Phenotype on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The term "phenotype" has sometimes been incorrectly used as a shorthand for the phenotypic difference between a mutant and its wild type, which (if not significant) leads to the statement that a
"mutation has no phenotype".
Another extension adds behavior to the phenotype, since behaviors are observable characteristics. Behavioral phenotypes include cognitive, personality, and behavioral patterns. Some behavioral phenotypes may characterize psychiatric disorders or syndromes.
The term "phenotype" has sometimes been incorrectly used as a shorthand for the phenotypic difference between a mutant and its wild type, which (if not significant) leads to the statement that a
"mutation has no phenotype".
Another extension adds behavior to the phenotype, since behaviors are observable characteristics. Behavioral phenotypes include cognitive, personality, and behavioral patterns. Some behavioral phenotypes may characterize psychiatric disorders or syndromes.


 Gene expression is regulated at various levels and thus each level can affect certain phenotypes, including transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.
Gene expression is regulated at various levels and thus each level can affect certain phenotypes, including transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.
 Changes in the levels of gene expression can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as environmental conditions,
Changes in the levels of gene expression can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as environmental conditions,
Mouse Phenome Database
Human Phenotype Ontology
Europhenome: Access to raw and annotated mouse phenotype data
"Wilhelm Johannsen's Genotype-Phenotype Distinction" by E. Peirson at the Embryo Project Encyclopedia
{{Authority control Classical genetics Polymorphism (biology)
 In
In genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar worki ...
, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as caddis-fly larva cases and beaver dams as "extended phenotypes".
Wilhelm Johannsen proposed the genotype–phenotype distinction in 1911 to make clear the difference between an organism's hereditary material and what that hereditary material produces. The distinction resembles that proposed by August Weismann (1834–1914), who distinguished between germ plasm (heredity) and somatic cells (the body). More recently, in '' the Selfish Gene'' (1976), Richard Dawkins distinguished these concepts as replicators and vehicles.
The genotype–phenotype distinction should not be confused with Francis Crick's central dogma of molecular biology, a statement about the directionality of molecular sequential information flowing from DNA to protein, and not the reverse.
Difficulties in definition
Despite its seemingly straightforward definition, the concept of the phenotype has hidden subtleties. It may seem that anything dependent on thegenotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
is a phenotype, including molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bio ...
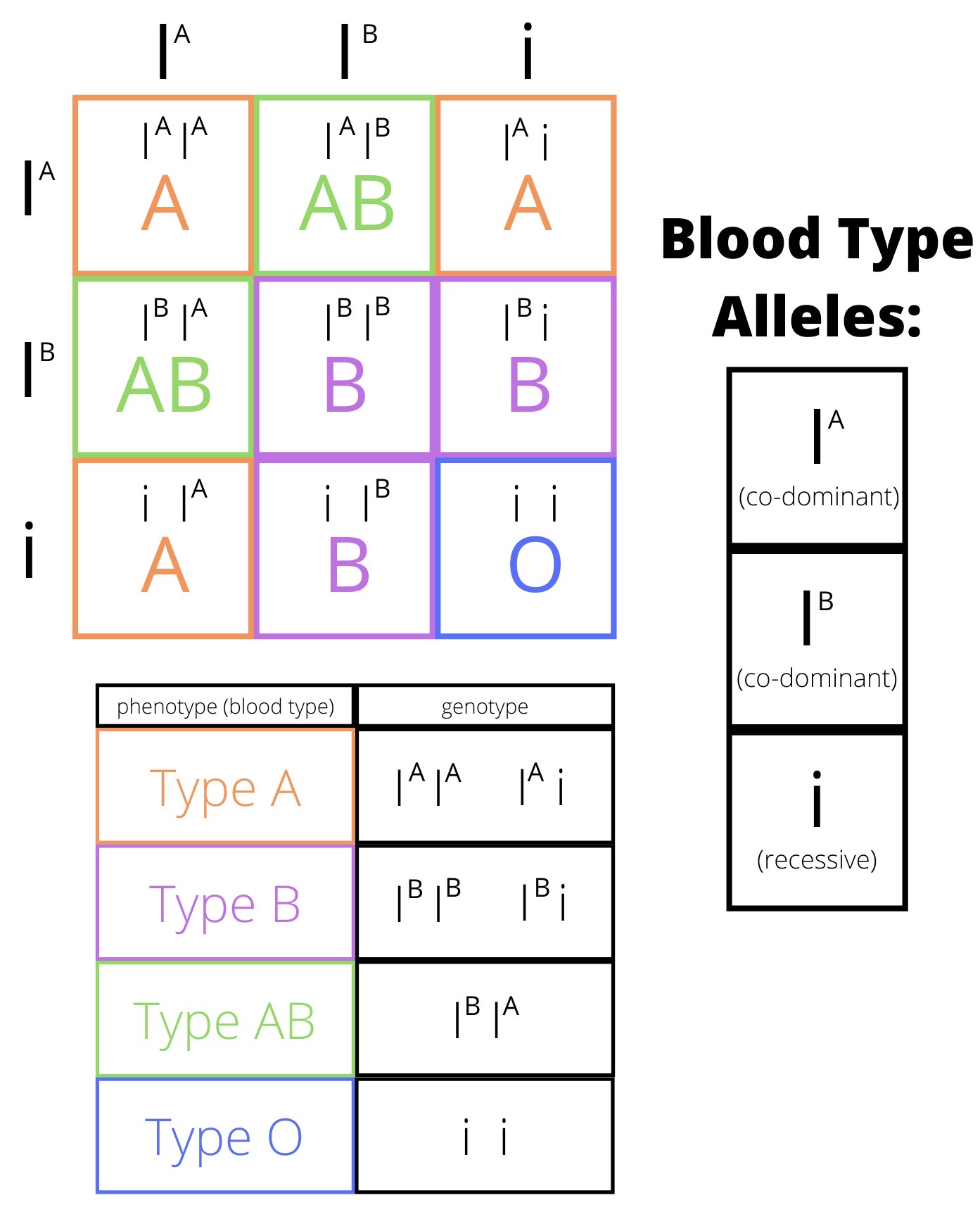
s such as RNA and proteins. Most molecules and structures coded by the genetic material are not visible in the appearance of an organism, yet they are observable (for example by Western blotting) and are thus part of the phenotype; human blood groups are an example. It may seem that this goes beyond the original intentions of the concept with its focus on the (living) organism in itself. Either way, the term phenotype includes inherent traits or characteristics that are observable or traits that can be made visible by some technical procedure. A notable extension to this idea is the presence of "organic molecules" or metabolites that are generated by organisms from chemical reactions of enzymes.
 The term "phenotype" has sometimes been incorrectly used as a shorthand for the phenotypic difference between a mutant and its wild type, which (if not significant) leads to the statement that a
"mutation has no phenotype".
Another extension adds behavior to the phenotype, since behaviors are observable characteristics. Behavioral phenotypes include cognitive, personality, and behavioral patterns. Some behavioral phenotypes may characterize psychiatric disorders or syndromes.
The term "phenotype" has sometimes been incorrectly used as a shorthand for the phenotypic difference between a mutant and its wild type, which (if not significant) leads to the statement that a
"mutation has no phenotype".
Another extension adds behavior to the phenotype, since behaviors are observable characteristics. Behavioral phenotypes include cognitive, personality, and behavioral patterns. Some behavioral phenotypes may characterize psychiatric disorders or syndromes.


Phenotypic variation
Phenotypic variation (due to underlying heritable genetic variation) is a fundamental prerequisite forevolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. It is the living organism as a whole that contributes (or not) to the next generation, so natural selection affects the genetic structure of a population indirectly via the contribution of phenotypes. Without phenotypic variation, there would be no evolution by natural selection.
The interaction between genotype and phenotype has often been conceptualized by the following relationship:
:genotype (G) + environment (E) → phenotype (P)
A more nuanced version of the relationship is:
:genotype (G) + environment (E) + genotype & environment interactions (GE) → phenotype (P)
Genotypes often have much flexibility in the modification and expression of phenotypes; in many organisms these phenotypes are very different under varying environmental conditions (see ecophenotypic variation). The plant '' Hieracium umbellatum'' is found growing in two different habitats in Sweden. One habitat is rocky, sea-side cliffs, where the plants are bushy with broad leaves and expanded inflorescences; the other is among sand dunes
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...
where the plants grow prostrate with narrow leaves and compact inflorescences. These habitats alternate along the coast of Sweden and the habitat that the seeds of ''Hieracium umbellatum'' land in, determine the phenotype that grows.
An example of random variation in ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many s ...
'' flies is the number of ommatidia, which may vary (randomly) between left and right eyes in a single individual as much as they do between different genotypes overall, or between clones raised in different environments.
The concept of phenotype can be extended to variations below the level of the gene that affect an organism's fitness. For example, silent mutations that do not change the corresponding amino acid sequence of a gene may change the frequency of guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
-cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleobases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached ...
base pairs ( GC content). These base pairs have a higher thermal stability (''melting point'') than adenine- thymine, a property that might convey, among organisms living in high-temperature environments, a selective advantage on variants enriched in GC content.
The extended phenotype
Richard Dawkins described a phenotype that included all effects that a gene has on its surroundings, including other organisms, as an extended phenotype, arguing that "An animal's behavior tends to maximize the survival of the genes 'for' that behavior, whether or not those genes happen to be in the body of the particular animal performing it." For instance, an organism such as a beaver modifies its environment by building a beaver dam; this can be considered an expression of itsgene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s, just as its incisor teeth are—which it uses to modify its environment. Similarly, when a bird feeds a brood parasite such as a cuckoo, it is unwittingly extending its phenotype; and when genes in an orchid affect orchid bee behavior to increase pollination, or when genes in a peacock affect the copulatory decisions of peahens, again, the phenotype is being extended. Genes are, in Dawkins's view, selected by their phenotypic effects.
Other biologists broadly agree that the extended phenotype concept is relevant, but consider that its role is largely explanatory, rather than assisting in the design of experimental tests.
Genes and phenotypes
Phenotypes are determined by and interaction of genes and the environment, but the mechanism for each gene and phenotype is different. For instance, analbino
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the term ...
phenotype may be caused by a mutation in the gene encoding tyrosinase which is a key enzyme in melanin formation. However, exposure to UV radiation can increase melanin production, hence the environment plays a role in this phenotype as well. For most complex phenotypes the precise genetic mechanism remains unknown. For instance, it is largely unclear how genes determine the shape of bones or the human ear.
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. ...
plays a crucial role in determining the phenotypes of organisms. The level of gene expression can affect the phenotype of an organism. For example, if a gene that codes for a particular enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
is expressed at high levels, the organism may produce more of that enzyme and exhibit a particular trait as a result. On the other hand, if the gene is expressed at low levels, the organism may produce less of the enzyme and exhibit a different trait.
 Gene expression is regulated at various levels and thus each level can affect certain phenotypes, including transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.
Gene expression is regulated at various levels and thus each level can affect certain phenotypes, including transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation.
 Changes in the levels of gene expression can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as environmental conditions,
Changes in the levels of gene expression can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as environmental conditions, genetic variations
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, b ...
, and epigenetic modifications. These modifications can be influenced by environmental factors such as diet, stress, and exposure to toxins, and can have a significant impact on an individual's phenotype. Some phenotypes may be the result of changes in gene expression due to these factors, rather than changes in genotype. An experiment involving Machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
methods utilizing gene expression measured from RNA sequencing can contain enough signal to separate individuals in the context of phenotype prediction.
Phenome and phenomics
Although a phenotype is the ensemble of observable characteristics displayed by an organism, the word '' phenome'' is sometimes used to refer to a collection of traits, while the simultaneous study of such a collection is referred to as '' phenomics''. Phenomics is an important field of study because it can be used to figure out which genomic variants affect phenotypes which then can be used to explain things like health, disease, and evolutionary fitness. Phenomics forms a large part of the Human Genome Project Phenomics has applications in agriculture. For instance, genomic variations such as drought and heat resistance can be identified through phenomics to create more durable GMOs. Phenomics may be a stepping stone towards personalized medicine, particularly drug therapy. Once the phenomic database has acquired more data, a person's phenomic information can be used to select specific drugs tailored to an individual.Large-scale phenotyping and genetic screens
Large-scale genetic screens can identify the genes ormutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
s that affect the phenotype of an organism. Analyzing the phenotypes of mutant genes can also aid in determining gene function. Most genetic screens have used microorganisms, in which genes can be easily deleted. For instance, nearly all genes have been deleted in '' E. coli'' and many other bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, but also in several eukaryotic model organisms such as baker's yeast and fission yeast. Among other discoveries, such studies have revealed lists of essential genes (a list gene deletion screens can be found on the essential gene page).
More recently, large-scale phenotypic screens have also been used in animals, e.g. to study lesser understood phenotypes such as behavior. In one screen, the role of mutations in mice were studied in areas such as learning and memory, circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
icity, vision, responses to stress and response to psychostimulants (see table for details).
This experiment involved the progeny of mice treated with ENU
ENU, also known as ''N''-ethyl-''N''-nitrosourea (chemical formula C3H7N3O2), is a highly potent mutagen. For a given gene in mice, ENU can induce 1 new mutation in every 700 loci. It is also toxic at high doses.
The chemical is an alkylating a ...
, or N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea, which is a potent mutagen that causes point mutations. The mice were phenotypically screened for alterations in the different behavioral domains in order to find the number of putative mutants (see table for details). Putative mutants are then tested for heritability in order to help determine the inheritance pattern as well as map out the mutations. Once they have been mapped out, cloned, and identified, it can be determined whether a mutation represents a new gene or not.
These experiments showed that mutations in the rhodopsin gene affected vision and can even cause retinal degeneration in mice. The same amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
change causes human familial blindness, showing how phenotyping in animals can inform medical diagnostics and possibly therapy.
Evolutionary origin of phenotype
The RNA world is the hypothesized pre-cellular stage in the evolutionary history of life on earth, in which self-replicatingRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
molecules proliferated prior to the evolution of DNA and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s. The folded three-dimensional physical structure of the first RNA molecule that possessed ribozyme activity promoting replication while avoiding destruction would have been the first phenotype, and the nucleotide sequence of the first self-replicating RNA molecule would have been the original genotype.
See also
* Ecotype * Endophenotype *Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
* Genotype-phenotype distinction
* Molecular phenotyping
* Race and genetics
References
External links
Mouse Phenome Database
Human Phenotype Ontology
Europhenome: Access to raw and annotated mouse phenotype data
"Wilhelm Johannsen's Genotype-Phenotype Distinction" by E. Peirson at the Embryo Project Encyclopedia
{{Authority control Classical genetics Polymorphism (biology)