|
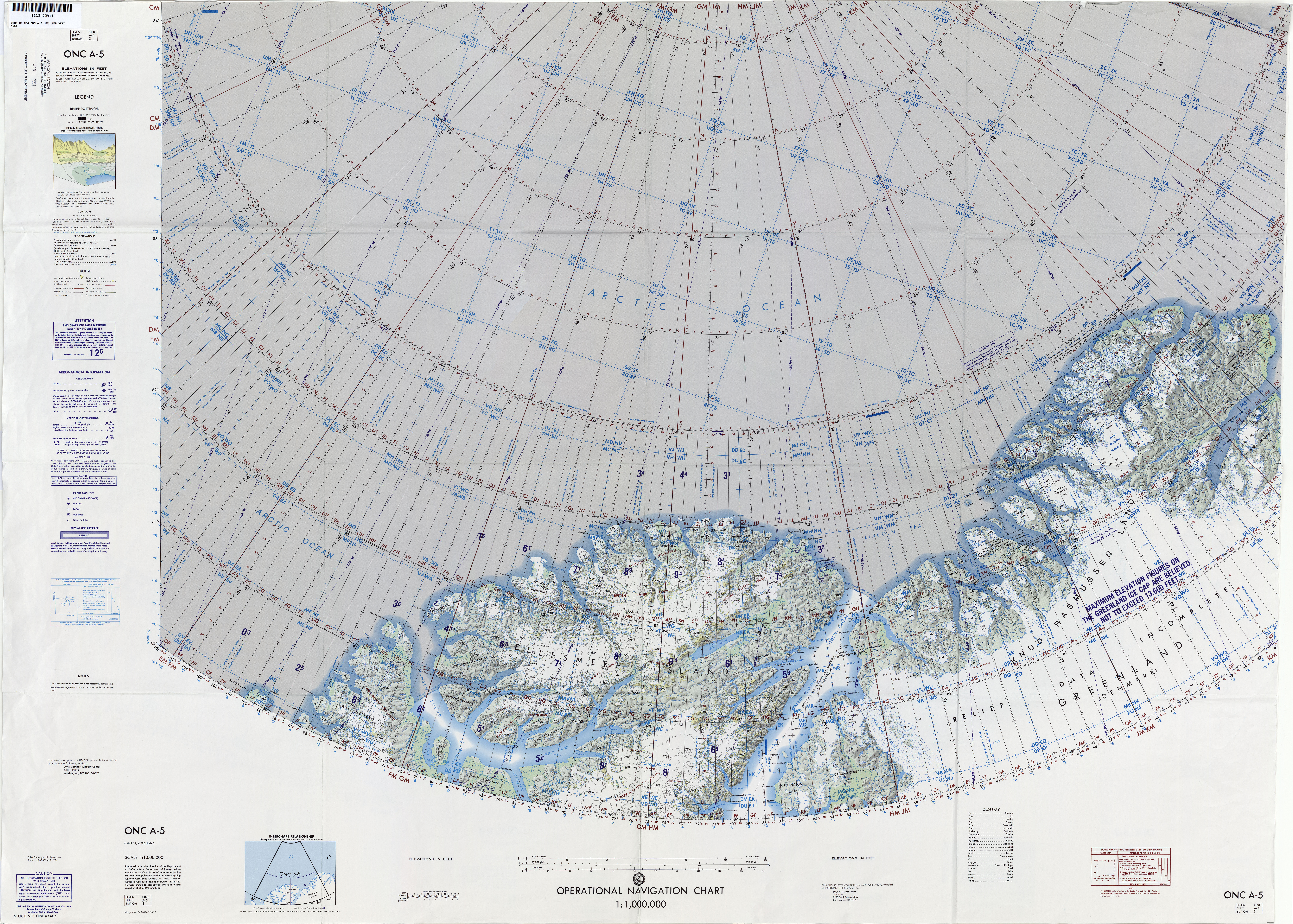
Hall Basin
Hall Basin is an Arctic waterway between Hall Land in Greenland to the east and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island, to the west. Hall Basin is named after American polar explorer Charles Francis Hall. Geography Hall Basin is located in Nares Strait with its entrance between Cape Baird on the eastern coast of Ellesmere Island and Cape Morton on the northwestern coast of Greenland. Robeson Channel is to the north of the basin, and Kennedy Channel to the south. The basin is irregularly shaped, the entrance to Lady Franklin Bay lies on its western shores, being deeply indented by an extensive fjord system. Although the eastern shore is more regular, it includes the Petermann Fjord of the Petermann Glacier Petermann Glacier ( da, Petermann Gletsjer) is a large glacier located in North-West Greenland to the east of Nares Strait. It connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean at 81°10' north latitude, near Hans Island. The glacier and its ... at its sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Indicating Hall Basin, Nunavut, Canada
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennedy Channel
Kennedy Channel ( da, Kennedykanalen; french: Passage Kennedy; ) is an Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Canada's most northerly island, Ellesmere Island. It was named by Elisha Kane around 1854 during his second Arctic voyage in search of the lost Franklin expedition. It is not entirely clear, however, for which Kennedy he named the channel. Kane may have had his fellow explorer William Kennedy in mind, whom he had met a few years previously while both were involved in earlier searches for Franklin's expedition. However, most historians believe it was named for John Pendleton Kennedy, the United States Secretary of the Navy during 1852 to 1853, under whose direction Kane's second Arctic voyage took place. Geography It forms part of Nares Strait, linking Kane Basin with Hall Basin. From the south, its beginning is marked by Capes Lawrence and Jackson; its junction with Hall Basin is marked by Capes Baird and Morton.''Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straits Of Qikiqtaaluk Region
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channel that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are either too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas. Terminology The terms '' channel'', ''pass'', or ''passage'' can be synonymous and used interchangeably with ''strait'', although each is sometimes differentiated with varying senses. In Scotland, ''firth'' or ''Kyle'' are also sometimes used as synonyms for strait. Many straits are economically important. Straits can be important shipping routes and wars have been fought for control of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straits Of Greenland
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channel that lies between two land masses. Some straits are not navigable, for example because they are either too narrow or too shallow, or because of an unnavigable reef or archipelago. Straits are also known to be loci for sediment accumulation. Usually, sand-size deposits occur on both the two opposite strait exits, forming subaqueous fans or deltas. Terminology The terms '' channel'', ''pass'', or ''passage'' can be synonymous and used interchangeably with ''strait'', although each is sometimes differentiated with varying senses. In Scotland, ''firth'' or ''Kyle'' are also sometimes used as synonyms for strait. Many straits are economically important. Straits can be important shipping routes and wars have been fought for control of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bays Of Qikiqtaaluk Region
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narrow entrance. A fjord is an elongated bay formed by glacial action. A bay can be the estuary of a river, such as the Chesapeake Bay, an estuary of the Susquehanna River. Bays may also be nested within each other; for example, James Bay is an arm of Hudson Bay in northeastern Canada. Some large bays, such as the Bay of Bengal and Hudson Bay, have varied marine geology. The land surrounding a bay often reduces the strength of winds and blocks waves. Bays may have as wide a variety of shoreline characteristics as other shorelines. In some cases, bays have beaches, which "are usually characterized by a steep upper foreshore with a broad, flat fronting terrace".Maurice Schwartz, ''Encyclopedia of Coastal Science'' (2006), p. 129. Bays were si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petermann Glacier
Petermann Glacier ( da, Petermann Gletsjer) is a large glacier located in North-West Greenland to the east of Nares Strait. It connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean at 81°10' north latitude, near Hans Island. The glacier and its fjord are named after German cartographer August Heinrich Petermann. Geography The tidewater glacier consists of a long and wide floating ice tongue whose thickness changes from about at its grounding line to about at its front. Rough mass balance estimates using these scales suggest that about 80% of its mass is lost as basal meltwater, yet little oceanographic data are available to connect Petermann Glacier to its fjord and adjacent Nares Strait. Even the sill depth and location is largely unknown as modern soundings of the fjord, with its mouth located between Cape Morton and Cape Tyson, are still lacking. Petermann Glacier marks the western limit of Hall Land and the eastern of Daugaard-Jensen Land. The Petermann Peninsula flan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petermann Fjord
Petermann Fjord is a fjord in northwestern Greenland. Administratively it marks the boundary between the Avannaata municipality and the Northeast Greenland National Park. The fjord and its glacier are named after German cartographer August Heinrich Petermann. Knud Rasmussen described the fjord entrance in the following terms: Geography Petermann Fjord stretches roughly from southeast to northwest for about 110 km. Its mouth opens in the Kennedy Channel and Hall Basin area, between Cape Lucie Marie, located east of Cape Morton, and Cape Tyson in the north, near Offley Island. It is a long and broad fjord lined with precipitous cliffs topped by glaciated plateaux. The Petermann Glacier, the longest glacier in Greenland, discharges into the fjord from the Greenland Ice Sheet, located further 80 km inland.''Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Iceland Enroute,'' p. 93 This fjord is located northeast of Daugaard-Jensen Land, between the Petermann Peninsula and Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lady Franklin Bay
Lady Franklin Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. The bay is located in Nares Strait northwest of Judge Daly Promontory and is an inlet into the northeastern shore of Ellesmere Island. Fort Conger—formerly an Arctic exploration camp—is located on its northern shore. Geography Lady Franklin Bay divides Grant Land to the north from Grinnell Land to the south. Lady Franklin Bay is in a generally northeast to southwest direction, and as such it spreads inland about from Hall Basin. The main bay contains one noted branch to the northwest known as Discovery Bay, and the interior lengths of Lady Franklin Bay extending southwest are sometimes shown on maps as Archer Fjord. The landscape surrounding Lady Franklin Bay is generally barren rocks, with some very shallow glacial till held in place with frost and permafrost. At this location, about above the Arctic Circle, sunlight is limited to perhaps three months of a year, snowfall is light, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robeson Channel
Robeson Channel () is a body of water lying between Greenland and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It is the most northerly part of Nares Strait, linking Hall Basin to the south with the Arctic Ocean to the north. The Newman Fjord in Greenland has its mouth in the Robeson Channel. It is about in length and between wide. Alert, the world's most northerly permanently inhabited settlement, lies nearby. It was named during the 1871 Polaris Expedition, for American George Robeson, Secretary of the Navy in the Ulysses S. Grant Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ... administration. Further reading * Chow, R. K. ''Near-Surface Current in Robeson Channel''. Defence Research Establishment Ottawa, 1975. * Dunbar, Moira, and John E. Keys. ''Robeson Channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia ( Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic. Definition and etymology The word Arctic comes from the Greek word ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Morton
Cape Morton ( da, Kap Morton) is a headland in North Greenland in Avannaata municipality. The cape is named after Arctic explorer William Morton, who surveyed the Nares Strait area together with Hans Hendrik in June 1854 during the Second Grinnell Expedition. Fossils dating back to the Homerian have been found in the area of the cape. They belong to the Kap Morton Formation of the Peary Land Group. Geography Cape Morton is located west of Cape Lucie Marie, off the mouth of the Petermann Fjord opposite Cape Tyson at the northern end of the Petermann Peninsula. Mushroom-shaped Joe Island lies 3.2 km from the shore west-north-west of the cape. Together with Cape Baird on the eastern coast of Ellesmere Island this cape marks the northern limit of the Kennedy Channel and the entrance of the Hall Basin, both part of the Nares Strait.''Prostar Sailing Directions 2005 Greenland and Iceland Enroute'', p. 93 See also *List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Greenland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Baird
A cape is a clothing accessory or a sleeveless outer garment which drapes the wearer's back, arms, and chest, and connects at the neck. History Capes were common in medieval Europe, especially when combined with a hood in the chaperon. They have had periodic returns to fashion - for example, in nineteenth-century Europe. Roman Catholic clergy wear a type of cape known as a ferraiolo, which is worn for formal events outside a ritualistic context. The cope is a liturgical vestment in the form of a cape. Capes are often highly decorated with elaborate embroidery. Capes remain in regular use as rainwear in various military units and police forces, in France for example. A gas cape was a voluminous military garment designed to give rain protection to someone wearing the bulky gas masks used in twentieth-century wars. Rich noblemen and elite warriors of the Aztec Empire would wear a tilmàtli; a Mesoamerican cloak/cape used as a symbol of their upper status. Cloth and clothing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |