|
LEDES
The Legal Electronic Data Exchange Standard is a set of file format specifications intended to facilitate electronic data transmission in the legal industry. The phrase is abbreviated LEDES and is usually pronounced as "leeds". The LEDES specifications are maintained by the LEDES Oversight Committee (LOC), which started informally as an industry-wide project led by the Law Firm and Law Department Services Group within PricewaterhouseCoopers in 1995. In 2001, the LEDES Oversight Committee was incorporated as a California mutual-benefit nonprofit corporation and is now led by a seven-member Board of Directors. The LOC maintains four types of data exchange standards for legal electronic billing (ebilling); budgeting; timekeeper attributes; and intellectual property matter management. The LOC also maintains five types of data elements in the LEDES data exchange standards: Uniform Task-Based Management System codes, which classify the work performed by type of legal matter; activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Task-Based Management System
The Uniform Task-Based Management System (UTBMS) is a set of codes designed to standardize categorization and facilitate analysis of legal work and expenses. UTBMS was produced through a collaborative effort among the American Bar Association Section of Litigation, the American Corporate Counsel Association, and a group of major corporate clients and law firms coordinated and supported by Price Waterhouse LLP (now PricewaterhouseCoopers). UTBMS codes are now maintained and developed by the Legal Electronic Data Exchange Standard (LEDES) Oversight Committee. Background UTBMS coding is reflected in legal bills sent from a law firm to its corporate clients. Law firms will usually use coding on time and expenses only for those clients who explicitly request it. Most clients who use UTBMS also require electronic billing, usually with an invoice in a LEDES e-billing format. Fees, which are charges for attorney and legal assistant time, are coded with task and activity codes. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invention Disclosure
An invention disclosure, or invention disclosure report, is a confidential document written by a scientist or engineer for use by a company's patent department, or by an external patent attorney, to determine whether patent protection should be sought for the described invention. It may follow a standardized form established within a company.M. Henry Heines, ''Patent Empowerment for Small Corporations'', Greenwood Publishing Group, 2001, , pages 122-123. See also * Inventor's notebook * Lab notebook ** Electronic lab notebook * Laboratory information management system A laboratory information management system (LIMS), sometimes referred to as a laboratory information system (LIS) or laboratory management system (LMS), is a software-based solution with features that support a modern laboratory's operations. K ... * LEDES invention disclosure data format * Scientific management References Scientific documents Research {{law-term-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
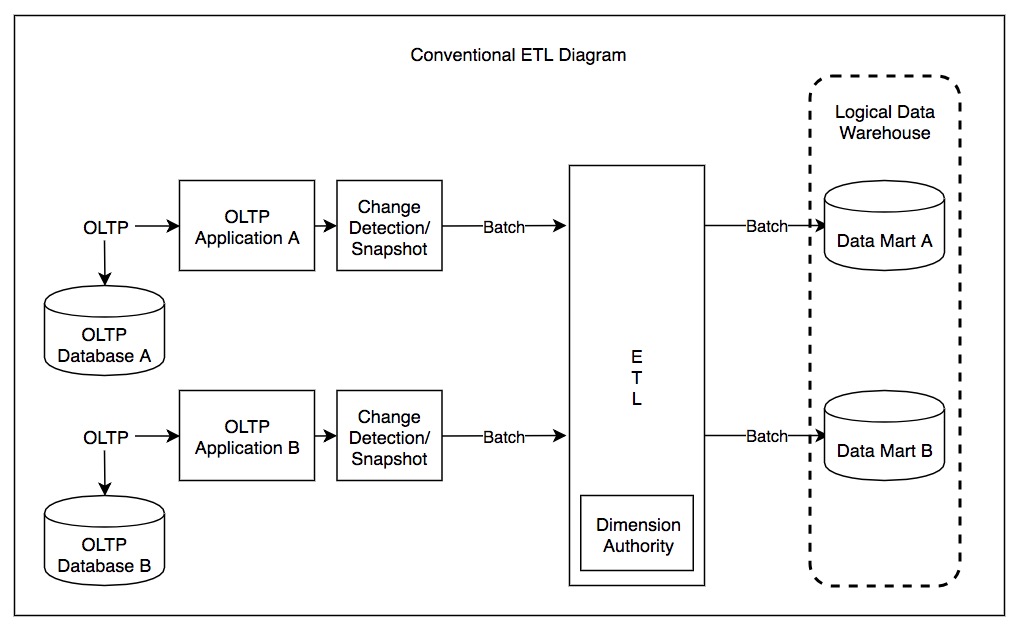
Expense And Cost Recovery System (ECRS)
An expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) is a specialized subset of "extract, transform, load" (ETL) functioning as a powerful and flexible set of applications, including programs, scripts and databases designed to improve the cash flow of businesses and organizations by automating the movement of data between cost recovery systems, electronic billing from vendors, and accounting systems. Expense and cost recovery system ECRS is an area of ETL most applicable to consulting businesses, accounting agencies, and law firms, companies that bill back clients for time and costs. As such, the terms "disbursement", "expense", "cost", and "charge" may be synonymous and can be industry-specific. Sometimes the terms refer to the state of a transaction as it is extracted from the vendor data, transformed in the ECRS and then loaded into the accounting system. The term "transaction", in an ECRS, is generally referring to a single record of a one-time business exchange incurring debt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extract, Transform, Load
In computing, extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase process where data is extracted, transformed (cleaned, sanitized, scrubbed) and loaded into an output data container. The data can be collated from one or more sources and it can also be outputted to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software applications but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on reoccurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs. A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions. The ETL process became a popular concept in the 1970s and is often used in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Transmission
Data transmission and data reception or, more broadly, data communication or digital communications is the transfer and reception of data in the form of a digital bitstream or a digitized analog signal transmitted over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication using radio spectrum, storage media and computer buses. The data are represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal. Analog transmission is a method of conveying voice, data, image, signal or video information using a continuous signal which varies in amplitude, phase, or some other property in proportion to that of a variable. The messages are either represented by a sequence of pulses by means of a line code (''baseband transmission''), or by a limited set of continuously varying waveforms (''passband transmission''), using a digital modulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PricewaterhouseCoopers
PricewaterhouseCoopers is an international professional services brand of firms, operating as partnerships under the PwC brand. It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is considered one of the Big Four accounting firms, along with Deloitte, EY and KPMG. PwC firms are in 157 countries, across 742 locations, with 284,000 people. As of 2019, 26% of the workforce was based in the Americas, 26% in Asia, 32% in Western Europe and 5% in Middle East and Africa. The company's global revenues were $42.4 billion in FY 2019, of which $17.4 billion was generated by its Assurance practice, $10.7 billion by its Tax and Legal practice and $14.4 billion by its Advisory practice. The firm in its recent actual form was created in 1998 by a merger between two accounting firms: Coopers & Lybrand, and Price Waterhouse. Both firms had histories dating back to the 19th century. The trading name was shortened to PwC (stylized p''w''c) in September 2010 as part of a rebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual-benefit Nonprofit Corporation
A mutual-benefit nonprofit corporation or membership corporation is a type of nonprofit corporation in the US, similar to other mutual benefit organizations found in some of common law nations, chartered by government with a mandate to serve the mutual benefit of its members. A mutual-benefit corporation can be non-profit or not-for-profit in the United States, but it cannot obtain IRS 501(c)(3) non-profit status as a charitable organization. It is distinct in U.S. law from public-benefit nonprofit corporations,_and_religious_corporation.html" ;"title="110. - 6910./ref> is a type of Nonprofit organization">nonprofit corporation chartered by a state governments of the United States, state gover ...s, and religious corporation">110. - 6910./ref> is a type of Nonprofit organization">nonprofit corporation chartered by a state governments of the United States, state gover ...s, and religious corporations. Mutual benefit corporations must still file tax returns and pay income tax because t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Billing
Electronic billing or electronic bill payment and presentment, is when a seller such as company, organization, or group sends its bills or invoices over the internet, and customers electronic bill payment, pay the bills electronically. This replaces the traditional method where invoices were sent in paper form and payments were done by manual means such as sending cheques. There are a number of advantages to electronic billing that include the faster presentation of invoices and reductions in costs in handling paper document. However to take full advantage of electronic billing both seller and buyer need to have in place computer systems able to handle electronic billing and have access to financial institutions that can do electronic payments. History The development of electronic billing and payments started in the late 20th century, and whilst its exact origins are unclear, it is generally agreed that development of electronic billing coincided with the rise of the Informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Firm
A law firm is a business entity formed by one or more lawyers to engage in the practice of law. The primary service rendered by a law firm is to advise clients (individuals or corporations) about their legal rights and responsibilities, and to represent clients in civil or criminal cases, business transactions, and other matters in which legal advice and other assistance are sought. Arrangements Law firms are organized in a variety of ways, depending on the jurisdiction in which the firm practices. Common arrangements include: * Sole proprietorship, in which the attorney ''is'' the law firm and is responsible for all profit, loss and liability; * General partnership, in which all the attorneys who are members of the firm share ownership, profits and liabilities; * Professional corporations, which issue stock to the attorneys in a fashion similar to that of a business corporation; * Limited liability company, in which the attorney-owners are called "members" but are not direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and recognized as such in law for certain purposes. Early incorporated entities were established by charter (i.e. by an ''ad hoc'' act granted by a monarch or passed by a parliament or legislature). Most jurisdictions now allow the creation of new corporations through registration. Corporations come in many different types but are usually divided by the law of the jurisdiction where they are chartered based on two aspects: by whether they can issue stock, or by whether they are formed to make a profit. Depending on the number of owners, a corporation can be classified as ''aggregate'' (the subject of this article) or '' sole'' (a legal entity consisting of a single incorporated office occupied by a single natural person). One of the most att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XML Schema (W3C)
XSD (XML Schema Definition), a recommendation of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), specifies how to formally describe the elements in an Extensible Markup Language (XML) document. It can be used by programmers to verify each piece of item content in a document, to assure it adheres to the description of the element it is placed in. Like all XML schema languages, XSD can be used to express a set of rules to which an XML document must conform to be considered "valid" according to that schema. However, unlike most other schema languages, XSD was also designed with the intent that determination of a document's validity would produce a collection of information adhering to specific data types. Such a post-validation ''infoset'' can be useful in the development of XML document processing software. History XML Schema, published as a W3C recommendation in May 2001, is one of several XML schema languages. It was the first separate schema language for XML to achieve Recommendation stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |