|
Khön Könchok Gyalpo
Khön Könchok Gyalpo (, 1034-1102) was the founder of the Sakya School of Tibetan Buddhism, and the founder of Sakya Monastery. Khön Könchok Gyalpo was born in Sa'gya, Tsang. He was a member of the Khön family, and his ancestry can be traced back to Khön Dorje Rinpoche, student of Padmasambhava. He followed his father and brother and learned doctrines of the Nyingma School at a young age, but studied newly translated Vajrayāna texts with Drogmi Shakya Yeshe later. Khön Könchok Gyalpo established Sakya Monastery in 1073, where the Sakya Tradition first developed. His son Khön Kunga Nyingpo was regarded as the first leader of Sakya, and Khön Könchok Gyalpo is known as the first Sakya Trizin Sakya Trizin ( "Sakya Throne-Holder") is the traditional title of the head of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism.''Holy Biographies of the Great Founders of the Glorious Sakya Order'', translated by Venerable Lama Kalsang Gyaltsen, Ani Kunga C .... References * Ngawang Gon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist School)
The ''Sakya'' (, 'pale earth') school is one of four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism, the others being the Nyingma, Kagyu, and Gelug. It is one of the Red Hat Orders along with the Nyingma and Kagyu. Origins Virūpa, 16th century. It depicts a famous episode in his hagiography when he stopped the sun in the sky. The name ''Sakya'' ("pale earth") derives from the unique grey landscape of the Ponpori Hills in southern Tibet near Shigatse, where Sakya Monastery, the first monastery of this tradition, and the seat of the Sakya School was built by Khon Konchog Gyalpo (1034–1102) in 1073. The Sakya tradition developed during the second period of translation of Buddhist scripture from Sanskrit into Tibetan in the late 11th century. It was founded by Drogmi, a famous scholar and translator who had studied at the Vikramashila directly under Naropa, Ratnākaraśānti, Vagishvakirti and other great panditas from India for twelve years. Khon Konchog Gyalpo became Drogmi's disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakya Monastery
Sakya Monastery (), also known as Pel Sakya (; "White Earth" or "Pale Earth") is a Buddhist monastery situated in Sa'gya Town (ས་སྐྱ་), Sa'gya County, about 127 km west of Shigatse in the Tibet Autonomous Region. History As the seat of the Sakya (or Sakyapa) school of Tibetan Buddhism, it was founded in 1073, by Khön Könchok Gyalpo (; 1034–1102), originally a Nyingmapa monk of the powerful noble family of the Tsang, who became the first Sakya Trizin. The "southern monastery" was founded under the orders of Drogön Chögyal Phagpa in 1268, across a river from the earlier structures. 130,000 workers were reportedly drafted for its construction. Its powerful abbots governed Tibet during the 13th and the 14th centuries under the overlordship of the Mongol Yuan dynasty after the downfall of the Tibetan Empire, until they were eclipsed by the rise of the new Kagyu and Gelug schools of Tibetan Buddhism. Most of the southern monastery was burned down in the 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sa'gya
Sa'gya County (; ) is a county under the prefecture-level city of Xigazê in the Tibet Autonomous Region. The county is named after Sakya Monastery, home of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. Towns and townships * Sa'gya Town (, ) * Gêding Town (, ) * Xungmai Township (, ) * Maja Township Maja can refer to: Places * Maja, Croatia, a village * Maja, Banten, a subdistrict in Lebak Regency, Banten, Indonesia ** Maja railway station * Maja, West Java, a subdistrict in Majalengka Regency, West Java, Indonesia * Maja River, a tributar ... (, ) * Zhungma Township (, ) * Tashigang Township (, ) * Chagjug Township (, ) * Së Township (, ) * Lalho Township (, ) * Drag'rong Township (, ) * Molha Township (, ) Counties of Tibet Shigatse {{Shigatse-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
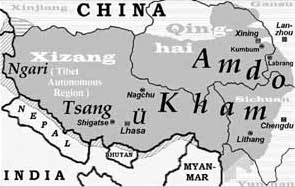
Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered the south-central of the Tibetan cultural area, including the Brahmaputra River watershed. The western districts surrounding and extending past Mount Kailash are included in Ngari, and much of the vast Changtang plateau to the north. The Himalayas defined Ü-Tsang's southern border. The present Tibet Autonomous Region corresponds approximately to what was ancient Ü-Tsang and western Kham. Ü-Tsang was formed by the merging of two earlier power centers: Ü () in central Tibet, controlled by the Gelug lineage of Tibetan Buddhism under the early Dalai Lamas, and Tsang () which extended from Gyantse to points west, controlled by the rival Sakya lineage. Military victories by the powerful Khoshut Mongol Güshi Khan that backed 5th Dalai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
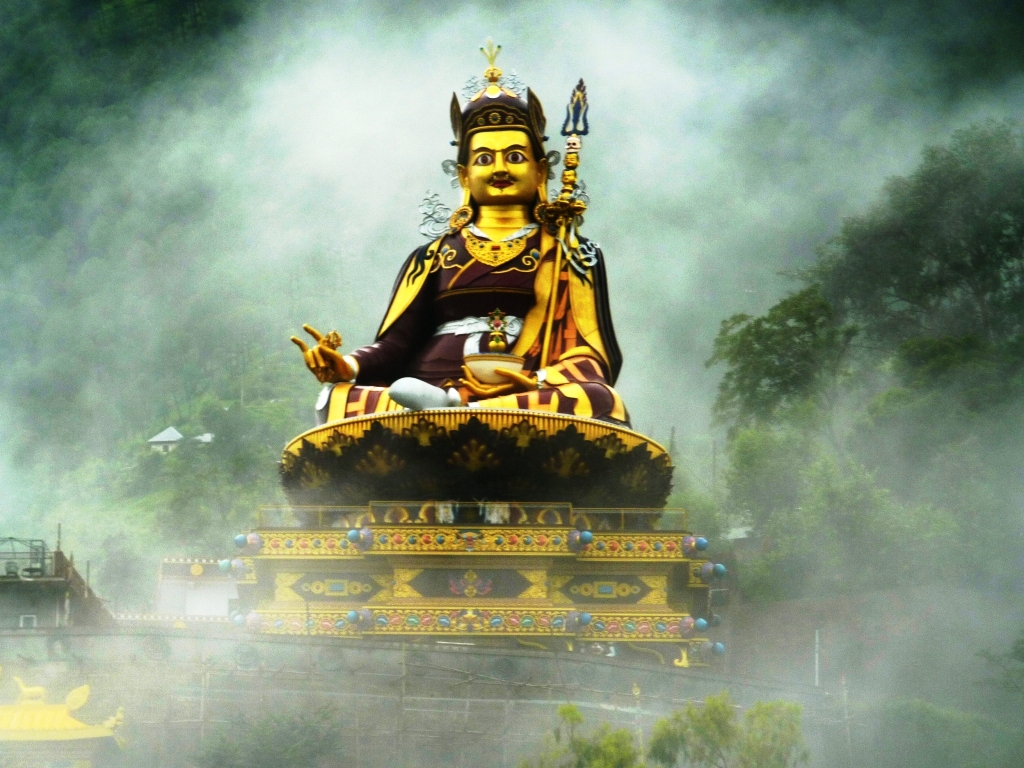
Padmasambhava
Padmasambhava ("Born from a Lotus"), also known as Guru Rinpoche (Precious Guru) and the Lotus from Oḍḍiyāna, was a tantric Buddhist Vajra master from India who may have taught Vajrayana in Tibet (circa 8th – 9th centuries)... According to some early Tibetan sources like the ''Testament of Ba'', he came to Tibet in the 8th century and helped construct Samye Monastery, the first Buddhist monastery in Tibet. However, little is known about the actual historical figure other than his ties to Vajrayana and Indian Buddhism. Padmasambhava later came to be viewed as a central figure in the transmission of Buddhism to Tibet. Starting from around the 12th century, hagiographies concerning Padmasambhava were written. These works expanded the profile and activities of Padmasambhava, now seen as taming all the Tibetan spirits and gods, and concealing various secret texts ('' terma'') for future tertöns. Nyangral Nyima Özer (1124–1192) was the author of the ''Zangling-ma'' (Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyingma
Nyingma (literally 'old school') is the oldest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. It is also often referred to as ''Ngangyur'' (, ), "order of the ancient translations". The Nyingma school is founded on the first lineages and translations of Buddhist scriptures from Sanskrit into Tibetan in the eighth century, during the reign of King Trisong Detsen (r. 710–755). Nyingma traditional histories consider their teachings to trace back to the first Buddha Samantabhadra (Güntu Sangpo) and Indian mahasiddhas such as Garab Dorjé, Śrī Siṃha and Jñānasūtra. Traditional sources trace the origin of the Nyingma order in Tibet to figures associated with the initial introduction of Buddhism in the 8th century, such as Padmasambhava, Yeshe Tsogyal, Vimalamitra, Vairotsana, Buddhaguhya and Śāntarakṣita, Shantaraksita. The Nyingma tradition is also seen having been founded at Samye, Samyé, the first monastery in Tibet. Nyingma teachings are also known for having be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drogmi
Drogmi (Drogmi Lotsāwa Śākya Yeshe) (c. 992-1064) transmitted the trantric system "Path and Fruit" (Lamdré) which came to be the central esoteric tradition of the Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist school), Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism. Drogmi was a famous scholar and translator who had studied at the Vikramashila monastery directly under Naropa, Ratnākaraśānti, Vagishvakirti and other great panditas from India for twelve years. He is famous for his beard. References Sakya Buddhists Tibetan Buddhism Monks of Vikramashila {{Buddhism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachen Kunga Nyingpo
Sachen Kunga Nyingpo () (1092–1158) was a Tibetan spiritual leader and the first of the Five Venerable Supreme Sakya Masters of Tibet. Sachen Kunga Nyinpo was the 3rd Sakya Trizin and son of Khon Konchok Gyalpo (1034–1102) who was the first Sakya Trizin and founder of the first Sakya Monastery in Tibet in 1073. Sachen Kunga Nyingpo, the son of Khon Konchok Gyalpo and an emanation of Manjushri, was born in 1092 into the prominent Khon clan of Sakya. From early childhood, Sachen showed great signs of wisdom. At the age of twelve, Sachen, under the guidance of his guru, Bari Lotsava, performed one-point meditation on Manjushri. After meditating on this for a continuous period of six months, the bodhisattva appeared in front of him and gave him the teachings on the parting of four attachments as follows: * If you cling to this life, then you are not a dharma practitioner; * If you cling to the wheel of existence, then you do not possess renunciation (nekkhamma); * If you look ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakya Trizin
Sakya Trizin ( "Sakya Throne-Holder") is the traditional title of the head of the Sakya school of Tibetan Buddhism.''Holy Biographies of the Great Founders of the Glorious Sakya Order'', translated by Venerable Lama Kalsang Gyaltsen, Ani Kunga Chodron and Victoria Huckenpahler. Published by Sakya Phuntsok Ling Publications, Silver Spring MD. June 2000. The Sakya school was founded in 1073CE, when Khön Könchog Gyalpo (; 1034–1102), a member of Tibet's noble Khön family, established a monastery in the region of Sakya, Tibet, which became the headquarters of the Sakya order.''The History of the Sakya Tradition'', by Chogay Trichen. Manchester Free Press, U.K. 1983. Since that time, its leadership has descended within the Khön family. The 41st Sakya Trizin, whose reign spanned more than fifty years, was the longest reigning Sakya Trizin. The current Sakya Trizin is Gyana Vajra Rinpoche, officially known as Kyabgon Gongma Trizin Rinpoche, the 43rd Sakya Trizin Gyana Vajra Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Qingying
Chen Qingying (Chinese 陈庆英, Pinyin Chén Qìngyīng ; born 21 October 1941 in Nanchong, Sichuan, Republic of China (1912–1949) , is a Chinese Tibetologist. He is the director of the History Research Institute under the China Tibetology Research Center (Zhongguo Zangxue yanjiu zhongxin). Education At the age of 17, Chen Qingyin and his parents moved to Qinghai province (northwest China). He began his studies in physics at the Qinghai Nationalities College. After completing his studies, in 1964 he became a teacher of physics in the Haixi Mongolian and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture first at Delingha High School, then at the Teachers' College for Ethnic Minorities. As Qinghai is home to many Tibetans, Chen Qingling, who learned Tibetan at school and did odd jobs in Tibetan areas, took an interest in the history and culture of Tibet. After ten years of teaching, he decided to change from a physics professor to a tibetologist and got a degree in Tibetan from the Central Instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakya Trizins
The ''Sakya'' (, 'pale earth') school is one of four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism, the others being the Nyingma, Kagyu, and Gelug. It is one of the Red Hat Orders along with the Nyingma and Kagyu. Origins Virūpa, 16th century. It depicts a famous episode in his hagiography when he stopped the sun in the sky. The name ''Sakya'' ("pale earth") derives from the unique grey landscape of the Ponpori Hills in southern Tibet near Shigatse, where Sakya Monastery, the first monastery of this tradition, and the seat of the Sakya School was built by Khon Konchog Gyalpo (1034–1102) in 1073. The Sakya tradition developed during the second period of translation of Buddhist scripture from Sanskrit into Tibetan in the late 11th century. It was founded by Drogmi, a famous scholar and translator who had studied at the Vikramashila directly under Naropa, Ratnākaraśānti, Vagishvakirti and other great panditas from India for twelve years. Khon Konchog Gyalpo became Drogmi's disciple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)