|
Frontal Bones
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.''Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure of the frontal bone The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, and ends in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
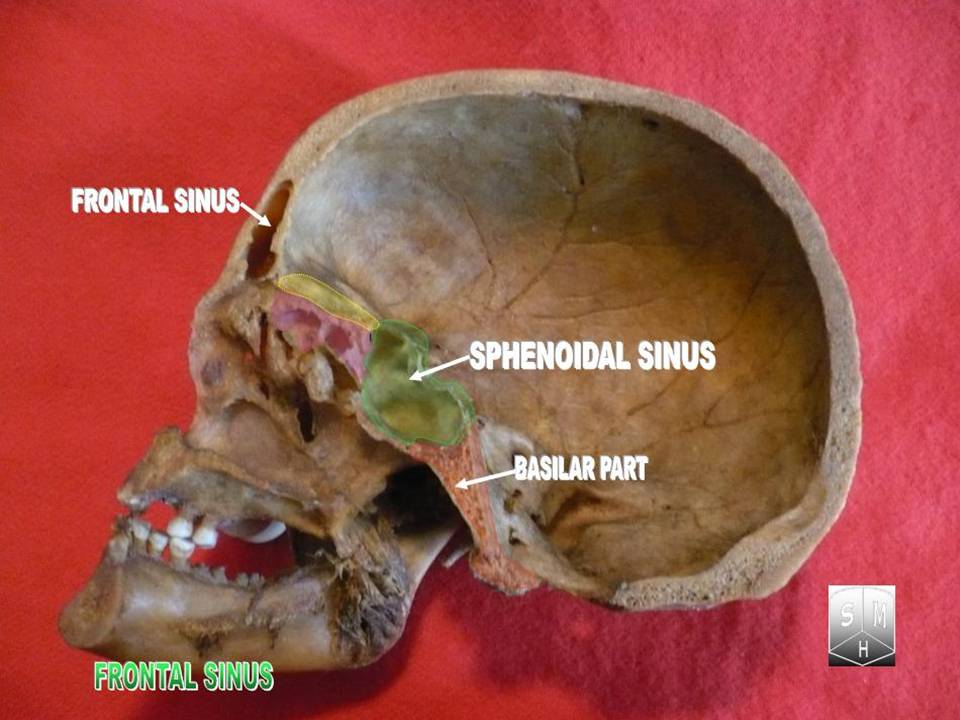
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal conchae are situated at the anterior and inferior part of the body. Intrinsic ligaments of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetrapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish boys and girls. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, girls begin puberty at ages 10–11 and complete puberty at ages 15–17; boys generally begin puberty at ages 11–12 and complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Sinuses
The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle nasal meatus of the nose through the frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of the ethmoid. These structures then open into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus. Structure Each frontal sinus is situated between the external and internal plates of the frontal bone.Frontal sinuses are rarely symmetrical. Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. Blood supply The mucous membrane of the frontal sinuses receives arterial supply via the supraorbital artery, and anterior ethmoidal artery. Innervation The mucous membrane in this sinus is innervated by the supraorbital nerve, which contains the postganglionic parasympathetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramembranous Ossification
Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created. Intramembranous ossification is also an essential process during the natural healing of bone fractures and the rudimentary formation of bones of the head. Unlike endochondral ossification, which is the other process by which bone tissue is created during fetal development, cartilage is not present during intramembranous ossification. Formation of woven bone Mesenchymal stem cells within mesenchyme or the medullary cavity of a bone fracture initiate the process of intramembranous ossification. A mesenchymal stem cell, or MSC, is an unspecialized cell that can develop into an osteoblast. Before it begins to develop, the morphological characteristics of a MSC are: A small cell body with a few cell processes that are long and thin; a large, round nucleus with a prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Suture
The frontal suture is a fibrous joint that divides the two halves of the frontal bone of the skull in infants and children. Typically, it completely fuses between three and nine months of age, with the two halves of the frontal bone being fused together. It is also called the metopic suture, although this term may also refer specifically to a ''persistent frontal suture''. If the suture is not present at birth because both frontal bones have fused ( craniosynostosis), it will cause a keel-shaped deformity of the skull called trigonocephaly. Its presence in a fetal skull, along with other cranial sutures and fontanelles, provides a malleability to the skull that can facilitate movement of the head through the cervical canal and vagina during delivery. The dense connective tissue found between the frontal bones is replaced with bone tissue as the child grows older. Persistent frontal suture In some individuals, the suture can persist (totally or partly) into adulthood, and is ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squama Frontalis
The squamous part of the frontal bone is the superior (approximately two thirds) portion when viewed in standard anatomical orientation. There are two surfaces of the squamous part of the frontal bone: the external surface, and the internal surface. External surface The external surface is convex and usually exhibits, in the lower part of the middle line, the remains of the frontal suture; in infancy this suture divides the frontal bone into two and later fuses. A condition where fusion has not taken place, may persist throughout life and is referred to as a ''metopic suture''. On either side of this suture, about 3 cm. above the supraorbital margin, is a rounded elevation, the frontal eminence (tuber frontale). These eminences vary in size in different individuals, are occasionally unsymmetrical, and are especially prominent in young skulls; the surface of the bone above them is smooth, and covered by the galea aponeurotica. Below the frontal eminences, and separated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Margin
The brow ridge, or supraorbital ridge known as superciliary arch in medicine, is a bony ridge located above the eye sockets of all primates. In humans, the eyebrows are located on their lower margin. Structure The brow ridge is a nodule or crest of bone situated on the frontal bone of the skull. It forms the separation between the forehead portion itself (the squama frontalis) and the roof of the eye sockets (the pars orbitalis). Normally, in humans, the ridges arch over each eye, offering mechanical protection. In other primates, the ridge is usually continuous and often straight rather than arched. The ridges are separated from the frontal eminences by a shallow groove. The ridges are most prominent medially, and are joined to one another by a smooth elevation named the glabella. Typically, the arches are more prominent in men than in women, and vary between different ethnic groups. Behind the ridges, deeper in the bone, are the frontal sinuses. Terminology The brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilization (or eleventh week gestational age) and continues until birth. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their final anatomical location. Etymology The word ''fetus'' (plural ''fetuses'' or '' feti'') is related to the Latin '' fētus'' ("offspring", "bringing forth", "hatching of young") and the Greek "φυτώ" to plant. The word "fetus" was used by Ovid in Metamorphoses, book 1, line 104. The predominant British, Irish, and Commonwealth spelling is ''fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by Cell (biology), cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor. In fracture healing, endochondral osteogenesis is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long Bone, bones treated by plaster of Paris, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation with metal plates, screws, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis. Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification is often confused with ossification. Calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulation (journal)
''Circulation'' is a scientific journal published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins for the American Heart Association. The journal publishes articles related to research in and the practice of cardiovascular diseases, including observational studies, clinical trials, epidemiology, health services and outcomes studies, and advances in applied (translational) and basic research. Its 2020 impact factor is 29.690, ranking it third among journals in the Cardiac and Cardiovascular Systems category and first in the Peripheral Vascular Disease category.2020 Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics, 2021) Articles become open access after a 12-month embargo period. 2008 saw the appearance of six subspecialty journals. The first edition of ''Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology'' appeared in April 2008, followed by an edition dedicated to heart failure in May titled ''Circulation: Heart Failure''. The remaining four journals launched once per month from July through October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Crest Cell
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. After gastrulation, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the neural plate and the non-neural ectoderm. During neurulation, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the neural folds, converge at the dorsal midline to form the neural tube. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition, delaminating from the neuroepithelium and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in vertebrate evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate clade. Underlying the development of neural crest is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)