|
Kosmodraco
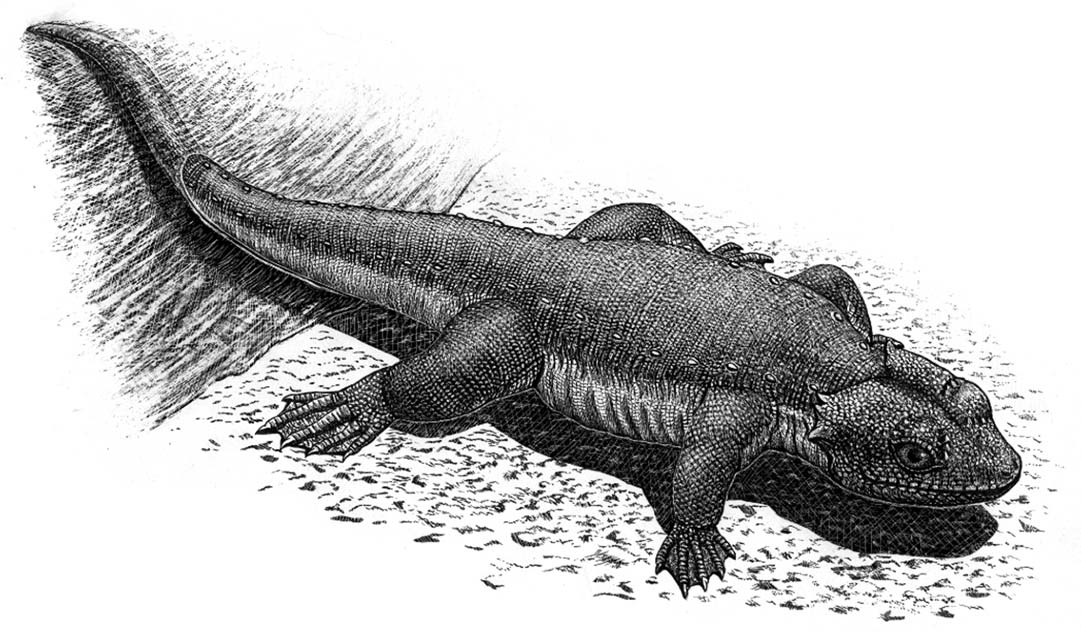
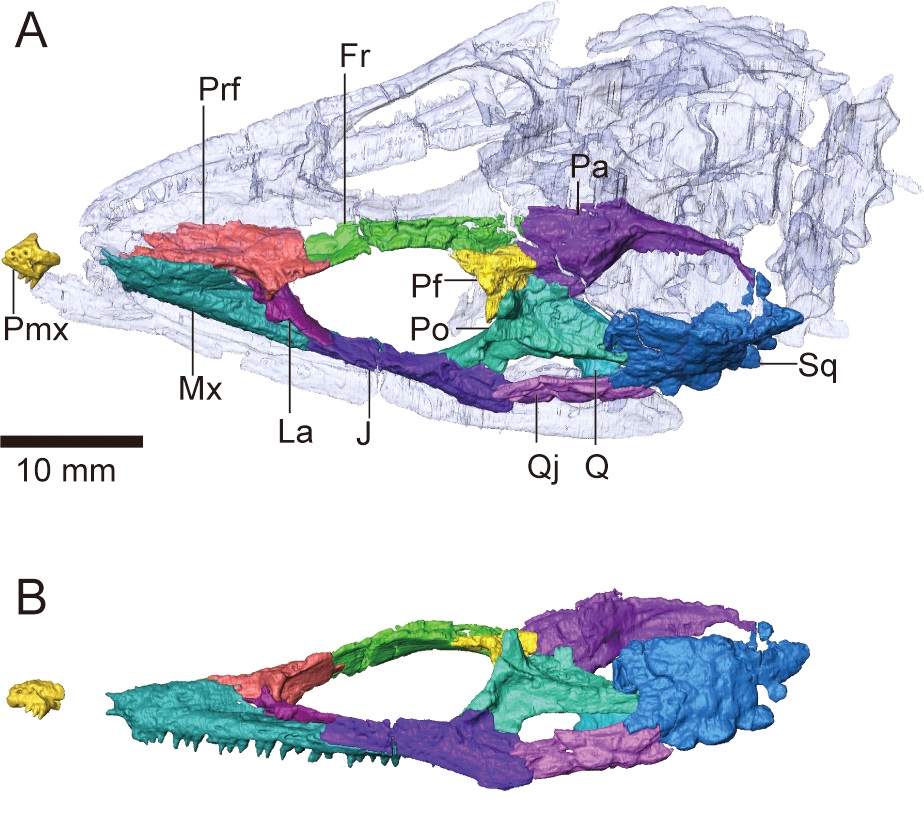
''Kosmodraco'' is a genus of large bodied choristodere from the Paleocene of North America. Originally described as a species of ''Simoedosaurus'', it was found to represent a distinct genus in 2022. Multiple fossil skulls show a relatively short and robust snout and a skull that is considerably wider behind the eyes. Two species are currently recognized, ''K. dakotensis'' and ''K. magnicornis''. History and naming The first specimen now known to belong to ''Kosmodraco'' was discovered in 1964 and 1968 in the Polecat Bench Formation (Wyoming). These two skulls, alongside others from Montana's Bear Creek, were reported on briefly by Sigogneau-Russell and Donald in 1978, who regarded them as evidence for the presence of the Eurasian genus ''Simoedosaurus'' in North America. However, at the time, these four specimens, although thought to be diagonstic at a genus level, were still unprepared and not assigned to a species. They were subsequently stored in the collection of the Princet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmodraco Lateral
''Kosmodraco'' is a genus of large bodied choristodere from the Paleocene of North America. Originally described as a species of ''Simoedosaurus'', it was found to represent a distinct genus in 2022. Multiple fossil skulls show a relatively short and robust snout and a skull that is considerably wider behind the eyes. Two species are currently recognized, ''K. dakotensis'' and ''K. magnicornis''. History and naming The first specimen now known to belong to ''Kosmodraco'' was discovered in 1964 and 1968 in the Polecat Bench Formation (Wyoming). These two skulls, alongside others from Montana's Bear Creek, were reported on briefly by Sigogneau-Russell and Donald in 1978, who regarded them as evidence for the presence of the Eurasian genus ''Simoedosaurus'' in North America. However, at the time, these four specimens, although thought to be diagonstic at a genus level, were still unprepared and not assigned to a species. They were subsequently stored in the collection of the Princet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmodraco Ornamentation
''Kosmodraco'' is a genus of large bodied choristodere from the Paleocene of North America. Originally described as a species of ''Simoedosaurus'', it was found to represent a distinct genus in 2022. Multiple fossil skulls show a relatively short and robust snout and a skull that is considerably wider behind the eyes. Two species are currently recognized, ''K. dakotensis'' and ''K. magnicornis''. History and naming The first specimen now known to belong to ''Kosmodraco'' was discovered in 1964 and 1968 in the Polecat Bench Formation (Wyoming). These two skulls, alongside others from Montana's Bear Creek, were reported on briefly by Sigogneau-Russell and Donald in 1978, who regarded them as evidence for the presence of the Eurasian genus ''Simoedosaurus'' in North America. However, at the time, these four specimens, although thought to be diagonstic at a genus level, were still unprepared and not assigned to a species. They were subsequently stored in the collection of the Princet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choristodere
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simoedosaurus
''Simoedosaurus'' is an extinct reptile known from the Paleocene of North America, Europe and western Asia, and a member of the Choristodera, a group of aquatic reptiles that lived in the Northern Hemisphere from the Jurassic to the early Cenozoic. Described other species, ''S. dakotensis'' later got its own genus, ''Kosmodraco''. Taxonomy French paleontologist Paul Gervais described ''Simoedosaurus'' in 1877. Though similar to and contemporaneous, ''Simoedosaurus'' is not closely related to the North American ''Champsosaurus'', instead it appears to be most closely related to ''Tchoiria'' and '' Ikechosaurus'' from the Early Cretaceous of Asia. It therefore may represent a species that immigrated into North America from Asia in the wake of the Cretaceous-Tertiary mass extinction event, though the absence of choristoderes in the Late Cretaceous of Asia makes this merely a paleogeographical speculation. Biology ''Simoedosaurus'' was an aquatic predator, specialised to a fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coeruleodraco
''Coeruleodraco'' is an extinct genus of choristoderan known from the Late Jurassic ( Oxfordian) Tiaojishan Formation in China. ''Coeruleodraco'' is significant as the most complete Jurassic choristodere taxon, as the only other named Jurassic choristodere ''Cteniogenys'' is based on fragmentary remains. Although similar to ''Philydrosaurus'' in its proportions and postcranial characters, it is distinct in retaining several apparently plesiomorphic characters, including a short snout, paired external nares and an open lower temporal fenestra. Description The skeleton was small, about 20.3 cm (8.0 inches) in length, not including the tail. The tail is incomplete, but including its estimated length, the total length of the skeleton would have been closer to 40.0 cm (15.7 inches). ''Coeruleodraco'' had a generalized, lizard-like body type. This is similar to some early choristoderes (like ''Cteniogenys'', ''Philydrosaurus'', and ''Monjurosuchus''), but contrasts with other choris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bones
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure of the frontal bone The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, and ends in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parietal Bones
The parietal bones () are two bones in the skull which, when joined at a fibrous joint, form the sides and roof of the cranium. In humans, each bone is roughly quadrilateral in form, and has two surfaces, four borders, and four angles. It is named from the Latin ''paries'' (''-ietis''), wall. Surfaces External The external surface ig. 1is convex, smooth, and marked near the center by an eminence, the parietal eminence (''tuber parietale''), which indicates the point where ossification commenced. Crossing the middle of the bone in an arched direction are two curved lines, the superior and inferior temporal lines; the former gives attachment to the temporal fascia, and the latter indicates the upper limit of the muscular origin of the temporal muscle. Above these lines the bone is covered by a tough layer of fibrous tissue – the epicranial aponeurosis; below them it forms part of the temporal fossa, and affords attachment to the temporal muscle. At the back part and close to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal Bones
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate and pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the quadrate and articular bones of the skull articulate to form the jaw joint. The squamosal bone lies anterior to the quadrate bone. Anatomy in synapsids Non-mammalian synapsids In non-mammalian synapsids, the jaw is composed of four bony elements and referred to as a quadro-articular jaw because the joint is between the articular an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monjurosuchus
''Monjurosuchus'' is a genus of choristoderan reptile that lived in what is now China and Japan during the Early Cretaceous. It has large eyes, a rounded skull, robust legs with short claws, and a long, thin tail. Fossils have been found that preserve soft tissue, showing that it had soft skin and webbed feet. Description and history ''Monjurosuchus'' was first found in China as part of the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota. Named in 1940, the type species ''M. splendens'' was the first reptile described from the Yixian Formation. The holotype specimen was lost during World War II but was replaced in 2000 by a recently discovered neotype preserving soft tissue. In 2007, remains were described from the Okurodani Formation of the Tetori Group of Japan. The Japanese material represents a different species of ''Monjurosuchus'' that has not yet been named. ''Monjurosuchus'' was a small choristodere, reaching a length of 40 cm with a 5 cm skull. Unlike related choristoderes, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Bone
In anatomy, the palatine bones () are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxillae, they comprise the hard palate. (''Palate'' is derived from the Latin ''palatum''.) Structure The palatine bones are situated at the back of the nasal cavity between the maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. They contribute to the walls of three cavities: the floor and lateral walls of the nasal cavity, the roof of the mouth, and the floor of the orbits. They help to form the pterygopalatine and pterygoid fossae, and the inferior orbital fissures. Each palatine bone somewhat resembles the letter L, and consists of a horizontal plate, a perpendicular plate, and three projecting processes—the pyramidal process, which is directed backward and lateral from the junction of the two parts, and the orbital and sphenoidal processes, which surmount the vertical part, and are separated by a dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The anterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)