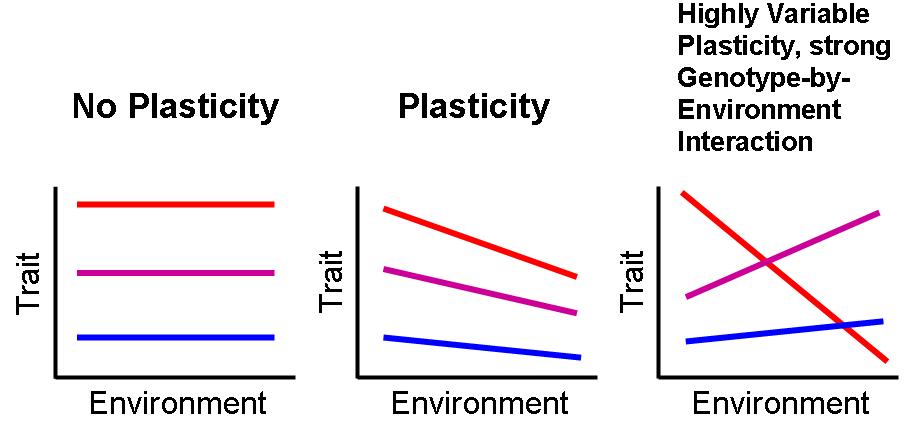
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Pathology
Forensic pathology is pathology that focuses on determining the cause of death by examining a corpse. A post mortem examination is performed by a medical examiner or forensic pathologist, usually during the investigation of criminal law cases and civil law cases in some jurisdictions. Coroners and medical examiners are also frequently asked to confirm the identity of remains. Duties Forensic pathology is an application of medical jurisprudence. A forensic pathologist is a medical doctor who has completed training in anatomical pathology and has subsequently specialized in forensic pathology. The requirements for becoming a "fully qualified" forensic pathologist vary from country to country. Some of the different requirements are discussed below. The forensic pathologist performs autopsies/postmortem examinations with the goal determining the cause of death as well as the possible manner of death. The autopsy report contains conclusions made relating to the following: * The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία '' -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases ( Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print around the same time.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blaschko's Lines
Blaschko's lines, also called the lines of Blaschko, are lines of normal cell development in the skin. These lines are only visible in those with a mosaic skin condition or in chimeras where different cell lines contain different genes. These lines may express different amounts of melanin, or become visible due to a differing susceptibility to disease. In such individuals, they can become apparent as whorls, patches, streaks or lines in a linear or segmental distribution over the skin. They follow a ''V'' shape over the back, ''S''-shaped whirls over the chest and sides, and wavy shapes on the head. Not all mosaic skin conditions follow Blascko's lines. The lines are believed to trace the migration of embryonic cells. They do not correspond to nervous, muscular, or lymphatic systems. The lines are not unique to humans and can be observed in other non-human animals with mosaicism. Alfred Blaschko is credited with the first demonstration of these lines in 1901. Signs and sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraissl's Lines
Kraissl's lines are a set of anatomical skin lines. They differ from Langer's lines in that unlike Langer's lines, which are defined in term of collagen orientation, Kraissl's lines are the lines of maximum skin tension. Whereas Langer's lines were defined in cadavers, Kraissl's lines have been defined in living individuals. Also, the method used to identify Kraissl's lines is not traumatic. See also * Blaschko's lines * Langer's lines Langer's lines, Langer lines of skin tension, or sometimes called cleavage lines, are topological lines drawn on a map of the human body. They are parallel to the natural orientation of collagen fibers in the dermis, and generally perpendicular to ... References Skin lines {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keloid
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar, is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation tissue (collagen type 3) at the site of a healed skin injury which is then slowly replaced by collagen type 1. Keloids are firm, rubbery lesions or shiny, fibrous nodules, and can vary from pink to the color of the person's skin or red to dark brown in color. A keloid scar is benign and not contagious, but sometimes accompanied by severe itchiness, pain, and changes in texture. In severe cases, it can affect movement of skin. In the United States keloid scars are seen 15 times more frequently in people of sub-Saharan African descent than in people of European descent. There is a higher tendency to develop a keloid among those with a family history of keloids and people between the ages of 10 and 30 years. Keloids should not be confused wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Surgery
Breast surgery is a form of surgery performed on the breast. Types Types include: *Breast reduction surgery *Augmentation mammoplasty *Mastectomy *Lumpectomy *Breast-conserving surgery, a less radical cancer surgery than mastectomy *Mastopexy, or breast lift surgery * Surgery for breast abscess, including incision and drainage as well as excision of lactiferous ducts * Surgical breast biopsy * Microdochectomy (removal of a lactiferous duct) Complications After surgical intervention to the breast, complications may arise related to wound healing. As in other types of surgery, hematoma (post-operative bleeding), seroma (fluid accumulation), or incision-site breakdown (wound infection) may occur. Breast hematoma due to an operation will normally resolve with time but should be followed up with more detailed evaluation if it does not. Breast abscess can occur as post-surgical complication, for example after cancer treatment or reduction mammaplasty.Noel Weidner, Chapter ''Infectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmetic Surgery
Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic (or aesthetic) surgery aims at improving the appearance of it. Etymology The word ''plastic'' in ''plastic surgery'' means "reshaping" and comes from the Greek πλαστική (τέχνη), ''plastikē'' (''tekhnē''), "the art of modelling" of malleable flesh. This meaning in English is seen as early as 1598. The surgical definition of "plastic" first appeared in 1839, preceding the modern "engineering material made from petroleum" sense by 70 years. History Treatments for the plastic repair of a broken nose are first mentioned in the Egyptian medical text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |