|
Lady Franklin Bay
Lady Franklin Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. The bay is located in Nares Strait northwest of Judge Daly Promontory and is an inlet into the northeastern shore of Ellesmere Island. Fort Conger—formerly an Arctic exploration camp—is located on its northern shore. Geography Lady Franklin Bay divides Grant Land to the north from Grinnell Land to the south. Lady Franklin Bay is in a generally northeast to southwest direction, and as such it spreads inland about from Hall Basin. The main bay contains one noted branch to the northwest known as Discovery Bay, and the interior lengths of Lady Franklin Bay extending southwest are sometimes shown on maps as Archer Fjord. The landscape surrounding Lady Franklin Bay is generally barren rocks, with some very shallow glacial till held in place with frost and permafrost. At this location, about above the Arctic Circle, sunlight is limited to perhaps three months of a year, snowfall is light, and wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin Bay
Franklin Bay () is a large inlet in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is a southern arm of the Amundsen Gulf, southeastern Beaufort Sea. The bay measures long, and wide at its mouth. The Parry Peninsula is to the east, and its southern area is called Langton Bay. Franklin Bay receives the Horton River. There are gales in the early winter months.Stefansson (1913), p. 233 Franklin Bay was named in honor of Arctic explorer Sir John Franklin by John Richardson in 1826. History Based on hearsay rather than exploration, Émile Petitot, a French Missionary Oblate and a notable Canadian northwest cartographer, ethnologist, and geographer charted the Hornaday River's mouth at Franklin Bay, instead of Darnley Bay in his flawed 1875 maps and account. Langton Bay was the base of operations for the three-year expedition, 1909 to 1912, of Arctic explorers Vilhjalmur Stefansson Vilhjalmur Stefansson (November 3, 1879 – August 26, 1962) was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith Sound
Smith Sound ( da, Smith Sund; french: Détroit de Smith) is an uninhabited Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It links Baffin Bay with Kane Basin and forms part of the Nares Strait. On the Greenland side of the sound were the now abandoned settlements of Etah and Annoatok. History The first known visit to the area by Europeans was in 1616 when the ''Discovery'', captained by Robert Bylot and piloted by William Baffin, sailed into this region. The sound was originally named ''Sir Thomas Smith's Bay'' after the English diplomat Sir Thomas Smythe. By the 1750s it regularly appeared on maps as ''Sir Thomas Smith's Sound'', though no further exploration of the area would be recorded until John Ross' 1818 expedition. By this time it had begun to be known simply as ''Smith Sound''. In 1852 Edward Augustus Inglefield penetrated a little further than Baffin, establishing a new furthest north in North America. References Further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Franklin Bay Expedition
* The Lady Franklin Bay Expedition of 1881–1884 to Lady Franklin Bay on Ellesmere Island in the Canadian Arctic was led by Lieutenant Adolphus Greely, and was promoted by the United States Army Signal Corps. Its purpose was to establish a meteorological-observation station as part of the First International Polar Year, and to collect astronomical and magnetic data. During the expedition, two members of the crew reached a new Farthest North record, but of the original twenty-five men, only seven survived to return. The expedition was under the auspices of the Signal Corps at a time when the Corps' Chief Disbursements officer, Henry W. Howgate, was arrested for embezzlement. However, that did not deter the planning and execution of the voyage. Expedition First year, 1881 The Lady Franklin Bay Expedition was led by Lieutenant Adolphus W. Greely of the Fifth United States Cavalry, with astronomer Edward Israel and photographer George W. Rice among the crew of twenty-one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Army Signal Corps
) , colors = Orange and white , colors_label = Corps colors , march = , mascot = , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = , anniversaries = 21 June 1860 , decorations = , battle_honours = , notable_commanders = BG Albert J. Myer BG Adolphus Greely , identification_symbol = , identification_symbol_label = Branch insignia , identification_symbol_2 = , identification_symbol_2_label = Regimental insignia , current_commander = , current_commander_label = , ceremonial_chief = Colonel Paul D. Howard , ceremonial_chief_label = Chief of Signal , command_sergeant_major = CSM Darien D. Lawshea , command_sergeant_major_label = Sergeant Major of the Regiment The United States Army Signal Corps (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Elizabeth Islands
The Queen Elizabeth Islands (french: Îles de la Reine-Élisabeth; formerly Parry Islands or Parry Archipelago) are the northernmost cluster of islands in Canada's Arctic Archipelago, split between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories in Northern Canada. The Queen Elizabeth Islands contain approximately 14% of the global glacier and ice cap area (excluding the inland and shelf ice sheets of Greenland and Antarctica). Geography The islands, together in area, were renamed as a group after Elizabeth II on her coronation as Queen of Canada in 1953. The islands cover an area approximately the shape of a right triangle, bounded by the Nares Strait on the east, Parry Channel on the south and the Arctic Ocean to the north and west. Most are uninhabited although the Natural Resources Canada's Climate Change Geoscience Program Earth Sciences Sector (ESS), has monitors on the islands. In 1969 Panarctic Oils, now part of Suncor Energy, began operating exploration oil wells in the Franklini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin's Lost Expedition
Franklin's lost expedition was a failed British voyage of Arctic exploration led by Captain Sir John Franklin that departed England in 1845 aboard two ships, and , and was assigned to traverse the last unnavigated sections of the Northwest Passage in the Canadian Arctic and to record magnetic data to help determine whether a better understanding could aid navigation. The expedition met with disaster after both ships and their crews, a total of 129 officers and men, became icebound in Victoria Strait near King William Island in what is today the Canadian territory of Nunavut. After being icebound for more than a year ''Erebus'' and ''Terror'' were abandoned in April 1848, by which point Franklin and nearly two dozen others had died. The survivors, now led by Franklin's second-in-command, Francis Crozier, and ''Erebus''s captain, James Fitzjames, set out for the Canadian mainland and disappeared, presumably having perished. Pressed by Franklin's wife, Jane, and others, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Franklin
Sir John Franklin (16 April 1786 – 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. After serving in wars against Napoleonic France and the United States, he led two expeditions into the Canadian Arctic and through the islands of the Arctic Archipelago, in 1819 and 1825, and served as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen's Land from 1839 to 1843. During his third and final expedition, an attempt to traverse the Northwest Passage in 1845, Franklin's ships became icebound off King William Island in what is now Nunavut, where he died in June 1847. The icebound ships were abandoned ten months later and the entire crew died, from causes such as starvation, hypothermia, and scurvy. Biography Early life Franklin was born in Spilsby, Lincolnshire, on , the ninth of twelve children born to Hannah Weekes and Willingham Franklin. His father was a merchant descended from a line of country gentlemen while his mother was the daughter of a farmer. One of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane Franklin
Jane, Lady Franklin (née Griffin; 4 December 1791 – 18 July 1875) was the second wife of the English explorer Sir John Franklin. During her husband's period as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen's Land, she became known for her philanthropic work and her travels throughout south-eastern Australia. After John Franklin's disappearance in search of the Northwest Passage, she sponsored or otherwise supported several expeditions to determine his fate. Early life Jane was the second daughter of John Griffin, a liveryman and later governor of the Goldsmith's Company, and his wife Jane Guillemard. There was Huguenot ancestry on both sides of her family. She was born in London, where she was raised with her sisters Frances and Mary at the family house, 21 Bedford Place, just off Russell Square. She was well educated, and her father being well-to-do had her education completed by much travel on the continent. Her portrait was chalked when she was 24 by Amélie Munier-Romilly in Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Basin
Hall Basin is an Arctic waterway between Hall Land in Greenland to the east and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island, to the west. Hall Basin is named after American polar explorer Charles Francis Hall. Geography Hall Basin is located in Nares Strait with its entrance between Cape Baird on the eastern coast of Ellesmere Island and Cape Morton on the northwestern coast of Greenland. Robeson Channel is to the north of the basin, and Kennedy Channel to the south. The basin is irregularly shaped, the entrance to Lady Franklin Bay lies on its western shores, being deeply indented by an extensive fjord system. Although the eastern shore is more regular, it includes the Petermann Fjord of the Petermann Glacier Petermann Glacier ( da, Petermann Gletsjer) is a large glacier located in North-West Greenland to the east of Nares Strait. It connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean at 81°10' north latitude, near Hans Island. The glacier and its f ... at its southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennedy Channel
Kennedy Channel ( da, Kennedykanalen; french: Passage Kennedy; ) is an Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Canada's most northerly island, Ellesmere Island. It was named by Elisha Kane around 1854 during his second Arctic voyage in search of the lost Franklin expedition. It is not entirely clear, however, for which Kennedy he named the channel. Kane may have had his fellow explorer William Kennedy in mind, whom he had met a few years previously while both were involved in earlier searches for Franklin's expedition. However, most historians believe it was named for John Pendleton Kennedy, the United States Secretary of the Navy during 1852 to 1853, under whose direction Kane's second Arctic voyage took place. Geography It forms part of Nares Strait, linking Kane Basin with Hall Basin. From the south, its beginning is marked by Capes Lawrence and Jackson; its junction with Hall Basin is marked by Capes Baird and Morton.''Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Iceland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
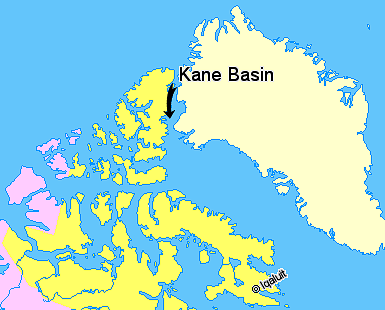
Kane Basin
Kane Basin ( da, Kane Bassin; french: Bassin (de) Kane) is an Arctic waterway lying between Greenland and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It links Smith Sound to Kennedy Channel and forms part of Nares Strait. It is approximately 180 kilometres in length and 130 km at its widest. It is named after the American explorer Elisha Kane, whose expedition in search of Franklin's lost expedition crossed it in 1854. Kane himself had named it "Peabody Bay," in honor of philanthropist George Peabody, the major funder of Kane's expedition. Currently Peabody Bay is a bay at the eastern side of the basin, off the southwestern end of the Humboldt Glacier Humboldt Glacier ( da, Humboldt Gletscher) is one of the major glaciers in northern Greenland. The glacier is named after German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt and is the widest tidewater glacier in the Northern Hemisphere. Geography The Humb ... in northern Greenland. Further reading * Cold Regions Research and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay ( Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about , known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of Baffin Bay as follows: History The area of the bay has been inhabited since BC. Around AD 1200, the initial Dorset settlers were replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Islands%2C_northern_Canada.png)