|
L-Deprenyl
Selegiline, also known as L-deprenyl and sold under the brand names Eldepryl and Emsam among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and major depressive disorder. It is provided in the form of a capsule or tablet taken by mouth for Parkinson's disease and as a patch applied to skin for depression. Selegiline acts as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, and increases levels of monoamine neurotransmitters in the brain. At typical clinical doses used for Parkinson's disease, selegiline is a selective and irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B), increasing levels of dopamine in the brain. In larger doses (more than 20 mg/day), it loses its specificity for MAO-B and also inhibits MAO-A, which increases serotonin and norepinephrine levels in the brain. Medical uses Parkinson's disease In its pill form, selegiline is used to treat symptoms of Parkinson's disease. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreversible Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy Category
The pregnancy category of a medication is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does ''not'' include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their metabolites in breast milk. Every drug has specific information listed in its product literature. The British National Formulary used to provide a table of drugs to be avoided or used with caution in pregnancy, and did so using a limited number of key phrases, but now Appendix 4 (which was the Pregnancy table) has been removed. Appendix 4 is now titled "Intravenous Additives". However, information that was previously available in the former Appendix 4 (pregnancy) and Appendix 5 (breast feeding) is now available in the individual drug monographs. United States American law requires that certain drugs and biological products must be labelled very specifically.Title 21, Part 201.57 (9)(i)of the Code of Federal Regulations lists specific requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Needed To Harm
In medicine, the number needed to harm (NNH) is an epidemiological measure that indicates how many persons on average need to be exposed to a risk factor over a specific period to cause harm in an average of one person who would not otherwise have been harmed. It is defined as the inverse of the absolute risk increase, and computed as 1/(I_e - I_u), where I_e is the incidence in the treated (exposed) group, and I_u is the incidence in the control (unexposed) group. Intuitively, the lower the number needed to harm, the worse the risk factor, with 1 meaning that every exposed person is harmed. NNH is similar to number needed to treat (NNT), where NNT usually refers to a positive therapeutic result and NNH to a detrimental effect or risk factor. A combined measure, the number needed to treat for an additional beneficial or harmful outcome (NNTB/H), is also used. Relevance The NNH is an important measure in evidence-based medicine and helps physicians decide whether it is prudent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effect Size
In statistics, an effect size is a value measuring the strength of the relationship between two variables in a population, or a sample-based estimate of that quantity. It can refer to the value of a statistic calculated from a sample of data, the value of a parameter for a hypothetical population, or to the equation that operationalizes how statistics or parameters lead to the effect size value. Examples of effect sizes include the correlation between two variables, the regression coefficient in a regression, the mean difference, or the risk of a particular event (such as a heart attack) happening. Effect sizes complement statistical hypothesis testing, and play an important role in power analyses, sample size planning, and in meta-analyses. The cluster of data-analysis methods concerning effect sizes is referred to as estimation statistics. Effect size is an essential component when evaluating the strength of a statistical claim, and it is the first item (magnitude) in the MAGI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Needed To Treat
The number needed to treat (NNT) or number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) is an epidemiological measure used in communicating the effectiveness of a health-care intervention, typically a treatment with medication. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional bad outcome (e.g. the number of patients that need to be treated for one of them to benefit compared with a control in a clinical trial). It is defined as the inverse of the absolute risk reduction, and computed as 1/(I_u - I_e), where I_e is the incidence in the treated (exposed) group, and I_u is the incidence in the control (unexposed) group. This calculation implicitly assumes monotonicity, that is, no individual can be harmed by treatment. The modern approach, based on counterfactual conditionals, relaxes this assumption and yields bounds on NNT. A type of effect size, the NNT was described in 1988 by McMaster University's Laupacis, Sackett and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
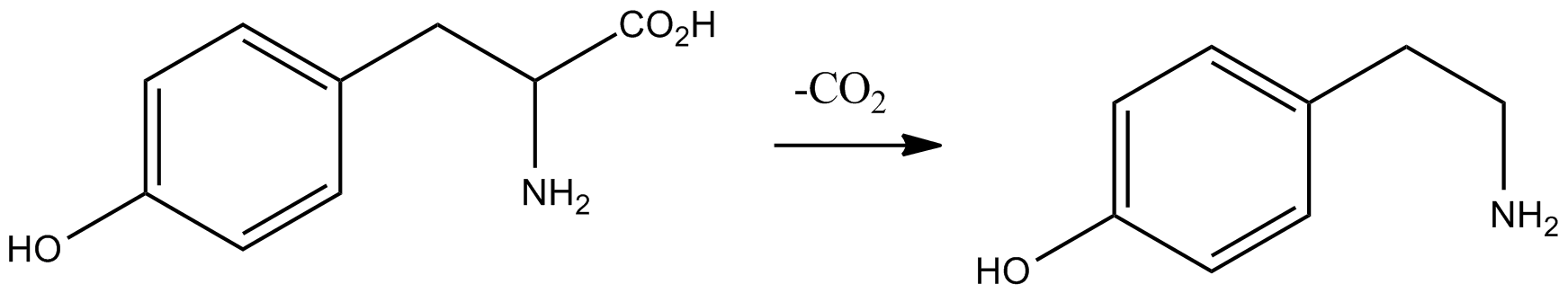
Tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals, and is metabolized by various enzymes, including monoamine oxidases. In foods, it often is produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods that are fermented, cured, pickled, aged, or spoiled have high amounts of tyramine. Tyramine levels go up when foods are at room temperature or go past their freshness date. Specific foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include: * strong or ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Pass Effect
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug, specifically when administered orally, is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemic circulation. It is the fraction of drug lost during the process of absorption which is generally related to the liver and gut wall. Notable drugs that experience a significant first-pass effect are buprenorphine, chlorpromazine, cimetidine, diazepam, ethanol (drinking alcohol), imipramine, insulin, lidocaine, midazolam, morphine, pethidine, propranolol, and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). First pass metabolism may occur in the liver (for propranolol, lidocaine, clomethiazole, and NTG) or in the gut (for benzylpenicillin and insulin). After a drug is swallowed, it is absorbed by the digestive system and enters the hepatic portal system. It is carried through the portal vein into the liver before it reaches the rest of the body. The liver met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levodopa
-DOPA, also known as levodopa and -3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize -DOPA, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid -tyrosine. -DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, -DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. -DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. -DOPA has a counterpart with opposite chirality, -DOPA. As is true for many molecules, the human body produces only one of these isomers (the -DOPA form). The enant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad'', "near", and '' ren'', "kidney") is more commonly used in the United Kingdom, whereas "norepinephrine" (from Ancient Greek ἐπῐ́ (''epí''), "upon", and νεφρός (''nephrós''), "kidney") is usually preferred in the United States. "Norepinephrine" is also the international nonproprietary name given to the drug. Regardless of which name is used for the substance itself, parts of the body that produce or are affected by it are referred to as noradrenergic. The general function of norepinephrine is to mobilize the brain and body for action. Norepinephrine release is lowest during sleep, rises during wakefulness, and reaches much higher levels during situations of stress or danger, in the so-called fight-or-flight response. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |