|
LNWR Waterloo Class
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Waterloo Class was a class of steam locomotives that was also known as the Whitworth Class. History The locomotives were introduced by F. W. Webb in 1889 as replacements for the ''Samson'' class, and 90 examples were built up to 1896. The LNWR reused numbers and names from withdrawn locomotives, with the result that the numbering system was completely haphazard. Withdrawals had started in 1907, following George Whale's succession of Francis Webb in 1903 and the introduction of Whale's stronger Precursor and Experiment tender engines. Thirty locomotives passed to the London, Midland and Scottish Railway at the 1923 grouping. They were given the power classification 1P, and renumbered 5080–5109. In addition, four other members of the class survived in departmental service. The last Waterloo was withdrawn in 1936. None were preserved. Accidents and incidents : *On 22 December 1894, a gust of wind blew a wagon into a rake of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Whitworth
Sir Joseph Whitworth, 1st Baronet (21 December 1803 – 22 January 1887) was an English engineer, entrepreneur, inventor and philanthropist. In 1841, he devised the British Standard Whitworth system, which created an accepted standard for screw threads. Whitworth also created the Whitworth rifle, often called the "sharpshooter" because of its accuracy, which is considered one of the earliest examples of a sniper rifle, used by some Confederate forces during the American Civil war. Whitworth was created a baronet by Queen Victoria in 1869. Upon his death in 1887, Whitworth bequeathed much of his fortune for the people of Manchester, with the Whitworth Art Gallery and Christie Hospital partly funded by Whitworth's money. Whitworth Street and Whitworth Hall in Manchester are named in his honour. Whitworth's company merged with the W.G. Armstrong & Mitchell Company to become Armstrong Whitworth in 1897. Biography Early life Whitworth was born in John Street, Stockport, Cheshire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimera (mythology)
According to Greek mythology, the Chimera, Chimaera, Chimæra, or Khimaira ( ; ) was a monstrous fire-breathing hybrid creature from Lycia, Asia Minor, composed of different animal parts. Typically, it is depicted as a lion with a goat's head protruding from its back and a tail ending with a snake's head. Some representations also include dragon's wings. It was an offspring of Typhon and Echidna and a sibling of monsters like Cerberus and the Lernaean Hydra. The term "chimera" has come to describe any mythical or fictional creature with parts taken from various animals, to describe anything composed of disparate parts or perceived as wildly imaginative, implausible, or dazzling. In other words, a chimera can be any hybrid creature. In figurative use, derived from the mythological meaning, "chimera" refers to an unrealistic, or unrealisable, wild, foolish or vain dream, notion or objective. Family According to Hesiod, the Chimera's mother was a certain ambiguous "she", wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prospero
Prospero ( ) is a fictional character and the protagonist of William Shakespeare's ''The Tempest''. Character Twelve years before the play begins, Prospero is usurped from his position as the rightful Duke of Milan by his brother Antonio, who puts Prospero and his three-year-old daughter Miranda to sea on a "rotten carcass" of a boat to die. Prospero and Miranda survived and found exile on a small island inhabited mostly by spirits. Prospero learned sorcery from books, and uses it to protect Miranda. Before the play begins, Prospero freed the magical spirit Ariel from entrapment within "a cloven pine". Ariel is beholden to Prospero after he is freed from his imprisonment inside the pine tree. Prospero then takes Ariel as a slave. Prospero's sorcery is sufficiently powerful to control Ariel and other spirits, as well as to alter weather and even raise the dead: "Graves at my command have waked their sleepers, oped, and let 'em forth, by my so potent Art." - Act V, scene 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vampire
A vampire is a mythical creature that subsists by feeding on the Vitalism, vital essence (generally in the form of blood) of the living. In European folklore, vampires are undead, undead humanoid creatures that often visited loved ones and caused mischief or deaths in the neighbourhoods which they inhabited while they were alive. They wore shrouds and were often described as bloated and of ruddy or dark countenance, markedly different from today's gaunt, pale vampire which dates from the early 19th century. Vampiric entities have been Vampire folklore by region, recorded in cultures around the world; the term ''vampire'' was popularized in Western Europe after reports of an 18th-century mass hysteria of a pre-existing folk belief in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Eastern Europe that in some cases resulted in corpses being staked and people being accused of vampirism. Local variants in Southeastern Europe were also known by different names, such as ''shtriga'' in Albanian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version of the myth, the centaurs were named after Centaurus (Greek mythology), Centaurus, and, through his brother Lapithes (hero), Lapithes, were kin to the legendary tribe of the Lapiths. Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as being as wild as untamed horses, and were said to have inhabited the region of Magnesia (regional unit), Magnesia and Mount Pelion in Thessaly, the Foloi oak forest in Ancient Elis, Elis, and the Malean peninsula in southern Laconia. Centaurs are subsequently featured in Roman mythology, and were familiar figures in the medieval bestiary. They remain a staple of modern fantastic literature. Etymology The Greek word ''kentauros'' is generally regarded as being of obscure origin. The etymology from ''ken'' + ''tau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odin
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Empire's partial occupation of Germania ( BCE), the Migration Period (4th–6th centuries CE) and the Viking Age (8th–11th centuries CE). Consequently, Odin has hundreds of names and titles. Several of these stem from the reconstructed Proto-Germanic theonym ''Wōðanaz'', meaning "lord of frenzy" or "leader of the possessed", which may relate to the god's strong association with poetry. Most mythological stories about Odin survive from the 13th-century ''Prose Edda'' and an earlier collection of Old Norse poems, the ''Poetic Edda'', along with other Old Norse items like '' Ynglinga saga''. The ''Prose Edda'' and other sources depict Odin as the head of the pantheon, sometimes called the Æsir, and bearing a spear and a ring. Wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiddaw
Skiddaw is a mountain in the Lake District National Park in England. Its summit is traditionally considered to be the List of Wainwrights, fourth-highest peak but depending on what topographic prominence is thought to be significant is also variously ranked as the List of Marilyns in the British Isles, third- and the List of Furths#England, sixth-highest in England. It lies just north of the town of Keswick, Cumbria, Keswick, Cumbria, and dominates the skyline in this part of the northern lakes. It is the simplest of the Lake District mountains of this height to ascend (as there is a well-trodden tourist track from a car park to the north-east of Keswick, near the summit of Latrigg) and, as such, many walking guides recommend it to the occasional walker wishing to climb a mountain. This is the first summit of the fell running challenge known as the Bob Graham Round when undertaken in a clockwise direction. The mountain lends its name to the surrounding areas of Skiddaw Fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falstaff
Sir John Falstaff is a fictional character who appears in three plays by William Shakespeare and is eulogised in a fourth. His significance as a fully developed character is primarily formed in the plays ''Henry IV, Part 1'' and '' Part 2'', where he is a companion to Prince Hal, the future King Henry V of England. Falstaff is also featured as the buffoonish suitor of two married women in ''The Merry Wives of Windsor''. Though primarily a comic figure, he embodies a depth common to Shakespeare's major characters. A fat, vain, and boastful knight, he spends most of his time drinking at the Boar's Head Inn with petty criminals, living on stolen or borrowed money. Falstaff leads the apparently wayward Prince Hal into trouble, and is repudiated when Hal becomes king. Falstaff has appeared in other works, including operas by Giuseppe Verdi, Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Otto Nicolai, a "symphonic study" by Edward Elgar, and in Orson Welles's 1966 film ''Chimes at Midnight''. The op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliban
Caliban ( ), the subhuman son of the sea witch Sycorax, is an important character in William Shakespeare's play ''The Tempest''. His character is one of the few Shakespearean figures to take on a life of its own "outside" Shakespeare's own work: as Russell Hoban put it, "Caliban is one of the hungry ideas, he's always looking for someone to word him into being . . . Caliban is a necessary idea". Character Caliban is half human, half monster. After his island becomes occupied by Prospero and his daughter Miranda, Caliban is forced into slavery. While he is referred to as a calvaluna or mooncalf, a freckled monster, he is the only human inhabitant of the island that is otherwise "not honour'd with a human shape" (Prospero, I.2.283). In some traditions, he is depicted as a wild man, or a deformed man, or a beast man, or sometimes a mix of fish and man, a dwarf or even a tortoise. Banished from Algiers, Sycorax was left on the isle, pregnant with Caliban, and died before Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
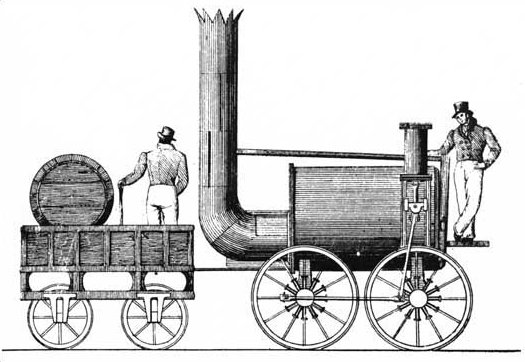
Sans Pareil
''Sans Pareil'' is a steam locomotive built by Timothy Hackworth which took part in the 1829 Rainhill Trials on the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, held to select a builder of locomotives. The name is French and means 'peerless' or 'without equal'. Design While a capable locomotive for the day, its technology was somewhat antiquated compared to George and Robert Stephenson's ''Rocket'', the winner of the Rainhill Trials and the £500 prize money. Instead of the fire tube boiler of ''Rocket'', ''Sans Pareil'' had a double return flue. To increase the heating surface area, the two flues were joined by a U-shaped tube at the forward end of the boiler; the firebox and chimney were both positioned at the same end, one on either side. ''Sans Pareil'' had two cylinders, mounted vertically at the opposite end to the chimney, and driving one pair of driving wheels directly - the other pair were driven via connecting rods, in the typical steam locomotive fashion. Railhill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet (locomotive)
''Planet'' was an early steam locomotive built in 1830 by Robert Stephenson and Company for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. History The ninth locomotive built for the L&MR, it was Stephenson's next major design change after the ''Rocket''. It was the first locomotive to employ inside cylinders, and subsequently the 2-2-0 type became known as ''Planets''. On 23 November 1830 ''No.9 Planet'' ran the approximately from Liverpool to Manchester in one hour. It only lasted in service about ten years; having been rebuilt in 1833, it was withdrawn circa 1840–1841. ''Planet''-type locomotives Six further of the type were ordered by the L&MR from Robert Stephenson & Co. Three more were supplied by Murray & Wood in Leeds, to whom Robert Stephenson & Co. had sent the drawings for their manufacture. The ''Planet'' (from 1830) and the '' Patentee'' (from 1834, also designed by Stephenson) were the first locomotive types to be built in large numbers. Improvements The ''Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Wellington (title)
Duke of Wellington is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. The name derived from Wellington in Somerset. The title was created in 1814 for Arthur Wellesley, 1st Marquess of Wellington (1769–1852; born as The Hon. Arthur Wesley), the Anglo-Irish military commander who is best known for leading the decisive victory with Field Marshal von Blücher over Napoleon's forces at Waterloo in Brabant (now Walloon Brabant, Belgium). Wellesley later served twice as British prime minister. In historical texts, unqualified use of the title typically refers to the 1st Duke. The first Duke's father, Garret Wesley, had been granted the title of Earl of Mornington in 1760. His male-line ancestors were wealthy agricultural and urban landowners in both countries, among the Anglo-Irish Protestant Ascendancy. The dukedom has descended to heirs male of the body, along with eleven other hereditary titles. History The titles of Duke of Wellington and Marquess Douro were bestowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |