|
Lactobacillus Vaginalis
''Limosilactobacillus vaginalis'' is a lactic acid bacterium that is a normal, but infrequent part of the vaginal microbiome. Discovery and taxonomy The species was identified by Embley and his coworkers in the course of a vaccine development against trichomoniasis. The vaginal secretions of women suffering from trichomoniasis were examined for the presence of certain proposed ''Lactobacillus'' strains exhibiting mutualistic behavior with ''Trichomonas vaginalis'', facilitating sustainment of infection. The isolates initially designated '' Limosilactobacillus fermentum'' were compared to the reference strains of a number of heterofermentative species using the DNA–DNA hybridization method, and have shown a maximal DNA homology of 35% with '' Limosilactobacillus reuteri'', far below the standard threshold of 70% recommended for species delineation. The new species ''L. vaginalis'' with type strain NCTC 12197 was proposed, and the description of its carbohydrate fermentation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactic Acid Bacterium
Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped (bacilli) or spherical (cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB). Production of lactic acid has linked LAB with food fermentations, as acidification inhibits the growth of spoilage agents. Proteinaceous bacteriocins are produced by several LAB strains and provide an additional hurdle for spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Furthermore, lactic acid and other metabolic products contribute to the organoleptic and textural profile of a food item. The industrial importance of the LAB is further evidenced by their generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, due to their ubiquitous appearance in food and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
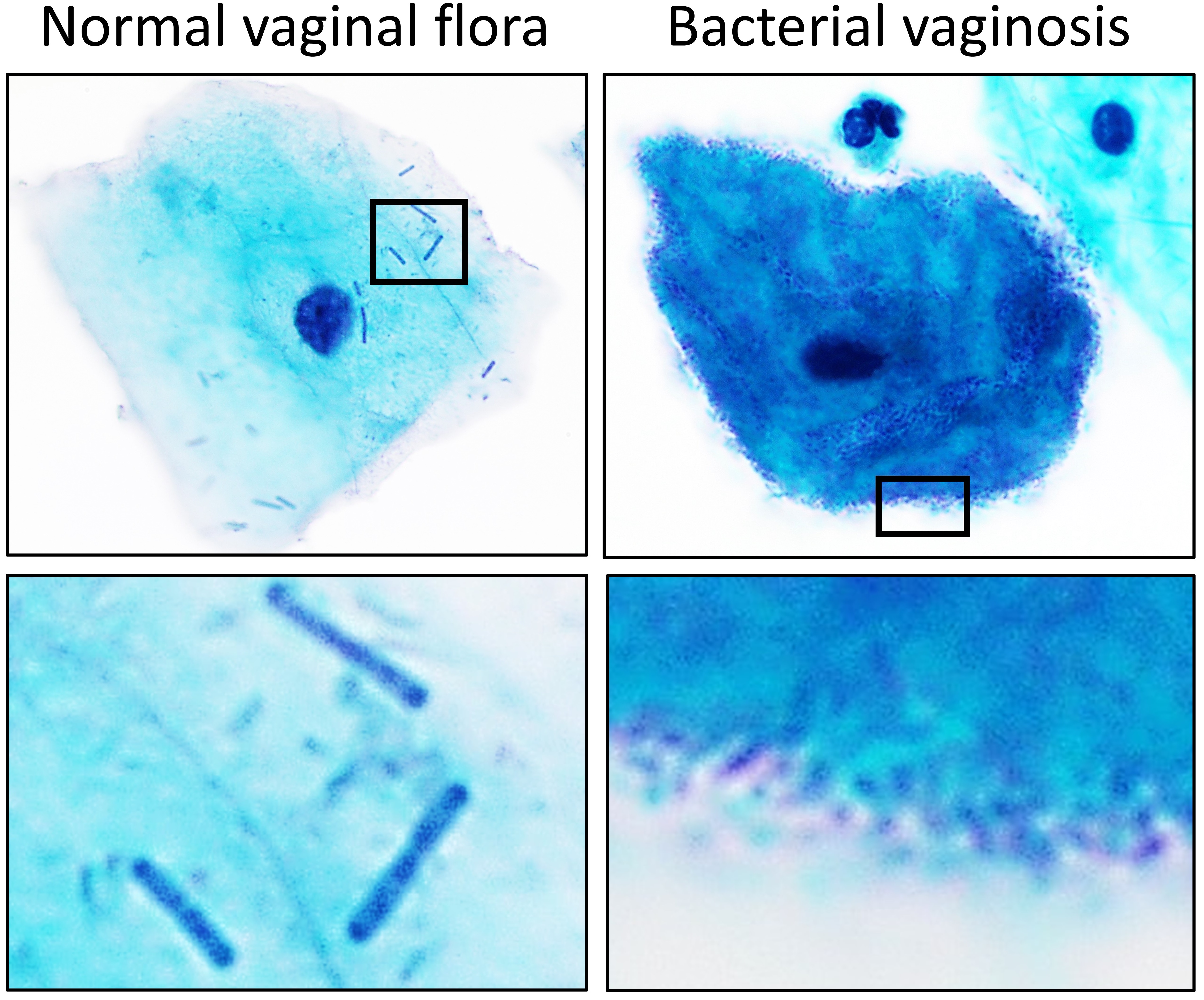
List Of Microbiota Species Of The Lower Reproductive Tract Of Women
This is the list of healthy vaginal microbiota (VMB), which is defined as the group of species and genera that generally are found to have lack of symptoms, absence of various infections, and result in good pregnancy outcomes. VMB is dominated mainly by Lactobacillus species. This is the list of organisms that are found in the lower reproductive tract of sexually mature women who are not immunocompromised. A partial description of pathogens that can be found in the lower and upper reproductive tract of women can be found in the article sexually transmitted disease. The organisms listed below are capable of causing illness if for some reason there is a change in vaginal pH or a change in the ratio of one organism to another. For example, '' Candida'' is a normal inhabitant of a healthy reproductive tract but an overgrowth of this organism can cause candidiasis. Normal microbiota This is the list of the normal flora that are found in the lower reproductive tract of sexually mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. About 70% of affected people do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms occur, they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms can include itching in the genital area, a bad smelling thin vaginal discharge, burning with urination, and pain with sex. Having trichomoniasis increases the risk of getting HIV/AIDS. It may also cause complications during pregnancy. Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) which is most often spread through vaginal, oral, or anal sex. It can also spread through genital touching. People who are infected may spread the disease even when symptoms are not present. Diagnosis is by finding the parasite in the vaginal fluid using a microscope, culturing the vaginal fluid or urine, or testing for the parasite's DNA. If present, other STIs should be tested for. Methods of prevention include not having sex, using condoms, not do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutualism (biology)
Mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction. Prominent examples include most vascular plants engaged in mutualistic interactions with mycorrhizae, flowering plants being pollinated by animals, vascular plants being dispersed by animals, and corals with zooxanthellae, among many others. Mutualism can be contrasted with interspecific competition, in which each species experiences ''reduced'' fitness, and exploitation, or parasitism, in which one species benefits at the expense of the other. The term ''mutualism'' was introduced by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden in his 1876 book ''Animal Parasites and Messmates'' to mean "mutual aid among species". Mutualism is often conflated with two other types of ecological phenomena: cooperation and symbiosis. Cooperation most commonly refers to increases in fitness through within-species (intraspecific) interactions, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomonas Vaginalis
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is an anaerobic, flagellated protozoan parasite and the causative agent of a sexually transmitted disease called trichomoniasis. It is the most common pathogenic protozoan that infects humans in industrialized countries. Infection rates in men and women are similar but women are usually symptomatic, while infections in men are usually asymptomatic. Transmission usually occurs via direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, most often through vaginal intercourse. The WHO has estimated that 160 million cases of infection are acquired annually worldwide. The estimates for North America alone are between 5 and 8 million new infections each year, with an estimated rate of asymptomatic cases as high as 50%. Usually treatment consists of metronidazole and tinidazole. Clinical History Alfred Francois Donné (1801–1878) was the first to describe a procedure to diagnose trichomoniasis through "the microscopic observation of motile protozoa i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limosilactobacillus Fermentum
''Limosilactobacillus fermentum'' is a Gram-positive species in the heterofermentative genus ''Limosilactobacillus.'' It is associated with active dental caries lesions. It is also commonly found in fermenting animal and plant material including sourdough and cocoa fermentation. A few strains are considered probiotic or "friendly" bacteria in animals and at least one strain has been applied to treat urogenital infections in women. Some strains of lactobacilli formerly mistakenly classified as ''L. fermentum'' (such as RC-14) have since been reclassified as ''Limosilactobacillus reuteri''. Commercialized strains of ''L. fermentum'' used as probiotics include PCC, ME-3 and CECT5716 Characteristics ''Limosilactobacillus fermentum'' belongs to the genus ''Limosilactobacillus.'' Species in this genus are heterofermentative and adapted to the intestinal tract of vertebrates but also used for a wide variety of applications including food and feed fermentation. ''L. fermentum'' differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA–DNA Hybridization
In genomics, DNA–DNA hybridization is a molecular biology technique that measures the degree of genetic similarity between pools of DNA sequences. It is usually used to determine the genetic distance between two organisms and has been used extensively in phylogeny and taxonomy. Method The DNA of one organism is labelled, then mixed with the unlabelled DNA to be compared against. The mixture is incubated to allow DNA strands to dissociate and then cooled to form renewed hybrid double-stranded DNA. Hybridized sequences with a high degree of similarity will bind more firmly, and require more energy to separate them: i.e. they separate when heated at a higher temperature than dissimilar sequences, a process known as "DNA melting". To assess the melting profile of the hybridized DNA, the double-stranded DNA is bound to a column and the mixture is heated in small steps. At each step, the column is washed; sequences that melt become single-stranded and wash off the column. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limosilactobacillus Reuteri
''Limosilactobacillus reuteri'' is a lactic acid bacterium found in a variety of natural environments, including the gastrointestinal tract of humans and other animals. It does not appear to be pathogenic and may have health effects. Discovery At the turn of the 20th century, ''L. reuteri'' was recorded in scientific classifications of lactic acid bacteria, though at this time it was mistakenly grouped as a member of ''Lactobacillus fermentum''. In the 1960s, further work by microbiologist Gerhard Reuter, for whom the species eventually was named, reclassified the species as ''L. fermentum'' biotype II. Significant differences were found between biotype II and other biotypes of ''L. fermentum'', to the point that in 1980 it was identified as a distinct species and the formal species identity, ''L. reuteri'', was proposed. In April 2020, ''L. reuteri'' was reassigned to the genus ''Limosilactobacillus''. Prevalence ''Limosilactobacillus reuteri'' is found in a variety of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16S Ribosomal RNA
16 S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome (SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA gene and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977. Multiple sequences of the 16S rRNA gene can exist within a single bacterium. Functions * Like the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, it has a structural role, acting as a scaffold defining the positions of the ribosomal proteins. * The 3-end contains the anti- Shine-Dalgarno sequence, which binds upstream to the AUG start codon on the mRNA. The 3-end of 16S RNA binds to the proteins S1 and S21 which are known to be involved in initiation of protein synthesis * Interacts with 23S, aiding in the binding of the two ribosomal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Analysis
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological databases, and others. Since the development of methods of high-throughput production of gene and protein sequences, the rate of addition of new sequences to the databases increased very rapidly. Such a collection of sequences does not, by itself, increase the scientist's understanding of the biology of organisms. However, comparing these new sequences to those with known functions is a key way of understanding the biology of an organism from which the new sequence comes. Thus, sequence analysis can be used to assign function to genes and proteins by the study of the similarities between the compared sequences. Nowadays, there are many tools and techniques that provide the sequence comparisons (sequence al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

