|
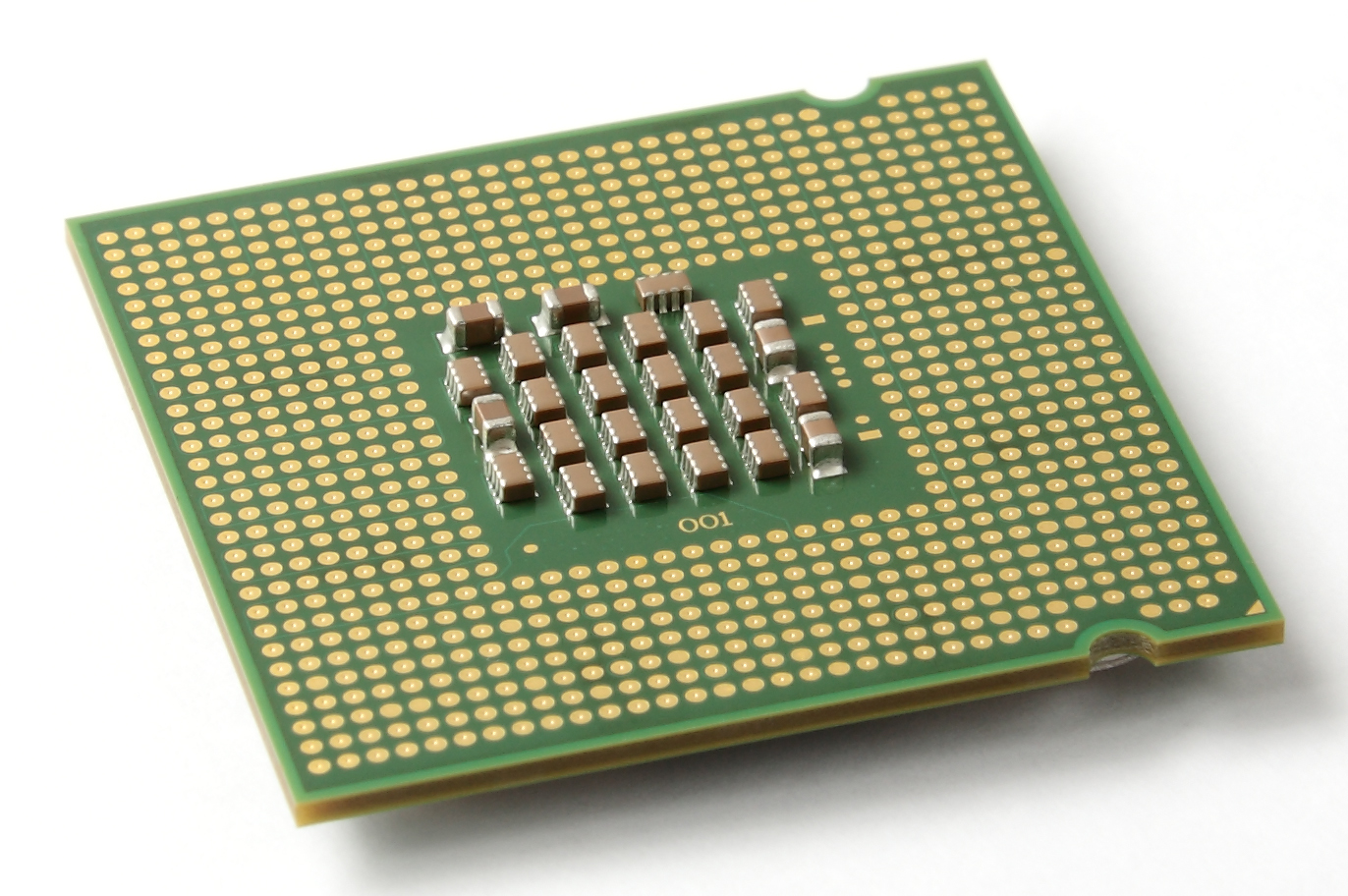
LGA 1248
LGA 1248 is an Intel CPU Socket for Itanium processors from the 9300-series to the 9700-series. It replaces PAC611 (also known as PPGA661) used by Itanium 9100-series processors and adds Intel QuickPath Interconnect functionalities. See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of Intel Itanium microprocessors * CPU socket In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the centr ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Lga 1248 Intel CPU sockets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 1248
LGA 1248 is an Intel CPU Socket for Itanium processors from the 9300-series to the 9700-series. It replaces PAC611 (also known as PPGA661) used by Itanium 9100-series processors and adds Intel QuickPath Interconnect functionalities. See also * List of Intel microprocessors * List of Intel Itanium microprocessors * CPU socket In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the centr ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Lga 1248 Intel CPU sockets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Grid Array
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket (when a socket is used) rather than the integrated circuit. An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board. Description The ''land grid array'' is a packaging technology with a grid of contacts, 'lands', on the underside of a package. The contacts are to be connected to a grid of contacts on the PCB. Not all rows and columns of the grid need to be used. The contacts can either be made by using an LGA socket, or by using solder paste. The grid elements found in use can be e.g. circular, triangular or other polygonal shapes and might have even different sizes. Grids might sometimes appear like honey comb patterns. Designs are often optimized for factors like contact likeliness despite tolerances, electrical gap to neighboring contacts and for allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for computer system manufacturers such as Acer, Lenovo, HP, and Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, graphics chips, embedded processors and other devices related to communications and computing. Intel (''int''egrated and ''el''ectronics) was founded on July 18, 1968, by semiconductor pioneers Gordon Moore (of Moore's law) and Robert Noyce ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAC611
{{Compu-hardware-stub ...
Socket PAC611 is a 611 pin microprocessor socket designed to interface an Intel Itanium 2 processor to the rest of the computer (usually via the motherboard). It provides both an electrical interface as well as physical support. This socket is designed to support a microprocessor module. Technical specifications Socket PAC611 was introduced with Intel's second generation Itanium in 2002. It supported bus speeds up to 200 MHz double-pumped. Socket PAC611 processors reach speeds up to 1.66 GHz. See also * List of Intel microprocessors References Socket 604 Socket 604 is a 604-pin microprocessor socket designed to interface an Intel's Xeon processor to the rest of the computer. It provides both an electrical interface as well as physical support. This socket is designed to support a heatsink. Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
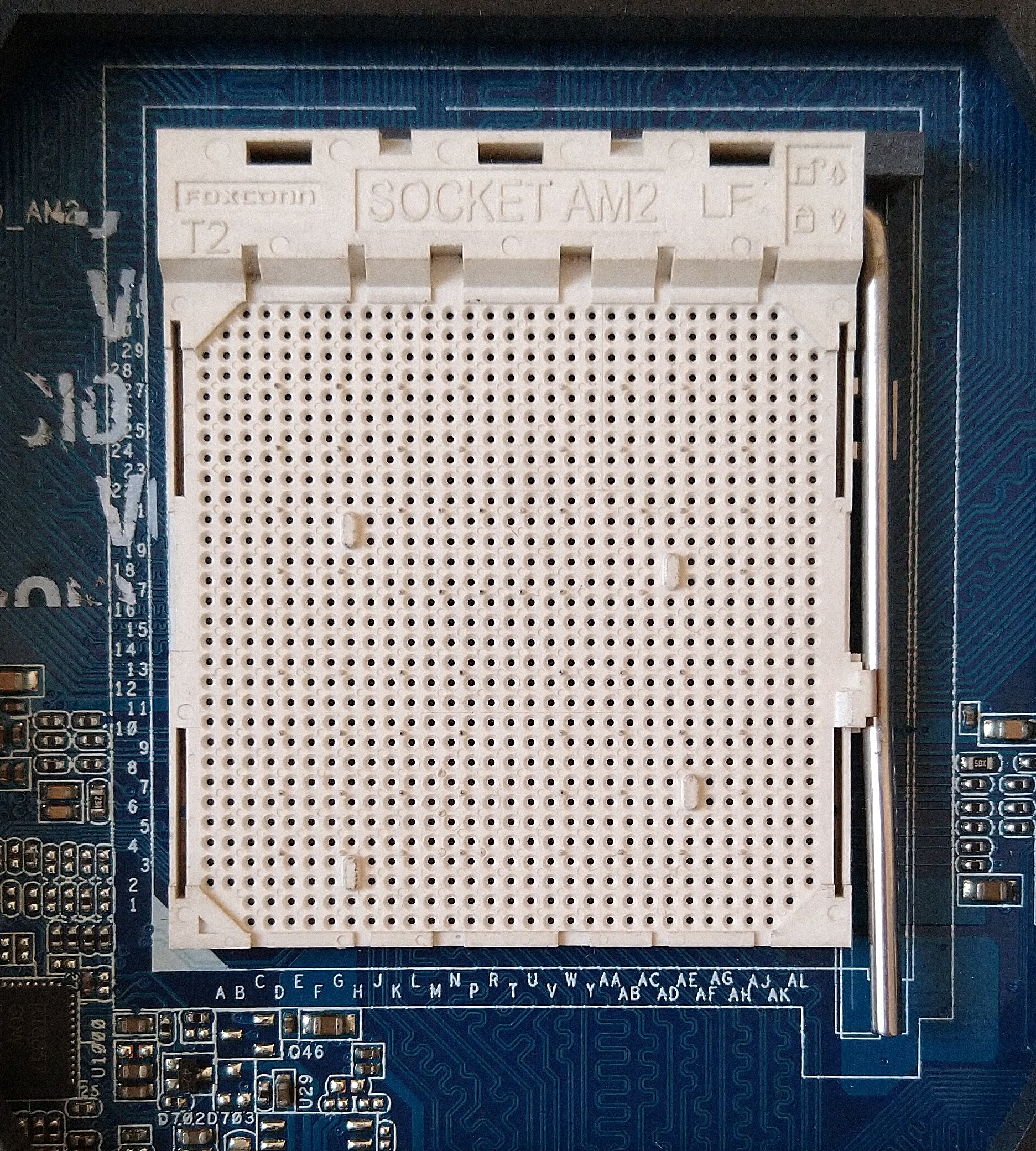
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include Pin Grid Array (PGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itanium
Itanium ( ) is a discontinued family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors that implement the Intel Itanium architecture (formerly called IA-64). Launched in June 2001, Intel marketed the processors for enterprise servers and high-performance computing systems. The Itanium architecture originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was later jointly developed by HP and Intel. Itanium-based systems were produced by HP/Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) (the HPE Integrity Servers line) and several other manufacturers. In 2008, Itanium was the fourth-most deployed microprocessor architecture for enterprise-class systems, behind x86-64, Power ISA, and SPARC. In February 2017, Intel released the final generation, Kittson, to test customers, and in May began shipping in volume. It was used exclusively in mission-critical servers from Hewlett Packard Enterprise. In 2019, Intel announced that new orders for Itanium would be accepted until January 30, 2020, and shipments would cease by July 29, 2021 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel QuickPath Interconnect
The Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) is a point-to-point microprocessor, processor electrical connection, interconnect developed by Intel which replaced the front-side bus (FSB) in Xeon, Itanium, and certain desktop platforms starting in 2008. It increased the scalability and available bandwidth. Prior to the name's announcement, Intel referred to it as Common System Interface (CSI). Earlier incarnations were known as Yet Another Protocol (YAP) and YAP+. QPI 1.1 is a significantly revamped version introduced with Sandy Bridge-EP (Romley platform). QPI was replaced by Intel Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) in Skylake (microarchitecture), Skylake-SP Xeon processors based on LGA 3647 socket. Background Although sometimes called a "bus", QPI is a point-to-point interconnect. It was designed to compete with HyperTransport that had been used by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) since around 2003. Intel developed QPI at its Massachusetts Microprocessor Design Center (MMDC) by members of what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Microprocessors
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of Intel's processors from the pioneering 4-bit 4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product. Latest 13th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Raptor Lake") 12th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Alder Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Alder Lake") 11th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Rocket Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Tiger Lake") 10th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Comet Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Comet Lake", " Ice Lake", and " Amber Lake") 9th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Coffee Lake Refresh") 8th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Coffee Lake") Mobile (codenamed "Coffee Lake", " Amber Lake" and " Whiskey Lake") 7th generation Core Desktop (codenamed "Kaby Lake" and "Skylake-X") Mobile (codenamed "Kaby Lake" and " Apollo Lake") All processors All processors are listed in chron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Itanium Microprocessors
The Itanium from Intel is a high-end Server (computing), server and supercomputer microprocessor. Itanium (2001) Merced (180 nm) Steppings: C0, C1 and C2. CPUID: 0007000604h (stepping C0), 0007000704h (stepping C1) or 0007000804h (stepping C2). Transistor count: 25.4 million for CPU, 295 million for the external L3 cache. The FSB data bus is 64 bits wide, not 128 like in Itanium 2. Itanium 2 (2002-2007) Itanium 2 uses socket PAC611 with a 128 bit wide Front Side Bus, FSB. The 90 nm CPUs (9000 and 9100 series) bring dual-core chips and an updated microarchitecture adding multithreading and splitting the L2 cache into a 256 KB data cache and 1 MB instruction cache per core (the pre-9000 series L2 cache being a 256 KB common cache). All Itaniums except some 130 nm models are capable of >2-socket Symmetric multiprocessing, SMP. McKinley (180 nm) Stepping: B3. Die size: 421 mm². Transistor count: 221 million. CPUID: 001F000704h Madison (130 nm) Stepping: B1. Die size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include Pin Grid Array (PGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |