|
Khawla Al-Hanafiyya
Khawla bint Jaʿfar al-Ḥanafīyya ( ar, خولة بنت جعفر الحنفية), also known as Umm Muḥammad ( ar, أُمّ مُحَمَّد, link=no), was one of the wives of the Muslim Caliph and Imam Ali ibn Abi Talib. Biography She was known as Hanafiyya after her tribe Banu Hanifa. When the people of Yamama were threatening the integrity of the newly emerging empire by refusing to pay the zakat (religious tax) to Abu Bakr, their men were all declared apostates and killed and she was brought to Medina as a slave girl together with the other womenfolk. When her tribesmen came to know her, they approached Ali and requested him to save her from the blemish of slavery and protect her family's honor and prestige. Consequently, Ali set her free after purchasing her and married her whereafter Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya was born. Her important descendants See also *Khawlah *Jaʽfar Jafar ( ar, جَعْفَر), meaning in Arabic "small stream/rivulet/creek", is a masculin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Yamama
Al-Yamama ( ar, اليَمامَة, al-Yamāma) is a historical region in the southeastern Najd in modern-day Saudi Arabia, or sometimes more specifically, the now-extinct ancient village of Jaww al-Yamamah, near al-Kharj, after which the rest of the region was named. Only a handful of centralized states ever arose in the Yamama, but it figured prominently in early Islamic history, becoming a central theater in the Ridda wars immediately following Muhammad's death. Despite being incorporated into the Najd region, the term 'al-Yamama' remains in use as a traditional and historical term to reference or emphasize the region's ancient past. The current headquarters of the Saudi government in Riyadh, for example, is known as the Palace of Yamamah. Etymology The 13th-century geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi mentions a number of etymologies for ''al-Yamama'', including the root word ''hamam'' (Arabic for 'domesticated pigeon) but the historian G. Rex Smith considers them unlikely. Inste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
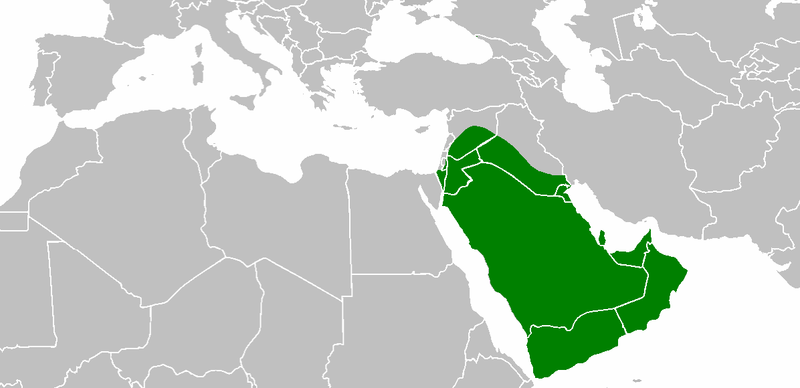
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At , the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Yemen, as well as the southern portions of Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the classical era, the southern portions of modern-day Syria, Jordan, and the Sinai Peninsula were also considered parts of Arabia (see Arabia Petraea). The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and southwest, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the northeast, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the Medina Province of Saudi Arabia. , the estimated population of the city is 1,488,782, making it the fourth-most populous city in the country. Located at the core of the Medina Province in the western reaches of the country, the city is distributed over , of which constitutes the city's urban area, while the rest is occupied by the Hejaz Mountains, empty valleys, agricultural spaces and older dormant volcanoes. Medina is generally considered to be the "cradle of Islamic culture and civilization". The city is considered to be the second-holiest of three key cities in Islamic tradition, with Mecca and Jerusalem serving as the holiest and third-holiest cities respectively. ''Al-Masjid al-Nabawi'' () is of exceptional importance in Islam a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Province" in Saudi Arabia.Mackey, p. 101. "The Western Province, or the Hejaz .. It is bordered in the west by the Red Sea, in the north by Jordan, in the east by the Najd, and in the south by the 'Asir Region. Its largest city is Jeddah (the second largest city in Saudi Arabia), with Mecca and Medina being the fourth and fifth largest cities respectively in the country. The Hejaz is the most cosmopolitan region in the Arabian Peninsula. The Hejaz is significant for being the location of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina, the first and second holiest sites in Islam, respectively. As the site of the two holiest sites in Islam, the Hejaz has significance in the Arab and Islamic historical and political landscape. The region of Hejaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Baqi Cemetery
''Jannat al-Baqīʿ'' ( ar, ٱلْبَقِيْع, "The Baqi'") is the oldest and the first Islamic cemetery of Medina in the Hejazi region of present-day Saudi Arabia. It is located to the southeast of the Prophet's Mosque, which contains the graves of some of the Islamic prophet Muhammad's family and friends. It is also known as ''Baqīʿ al-Gharqad'' ( ar, بَقِيْع الْغَرْقَد, meaning "Baqiʿ of the Boxthorn"). The grounds hold much significance for Muslims, being the resting place of many of Muhammad's relatives and companions, thus marking it as one of the two holiest cemeteries in Islamic tradition. Many narrations relate Muhammad issuing a prayer every time he passed it. History When Muhammad arrived at Medina from Mecca in September 622 Common Era, CE, al-Baqi' was a land covered with ''Lycium shawii'' boxthorn trees. According to historical records, after the arrival of Muhammad, the houses of Medina developed near al-Baqi', which was therefore considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Al-Hanafiyya
Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib () also known as Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥanafīyya () (15 AH – 81 AH; AD 637 – 700) and surnamed Abū al-Qāsim. He was the third son of Ali ibn Abi Talib (the fourth rightly-guided caliph and the first Shia Imam). Biography Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya (Muhammad al-Akbar) was born in Medina about AD 633 (though also said to be during Umar's era), the third of Ali's sons. He was called Ibn al-Hanafiyya after his mother, Khawla bint Ja'far; she was known as Hanafiyya, "the Hanafi woman", after her tribe Banu Hanifa. After the death of Muhammad, the people of Yamama were declared apostates by the Muslims for refusing to pay the zakat (religious tax); the men were killed (see Ridda Wars), and the women were taken to Medina as slaves, Khawla bint Ja'far among them. When her tribesmen found out, they approached Ali and asked him to save her from slavery and to protect her family's honor and prestige. Consequently, Ali ibn Abi Talib purcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Hanifa
Banu Hanifa ( ar, بنو حنيفة) is an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belongs to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdul Qays, Taghlib, al-Nammir ibn Qasit, and Anazzah. Though counted by the classical Arab genealogists as a Christian branch of Bani Bakr, they led an independent existence prior to Islam.Muhammad Zafrulla Khan, ''Muhammad, Seal of the Prophets'', Routledge, 1980, Google Print, p. 247 The ruling House of Saud of Saudi Arabia belongs to it. Pre-Islamic Era The tribe's members appear to have been mostly sedentary farmers at the dawn of Islam, living in small settlements along the '' wadis'' of eastern Nejd (known back then as al-Yamama), particularly the valley of Al-'Irdh, which later came to bear their name (see Wadi Hanifa). Sources such as Yaqut's 13th century encyclopedia credit them with the founding of the towns of Hadjr (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zakat
Zakat ( ar, زكاة; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is next after prayer ('' salat'') in importance. As one of the Five Pillars of Islam, zakat is a religious duty for all Muslims who meet the necessary criteria of wealth to help the needy. It is a mandatory charitable contribution, often considered to be a tax.Muḥammad ibn al-Ḥasan Ṭūsī (2010), ''Concise Description of Islamic Law and Legal Opinions'', , pp. 131–135. The payment and disputes on zakat have played a major role in the history of Islam, notably during the Ridda wars. Zakat on wealth is based on the value of all of one's possessions. It is customarily 2.5% (or ) of a Muslim's total savings and wealth above a minimum amount known as ''nisab'' each lunar year, but Islamic scholars differ on how much ''nisab'' is and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr Abdallah ibn Uthman Abi Quhafa (; – 23 August 634) was the senior companion and was, through his daughter Aisha, a father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, as well as the first caliph of Islam. He is known with the honorific title al-Siddiq by Sunni Muslims. Abu Bakr became one of the first converts to Islam and extensively contributed his wealth in support of Muhammad's work. He was among Muhammad's closest companions, accompanying him on his migration to Medina and being present at a number of his military conflicts, such as the battles of Badr and Uhud. Following Muhammad's death in 632, Abu Bakr succeeded the leadership of the Muslim community as the first Rashidun Caliph. During his reign, he overcame a number of uprisings, collectively known as the Ridda Wars, as a result of which he was able to consolidate and expand the rule of the Muslim state over the entire Arabian Peninsula. He also commanded the initial incursions into the neighbouring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khawlah
Khawlah or Khawla () is a feminine Arabic given name, meaning "female deer." Notable people named Khawlah or Khawla include: Khawlah *Khawlah bint Ja'far * Khawlah bint Hakim *Khawla bint Tha'labah *Khawlah bint al-Azwar * Zainab Khawla Khawla * Khawla Al Kuraya, Saudi physician and cancer specialist *Khawla al-Qazwini Khawla al-Qazwini is a Kuwaiti novelist. She has published several novels, beginning with ''Divorced from Reality'' in 1986; she has also produced a volume of nonfiction, ''Letters from Our Life'' (1988). She began writing at a time when Kuwaiti ..., Kuwaiti novelist * Khawla Hamdan al-Zahiri (born 1969), Omani short story writer * Khawla Armouti, Jordanian politician and the Minister of Social Development * Khawla Dunia, Syrian writer, researcher and humanitarian aid and relief organizer See also * Arabic name * {{given name Arabic feminine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaʽfar
Jafar ( ar, جَعْفَر), meaning in Arabic "small stream/rivulet/creek", is a masculine Arabic given name, common among Muslims especially Arabs It may also be transliterated Jafar, Jaffar, Jafer, Jaffer, Jafur or, in Egyptian Arabic pronunciation, Gafar. The Turkish spelling of the name is Cafer, the Azerbaijani Cəfər, the Bosniak Džafer and the Albanian Xhafer. Historical persons *Ja'far ibn Abi Talib (died 629), companion of Muhammad, older brother of Ali * Jafar ibn Ali, son of Ali and Umm ul-Banin *Ja'far al-Sadiq (702–765), descendant of Ali, sixth imam of Shia Islam *Ja'far ibn Yahya (767–803), one of the Barmakids, vizier of Caliph Harun al-Rashid * Ja'far al-Mutawakkil (822–861), the tenth Abbasid caliph * Abu Ma'shar Jaʿfar ibn Muhammad al-Balkhi (787–886), Persian scholar * Mir Jafar (1691–1765), military commander who betrayed the Nawab of Bengal Siraj ud-Daulah * Mir Jafar Dasni (died 841), a rebel, who rebelled against Abbasid caliph al- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabi‘un
The tābi‘ūn ( ar, اَلتَّابِعُونَ, also accusative or genitive tābi‘īn , singular ''tābi‘'' ), "followers" or "successors", are the generation of Muslims who followed the companions (''ṣaḥābah'') of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and thus received their teachings secondhand. A ''tābi‘'' knew at least one ''ṣaḥābiyy''. As such, they played an important part in the development of Islamic thought and knowledge, and in the political development of the early caliphate. The next generation of Muslims after the ''tabi‘ūn'' are called the '' tābi‘ al-tabi‘īn'' . The first three generations of Muhammad’s followers make up the '' salaf'' of Islam. Sunni definition Muslims from the Sunni branch of Islam define a ''tābiʻ'' as a Muslim who: # Saw at least one of the companions of Muhammad # Was rightly-guided # One who died in that state. The Khawarij are therefore not referred to as tābiʻūn even though they saw many of Muhammad's compani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)

.jpg)