|
LEM Domain-containing Protein 3
LEM domain-containing protein 3 (LEMD3), also known as MAN1, is an integral protein in the inner nuclear membrane (INM) of the nuclear envelope. It is encoded by the ''LEMD3'' gene and was first identified after it was isolated from the serum of a patient with a collagen vascular disease. Structure The protein is 82.3 kDa and has a 40 amino acid long LEM domain located at its amino-terminal region. In its carboxyl end it has a RNA recognition motif (RRM). The LEM domain is also common to two other integral proteins of the INM: lamina-associated polypeptide 2 (LAP2) and emerin. The LEM segment enables LEMD3 to attach to the barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF), and therefore, indirectly interact with the chromatin. LEMD3 also has several implications in regulating the cytokine family such as the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) and bone morphogenic protein (BMPs). The RRM domain in its carboxylic region attaches to the SMAD (protein) proteins, which is involved in med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Nuclear Membrane Proteins
Inner nuclear membrane proteins (INM proteins) are membrane proteins that are embedded in or associated with the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are about 60 INM proteins, most of which are poorly characterized with respect to structure and function. Among the few well-characterized INM proteins are lamin B receptor (LBR), lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1), lamina-associated polypeptide-2 (LAP2), emerin and MAN1. Common structural features Several integral nuclear membrane proteins of different size and structure have been identified. It is proposed that they share some structural features with respect to nucleoplasmic domain(s) and lipid-soluble domain(s). Some INM proteins contain common protein domain structures, and can thus be categorised into known protein domain families. These include the LEM-, SUN-, and KASH-domain families. Members of the LEM-domain family play a part in chromatin organisation . SUN- and KASH-domains participate in linking t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling as immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the balance between humoral and cell-based immune responses, and they regulate the maturation, growth, and res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melorheostosis
Melorheostosis is a medical developmental disorder and mesenchymal dysplasia in which the bony cortex widens and becomes hyperdense in a sclerotomal distribution. The condition begins in childhood and is characterized by thickening of the bones. Pain is a frequent symptom and the bone can have the appearance of dripping candle wax. Cause A randomly occurring somatic mutation of the MAP2K1 gene during fetal development is believed to be the cause. It is not known if LEMD3 mutations can cause isolated melorheostosis in the absence of osteopoikilosis or Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome. Diagnosis Melorheostosis is a mesenchymal dysplasia manifesting as regions of dripping wax appearance or flowing candle wax appearance. The disorder can be detected by radiograph due to thickening of bony cortex resembling "dripping candle wax." It is included on the spectrum of developmental bone dysplasias including pycnodysostosis and osteopoikilosis. The disorder tends to be unilateral and monostot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteopoikilosis
Osteopoikilosis is a benign, autosomal dominant sclerosing dysplasia of bone characterized by the presence of numerous bone islands in the skeleton. Presentation The radiographic appearance of osteopoikilosis on an X-ray is characterized by a pattern of numerous white densities of similar size spread throughout all the bones. This is a systemic condition. It must be differentiated from blastic metastasis, which can also present radiographically as white densities interspersed throughout bone. Blastic metastasis tends to present with larger and more irregular densities in less of a uniform pattern. Another differentiating factor is age, with blastic metastasis mostly affecting older people, and osteopoikilosis being found in people 20 years of age and younger. The distribution is variable, though it does not tend to affect the ribs, spine, or skull. Cause Epidemiology Men and women are affected in equal number, reflecting the fact that osteopoikilosis attacks indiscriminately. Ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminopathies
Laminopathies ('' lamino-'' + '' -opathy'') are a group of rare genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes encoding proteins of the nuclear lamina. They are included in the more generic term ''nuclear envelopathies'' that was coined in 2000 for diseases associated with defects of the nuclear envelope. Since the first reports of laminopathies in the late 1990s, increased research efforts have started to uncover the vital role of nuclear envelope proteins in cell and tissue integrity in animals. Symptoms and signs Laminopathies and other nuclear envelopathies have a large variety of clinical symptoms including skeletal and/or cardiac muscular dystrophy, lipodystrophy and diabetes, dysplasia, dermo- or neuropathy, leukodystrophy, and progeria (premature aging). Most of these symptoms develop after birth, typically during childhood or adolescence. Some laminopathies however may lead to an early death, and mutations of lamin B1 (LMNB1 gene) may be lethal before or at birth. Geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
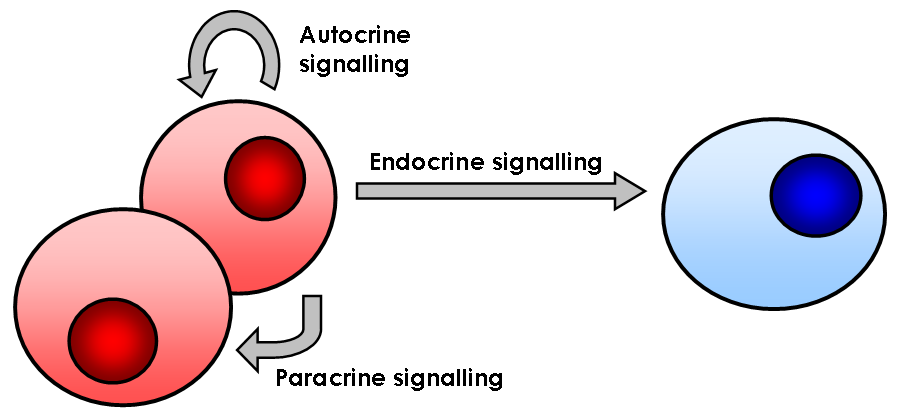
Cellular Signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Signals that originate from outside a cell (or extracellular signals) can be physical agents like mechanical pressure, voltage, temperature, light, or chemical signals (e.g., small molecules, peptides, or gas). Cell signaling can occur over short or long distances, and as a result can be classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, intracrine, paracrine, or endocrine. Signaling molecules can be synthesized from various biosynthetic pathways and released through passive or active transports, or even from cell damage. Receptors play a key role in cell signaling as they are able to detect chemical signals or physical stimuli. Receptors are generally proteins located on the cell surface or within the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Morphogenic Protein
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Originally discovered by their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now considered to constitute a group of pivotal morphogenetic signals, orchestrating tissue architecture throughout the body. The important functioning of BMP signals in physiology is emphasized by the multitude of roles for dysregulated BMP signalling in pathological processes. Cancerous disease often involves misregulation of the BMP signalling system. Absence of BMP signalling is, for instance, an important factor in the progression of colon cancer, and conversely, overactivation of BMP signalling following reflux-induced esophagitis provokes Barrett's esophagus and is thus instrumental in the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Recombinant human BMPs (rhBMPs) are used in orthopedic applications such as spinal fusions, nonunions, and oral surgery. rhBMP-2 and rhBMP-7 are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transforming Growth Factor Beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages. Activated TGF-β complexes with other factors to form a serine/threonine kinase complex that binds to TGF-β receptors. TGF-β receptors are composed of both type 1 and type 2 receptor subunits. After the binding of TGF-β, the type 2 receptor kinase phosphorylates and activates the type 1 receptor kinase that activates a signaling cascade. This leads to the activation of different downstream substrates and regulatory proteins, inducing transcription of different target genes that function in differentiation, chemotaxis, proliferation, and activation of many immune cells. TGF-β is secreted by many cell types, including macrophages, in a latent form in which it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier-to-autointegration Factor
In molecular biology, barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF) is a family of essential proteins that is highly conserved in metazoan evolution, and which may act as DNA-bridging proteins. BAF binds directly to double-stranded DNA, to transcription activators, and to inner nuclear membrane proteins, including lamin A filaments that anchor nuclear pore complexes in place, and nuclear LEM-domain proteins that bind to laminin filaments and chromatin. New findings suggest that BAF has structural roles in nuclear assembly and chromatin organization, represses gene expression and might interlink chromatin structure, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in metazoans. BAF can be exploited by retroviruses to act as a host component of pre-integration complexes, which promote the integration of the retroviral DNA into the host chromosome by preventing autointegration (integration into itself). BAF might contribute to the assembly or activity of retroviral pre-integration complexes throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |