|
Laguna Socompa
Laguna Socompa is a small lake in the Salta Province of Argentina, at the foot of Socompa volcano. It covers an area of about and has an average depth of about . The lake is fed by arroyos and springs, some of which are hot springs. Its waters are very rich in arsenic and otherwise salty and slightly alkaline; these properties and the regionally high UV radiation give Laguna Socompa extreme environmental conditions. The lake features the world's highest known stromatoliths, mineralized structures formed by microorganisms. Stromatolith-forming microbes were the dominant lifeforms on Earth fossilized between 3.5 and 1.5 billion years ago and may give insight on early life on Earth. These stromatoliths are found on the southern shore of the lake and led to Laguna Socompa being declared a protected area. Geography and geomorphology Laguna Socompa is located at an elevation of in the Los Andes Department of the Salta Province in Argentina, close to the border with Chile. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salta Province
Salta () is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the east clockwise Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán and Catamarca. It also surrounds Jujuy. To the north it borders Bolivia and Paraguay and to the west lies Chile. History Before the Spanish conquest, numerous native peoples (now called Diaguitas and Calchaquíes) lived in the valleys of what is now Salta Province; they formed many different tribes, the Quilmes and Humahuacas among them, which all shared the Cacán language. The Atacamas lived in the Puna, and the Wichís (Matacos), in the Chaco region. The first conquistador to venture into the area was Diego de Almagro in 1535; he was followed by Diego de Rojas. Hernando de Lerma founded San Felipe de Lerma in 1582, following orders of the viceroy Francisco de Toledo, Count of Oropesa; the name of the city was soon changed to "San Felipe de Salta". By 1650, the city had around five hundred inhabitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 26 countries,Geothermal Energy AssociationGeothermal Energy: International Market Update May 2010, p. 4-6. while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries. As of 2019, worldwide geothermal power capacity amounts to 15.4 gigawatts (GW), of which 23.9 percent or 3.68 GW are installed in the United States. International markets grew at an average annual rate of 5 percent over the three years to 2015, and global geothermal power capacity is expected to reach 14.5–17.6 GW by 2020. Based on current geologic knowledge and technology the Geothermal Energy Association (GEA) publicly discloses, the GEA estimates that only 6.9 percent of total global potential has been tapped so far, while the IPCC reported geothermal power potential to be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brine
Brine is a high-concentration solution of salt (NaCl) in water (H2O). In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawater, on the lower end of that of solutions used for brining foods) up to about 26% (a typical saturated solution, depending on temperature). Brine forms naturally due to evaporation of ground saline water but it is also generated in the mining of sodium chloride. Brine is used for food processing and cooking (pickling and brining), for de-icing of roads and other structures, and in a number of technological processes. It is also a by-product of many industrial processes, such as desalination, so it requires wastewater treatment for proper disposal or further utilization (fresh water recovery). In nature Brines are produced in multiple ways in nature. Modification of seawater via evaporation results in the concentration of salts in the residual fluid, a characteristic geologic deposit call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersaline
A hypersaline lake is a landlocked body of water that contains significant concentrations of sodium chloride, brines, and other salts, with saline levels surpassing that of ocean water (3.5%, i.e. ). Specific microbial species can thrive in high-salinity environments that are inhospitable to most lifeforms, including some that are thought to contribute to the colour of pink lakes. Some of these species enter a dormant state when desiccated, and some species are thought to survive for over 250 million years. The water of hypersaline lakes has great buoyancy due to its high salt content. Hypersaline lakes are found on every continent, especially in arid or semi-arid regions. In the Arctic, the Canadian Devon Ice Cap contains two subglacial lakes that are hypersaline. In Antarctica, there are larger hypersaline water bodies, lakes in the McMurdo Dry Valleys such as Lake Vanda with salinity of over 35% (i.e. 10 times as salty as ocean water). The most saline water body in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a specific grav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a base (chemistry), basic, ionic compound, ionic salt (chemistry), salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English language, English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the acid-base reaction theories#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word "alkali" is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning ''the calcined ashes'' (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatomite
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 μm to less than 1 mm, but typically 10 to 200 μm. Depending on the granularity, this powder can have an abrasive feel, similar to pumice powder, and has a low density as a result of its high porosity. The typical chemical composition of oven-dried diatomaceous earth is 80–90% silica, with 2–4% alumina (attributed mostly to clay minerals), and 0.5–2% iron oxide. Diatomaceous earth consists of the fossilized remains of diatoms, a type of hard-shelled microalgae. It is used as a filtration aid, mild abrasive in products including metal polishes and toothpaste, mechanical insecticide, absorbent for liquids, matting agent for coatings, reinforcing filler in plastics and rubber, anti-block in plastic films, porous support for chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
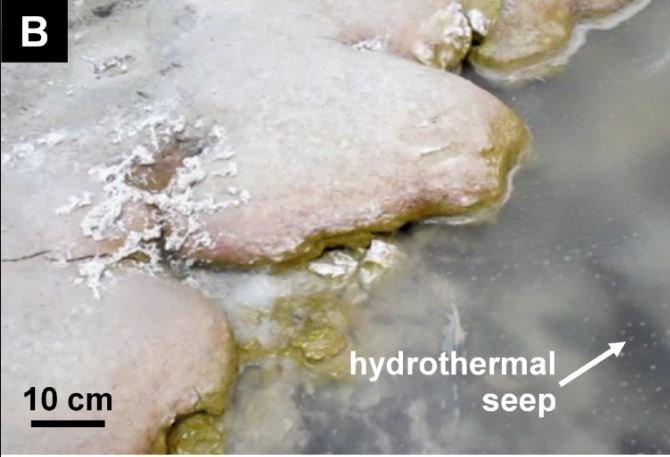
Hot Spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circulation through faults to hot rock deep in the Earth's crust. In either case, the ultimate source of the heat is radioactive decay of naturally occurring radioactive elements in the Earth's mantle, the layer beneath the crust. Hot spring water often contains large amounts of dissolved minerals. The chemistry of hot springs ranges from acid sulfate springs with a pH as low as 0.8, to alkaline chloride springs saturated with silica, to bicarbonate springs saturated with carbon dioxide and carbonate minerals. Some springs also contain abundant dissolved iron. The minerals brought to the surface in hot springs often feed communities of extremophiles, microorganisms adapted to extreme conditions, and it is possible that life on Earth had its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring (hydrology)
A spring is a point of exit at which groundwater from an aquifer flows out on top of Earth's crust (pedosphere) and becomes surface water. It is a component of the hydrosphere. Springs have long been important for humans as a source of fresh water, especially in arid regions which have relatively little annual rainfall. Springs are driven out onto the surface by various natural forces, such as gravity and hydrostatic pressure. Their yield varies widely from a volumetric flow rate of nearly zero to more than for the biggest springs. Formation Springs are formed when groundwater flows onto the surface. This typically happens when the groundwater table reaches above the surface level. Springs may also be formed as a result of karst topography, aquifers, or volcanic activity. Springs also have been observed on the ocean floor, spewing hot water directly into the ocean. Springs formed as a result of karst topography create karst springs, in which ground water travels through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill (grinding)
A mill is a device, often a structure, machine or kitchen appliance, that breaks solid materials into smaller pieces by grinding, crushing, or cutting. Such comminution is an important unit operation in many processes. There are many different types of mills and many types of materials processed in them. Historically mills were powered by hand or by animals (e.g., via a hand crank), working animal (e.g., horse mill), wind (windmill) or water (watermill). In modern era, they are usually powered by electricity. The grinding of solid materials occurs through mechanical forces that break up the structure by overcoming the interior bonding forces. After the grinding the state of the solid is changed: the grain size, the grain size disposition and the grain shape. Milling also refers to the process of breaking down, separating, sizing, or classifying aggregate material (e.g. mining ore). For instance rock crushing or grinding to produce uniform aggregate size for construction purp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bush (plant)
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about five y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


