|
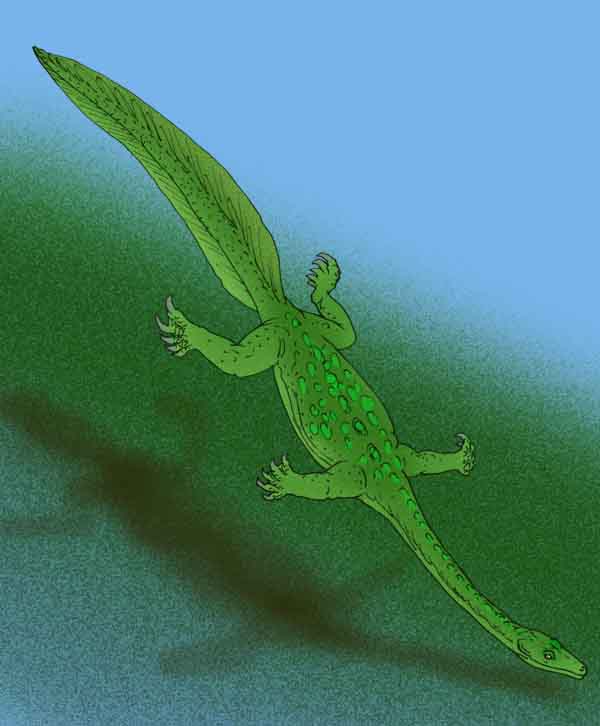
Monjurosuchus
''Monjurosuchus'' is a genus of choristoderan reptile that lived in what is now China and Japan during the Early Cretaceous. It has large eyes, a rounded skull, robust legs with short claws, and a long, thin tail. Fossils have been found that preserve soft tissue, showing that it had soft skin and webbed feet. Description and history ''Monjurosuchus'' was first found in China as part of the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota. Named in 1940, the type species ''M. splendens'' was the first reptile described from the Yixian Formation. The holotype specimen was lost during World War II but was replaced in 2000 by a recently discovered neotype preserving soft tissue. In 2007, remains were described from the Okurodani Formation of the Tetori Group of Japan. The Japanese material represents a different species of ''Monjurosuchus'' that has not yet been named. ''Monjurosuchus'' was a small choristodere, reaching a length of 40 cm with a 5 cm skull. Unlike related choristoderes, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monjurosuchus
''Monjurosuchus'' is a genus of choristoderan reptile that lived in what is now China and Japan during the Early Cretaceous. It has large eyes, a rounded skull, robust legs with short claws, and a long, thin tail. Fossils have been found that preserve soft tissue, showing that it had soft skin and webbed feet. Description and history ''Monjurosuchus'' was first found in China as part of the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota. Named in 1940, the type species ''M. splendens'' was the first reptile described from the Yixian Formation. The holotype specimen was lost during World War II but was replaced in 2000 by a recently discovered neotype preserving soft tissue. In 2007, remains were described from the Okurodani Formation of the Tetori Group of Japan. The Japanese material represents a different species of ''Monjurosuchus'' that has not yet been named. ''Monjurosuchus'' was a small choristodere, reaching a length of 40 cm with a 5 cm skull. Unlike related choristoderes, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
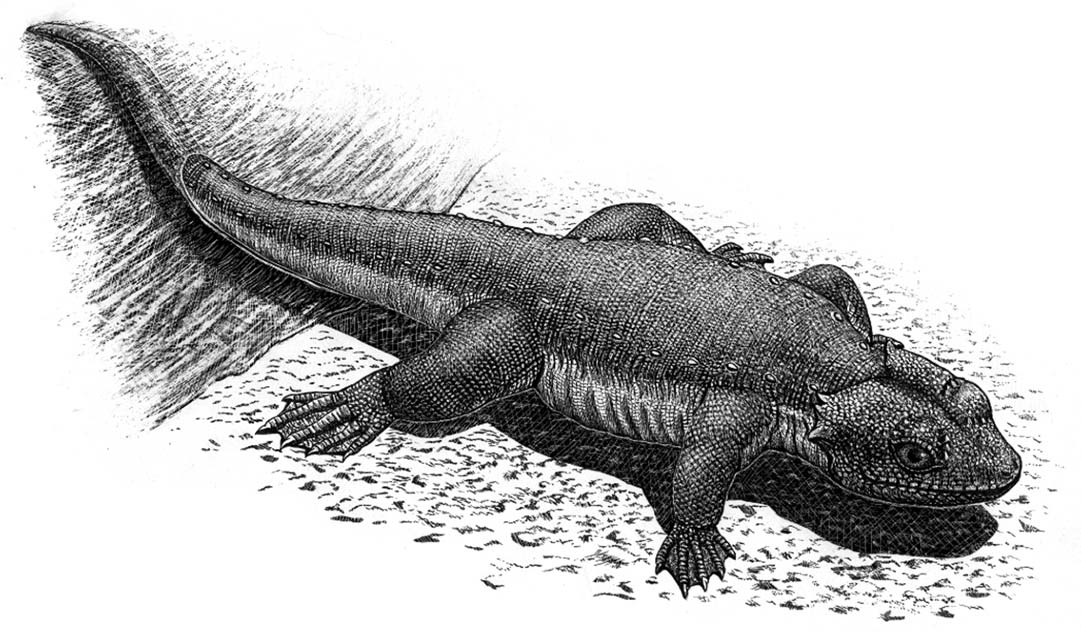
Monjurosuchus Splendens 2
''Monjurosuchus'' is a genus of choristoderan reptile that lived in what is now China and Japan during the Early Cretaceous. It has large eyes, a rounded skull, robust legs with short claws, and a long, thin tail. Fossils have been found that preserve soft tissue, showing that it had soft skin and webbed feet. Description and history ''Monjurosuchus'' was first found in China as part of the Early Cretaceous Jehol Biota. Named in 1940, the type species ''M. splendens'' was the first reptile described from the Yixian Formation. The holotype specimen was lost during World War II but was replaced in 2000 by a recently discovered neotype preserving soft tissue. In 2007, remains were described from the Okurodani Formation of the Tetori Group of Japan. The Japanese material represents a different species of ''Monjurosuchus'' that has not yet been named. ''Monjurosuchus'' was a small choristodere, reaching a length of 40 cm with a 5 cm skull. Unlike related choristoderes, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monjurosuchidae
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choristoderan
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the late Miocene (168 to 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as ''Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of Discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain ''Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper. A year later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jehol Biota
The Jehol Biota includes all the living organisms – the ecosystem – of northeastern China between 133 and 120 million years ago. This is the Lower Cretaceous ecosystem which left fossils in the Yixian Formation and Jiufotang Formation. These deposits are composed of layers of tephra and sediment. It is also believed to have left fossils in the Sinuiju series of North Korea.Li, Quanguo, Gao, Ke-qin (2007). "Lower Cretaceous vertebrate fauna from the Sinuiju basin, North Korea as evidence of geographic extension of the Jehol Biota into the Korean Peninsula". ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'' 27, supplement to number (3). pp.106A. The ecosystem in the Lower Cretaceous was dominated by wetlands and numerous lakes (not rivers, deltas, or marine habitats). Rainfall was seasonal, alternating between semiarid and Mesic habitat, mesic conditions. The climate was temperate. The Jehol ecosystem was interrupted periodically by ash eruptions from volcanoes to the west. The word "Jehol" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okurodani Formation
The Okurodani Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic Formation (geology), formation in central Honshu, Japan. Part of the Tetori Group, it primarily consists of freshwater continental sediments deposited in a floodplain environment, with occasional volcanic tuffite horizons. It has an uncertain age, probably dating between the Hauterivian and Aptian. An indeterminate Iguanodontia, iguanodontian dinosaur tooth has been recovered from the formation. Many other fossil vertebrates are known from the KO2 locality Vertebrate Paleobiota Amphibians Squamates Turtles Choristoderes See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils Footnotes References * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. 861 pp. . {{coord missing, Japan Lower Cretaceous Series of Asia Hauterivian Stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Fenestra
An infratemporal fenestra, also called the lateral temporal fenestra or simply temporal fenestra, is an opening in the skull behind the orbit in some animals. It is ventrally bordered by a zygomatic arch. An opening in front of the eye sockets, conversely, is called an antorbital fenestra. Both of these openings reduce the weight of the skull. Infratemporal fenestrae are commonly (although not universally) seen in the fossilized skulls of dinosaurs. Synapsids, including mammals, have one temporal fenestra, while sauropsids Sauropsida ("lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the class Reptilia. Sauropsida is the sister taxon to Synapsida, the other clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early sy ..., the birds and reptiles, have two. References {{ref list Dinosaur anatomy Foramina of the skull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The group first appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are sometimes placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals are extant: 9,159 birds, and 7,925 snakes, lizards, tuatara, turtles, and crocodiles. Characteristics The name Diapsida means "two arches", and diapsids are tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians. Anatomy and function In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ... bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies Anatomical terms of location, ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the Postorbital bone, postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate bone, quadrate and Pterygoid bone, pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the Quadrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Crocodile Lizard
The Chinese crocodile lizard (''Shinisaurus crocodilurus'') is a semiaquatic anguimorph lizard found only in cool forests in southeast China and northeast Vietnam. The Chinese crocodile lizard spends much of its time in shallow water or in overhanging branches and vegetation, where it hunts its prey of insects, snails, tadpoles, and worms. Individuals in captivity may be fed baby mice.Chinese Crocodile Lizard (''Shinisaurus crocodilurus''). The Sacramento Zoological Society. A rare and little-studied lizard, it is listed in Appendix I, which regulates international trade of specimens. This is the only species in the |
Scute
A scute or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of birds. The term is also used to describe the anterior portion of the mesonotum in insects as well as some arachnids (e.g., the family Ixodidae, the scale ticks). Properties Scutes are similar to scales and serve the same function. Unlike the scales of lizards and snakes, which are formed from the epidermis, scutes are formed in the lower vascular layer of the skin and the epidermal element is only the top surface . Forming in the living dermis, the scutes produce a horny outer layer that is superficially similar to that of scales. Scutes will usually not overlap as snake scales (but see the pangolin). The outer keratin layer is shed piecemeal, and not in one continuous layer of skin as seen in snakes or lizards. The dermal base may contain bone and produce dermal armour. Scutes with a bony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastralia
Gastralia (singular gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these reptiles, gastralia provide support for the abdomen and attachment sites for abdominal muscles. The possession of gastralia may be ancestral for Tetrapoda and were possibly derived from the ventral scales found in animals like rhipidistians, labyrinthodonts, and ''Acanthostega'', and may be related to ventral elements of turtle plastrons. Similar, but not homologous cartilagenous elements, are found in the ventral body walls of lizards and anurans. These structures have been referred to as inscriptional ribs, based on their alleged association with the inscriptiones tendinae (the tendons that form the six pack in humans). However, the terminology for these gastral-like structures remains confused. Both types, along with sternal ribs ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_NMNS.jpg)