|
Barrier-to-autointegration Factor
In molecular biology, barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF) is a family of essential proteins that is highly conserved in metazoan evolution, and which may act as DNA-bridging proteins. BAF binds directly to double-stranded DNA, to transcription activators, and to inner nuclear membrane proteins, including lamin A filaments that anchor nuclear pore complexes in place, and nuclear LEM-domain proteins that bind to laminin filaments and chromatin. New findings suggest that BAF has structural roles in nuclear assembly and chromatin organization, represses gene expression and might interlink chromatin structure, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in metazoans. BAF can be exploited by retroviruses to act as a host component of pre-integration complexes, which promote the integration of the retroviral DNA into the host chromosome by preventing autointegration (integration into itself). BAF might contribute to the assembly or activity of retroviral pre-integration complexes throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation (genetics)
In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar Sequence (biology), sequences in nucleic acids (DNA sequence, DNA and RNA) or peptide sequence, proteins across species (homology (biology)#Orthology, orthologous sequences), or within a genome (homology (biology)#Paralogy, paralogous sequences), or between donor and receptor taxa (Sequence homology#Xenology, xenologous sequences). Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection. A highly conserved sequence is one that has remained relatively unchanged far back up the phylogenetic tree, and hence far back in geological time. Examples of highly conserved sequences include the Ribosomal RNA, RNA components of ribosomes present in all domain (biology), domains of life, the homeobox sequences widespread amongst Eukaryotes, and the tmRNA in Bacteria. The study of sequence conservation overlaps with the fields of genomics, proteomics, evolutionary biology, phylogenetics, bioinformatics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilateral symmetry, bilat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding (molecular)
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules that results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other. It is formed when atoms or molecules bind together by sharing of electrons. It often, but not always, involves some chemical bonding. In some cases, the associations can be quite strong—for example, the protein streptavidin and the vitamin biotin have a dissociation constant (reflecting the ratio between bound and free biotin) on the order of 10−14—and so the reactions are effectively irreversible. The result of molecular binding is sometimes the formation of a molecular complex in which the attractive forces holding the components together are generally non-covalent, and thus are normally energetically weaker than covalent bonds. Molecular binding occurs in biological complexes (e.g., between pairs or sets of proteins, or between a protein and a small molecule ligand it binds) and also in abiologic chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein
Inner nuclear membrane proteins (INM proteins) are membrane proteins that are embedded in or associated with the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are about 60 INM proteins, most of which are poorly characterized with respect to structure and function. Among the few well-characterized INM proteins are lamin B receptor (LBR), lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1), lamina-associated polypeptide-2 (LAP2), emerin and MAN1. Common structural features Several integral nuclear membrane proteins of different size and structure have been identified. It is proposed that they share some structural features with respect to nucleoplasmic domain(s) and lipid-soluble domain(s). Some INM proteins contain common protein domain structures, and can thus be categorised into known protein domain families. These include the LEM-, SUN-, and KASH-domain families. Members of the LEM-domain family play a part in chromatin organisation . SUN- and KASH-domains participate in linking the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamin A
Pre-lamin A/C or lamin A/C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LMNA'' gene. Lamin A/C belongs to the lamin family of proteins. Function In the setting of ZMPSTE24 deficiency, the final step of lamin processing does not occur, resulting in an accumulation of farnesyl-prelamin A. In Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome, a 50-amino acid deletion in prelamin A (amino acids 607–656) removes the site for the second endoproteolytic cleavage. Consequently, no mature lamin A is formed, and a farnesylated mutant prelamin A (progerin) accumulates in cells. The nuclear lamina consist of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane. The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. During mitosis, the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability, chromatin structure and gene expression. Vertebrate lami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Pore Complex
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in the nuclear envelope of a vertebrate cell, but this number varies depending on cell type and the stage in the life cycle. The human nuclear pore complex (hNPC) is a 110 megadalton (MDa) structure. The proteins that make up the nuclear pore complex are known as nucleoporins; each NPC contains at least 456 individual protein molecules and is composed of 34 distinct nucleoporin proteins. About half of the nucleoporins typically contain solenoid protein domains—either an alpha solenoid or a beta-propeller fold, or in some cases both as separate structural domains. The other half show structural characteristics typical of "natively unfolded" or intrinsically disordered proteins, i.e. they are highly flexible proteins that lack ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
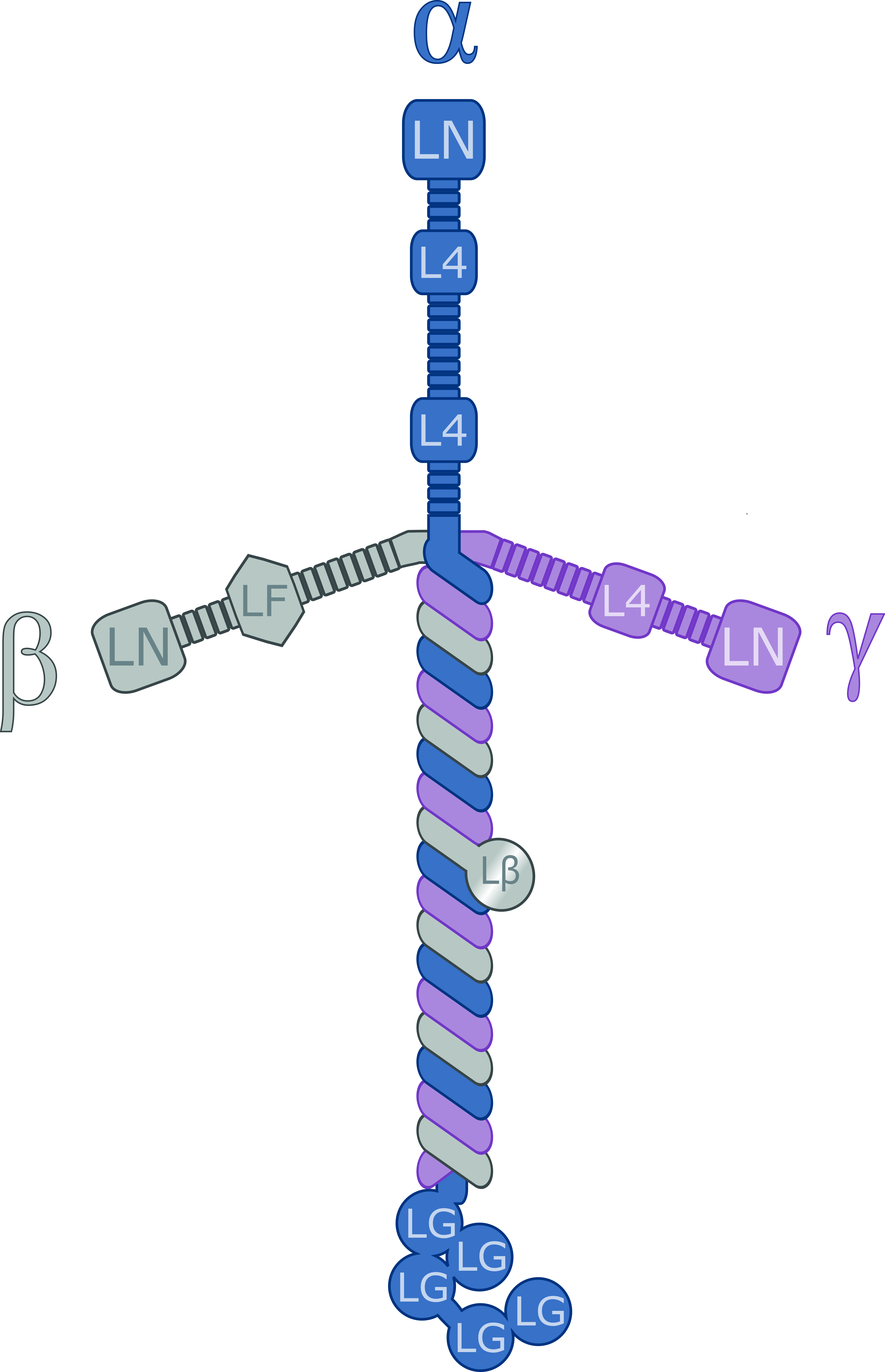
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Regulation
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network. Gene regulation is essential for viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes as it increases the versatility and adaptability of an organism by allowing the cell to express protein when needed. Although as early as 1951, Barbara McClintock showed interaction between two genetic loci, Activator (''Ac'') and Dissociator (''Ds''), in the color formation of maize seeds, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |