|
Kazoku
The was the hereditary peerage of the Empire of Japan, which existed between 1869 and 1947. They succeeded the feudal lords () and court nobles (), but were abolished with the 1947 constitution. Kazoku ( 華族) should not be confused with ''"kazoku ( 家族)"'', which is pronounced the same in Japanese, but with a different character reading that means "immediate family" (as in the film ''Kazoku'' above). Origins Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the ancient court nobility of Kyoto, the , regained some of its lost status. Several members of the , such as Iwakura Tomomi and Nakayama Tadayasu, played a crucial role in the overthrow of the Tokugawa shogunate, and the early Meiji government nominated to head all seven of the newly established administrative departments. The Meiji oligarchs, as part of their Westernizing reforms, merged the with the former into an expanded aristocratic class on 25 July 1869, to recognize that the and former were a social class d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazoku (film)
is a 1970 Japanese film directed by Yoji Yamada. Plot The Kazami family live on the island of Iōjima, Nagasaki, where Seiichi Kamazi works in a coal mine. With the coal mine closing, Seiichi decides to move to Hokkaido and become a dairy farmer. The family rides the train between the two islands (a roughly 3,000-mile journey). Along the way, they stop in Fukuyama, where Seiichi's brother Tsutomu lives, Osaka, where they attend Expo '70, and Tokyo. In Tokyo, the family's youngest daughter passes away. Genzō, Seiichi's father, reaches Hokkaido but passes away shortly after. He is buried in a Catholic ceremony. Despite Seiichi's misgivings, Tamiko (his wife) convinces him to stay and forge a new life for themselves. Cast * Chieko Baisho as Tamiko Kazami * Hisashi Igawa as Seiichi Kazami * Chishū Ryū as Genzō Kazami * Gin Maeda * Hiroshi Inuzuka as Comedian * Kiyoshi Atsumi * Shūichi Ikeda Awards 25th Mainichi Film Award *Won: Best Film This is a list of categories of awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Iesato
Prince was the first head of the Tokugawa clan after the overthrow of the Tokugawa bakufu, and a significant figure in Japanese politics and diplomacy during the Meiji, Taishō and early Shōwa period Japan. When Prince Tokugawa travelled to other nations representing Japan during his diplomatic journeys, he usually presented his name being Prince Iyesato Tokugawa. Prince Tokugawa held the influential position of president of Japan's upper house of congress the Diet for 30 years. Tokugawa promoted democratic principles and international goodwill. It was only after his passing in 1940 that Japanese militants were able to push Japan into joining the Axis Powers in WWII. Early life Tokugawa Iesato was born to the Tayasu branch of the Tokugawa clan, under the name Kamenosuke, he became its 16th head on June 19, 1868, following the resignation of the last ''shōgun,'' Tokugawa Yoshinobu. His brothers were Tokugawa Satotaka and Tokugawa Takachiyo, who also held the Tayasu headshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
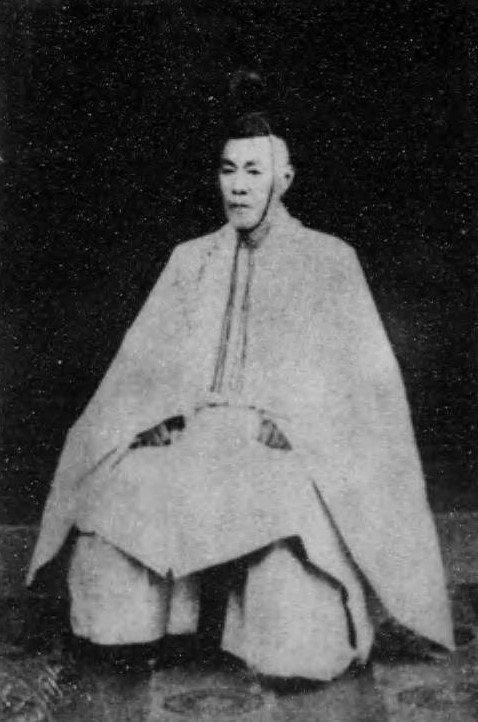
Nakayama Tadayasu
Marquess Nakayama Tadayasu (Japanese 中山 忠能, 17 December 1809 – 12 June 1888) was a Japanese nobleman and courtier of the Edo period and then one of the Kazoku of the post-1867 Empire of Japan. He was the father of Nakayama Yoshiko (1836–1907), mother of the Emperor Meiji, who was born and brought up in Nakayama's household. He had the rare honour of being awarded the Order of the Chrysanthemum while still alive.''The "Japan Gazette" Peerage of Japan'' (Japan Gazette, 1st edition, 1912), p. 57 Early life The second son of Nakayama Tadayori, a member of the Kuge, or court nobility, in 1821, at the age of eleven, Nakayama was named as Provisional Major-General of the Imperial Guard of the Left.Takeda HideakiNakayama Tadayasu (1809–88)at kokugakuin.ac, accessed 24 September 2013 Nakayama married Matsura Aiko (1818–1906), a daughter of Matsura Kiyoshi (1760–1841), ninth ''daimyō'' (feudal ruler) of Hirado and a famous swordsman. Courtier Nakayama received a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itō Hirobumi
was a Japanese politician and statesman who served as the first Prime Minister of Japan. He was also a leading member of the ''genrō'', a group of senior statesmen that dictated Japanese policy during the Meiji era. A London-educated samurai of the Chōshū Domain and a central figure in the Meiji Restoration, Itō Hirobumi chaired the bureau which drafted the Constitution for the newly formed Empire of Japan. Looking to the West for inspiration, Itō rejected the United States Constitution as too liberal and the Spanish Restoration as too despotic. Instead, he drew on British and German models, particularly the Prussian Constitution of 1850. Dissatisfied with Christianity's pervasiveness in European legal precedent, he replaced such religious references with those rooted in the more traditionally Japanese concept of a ''kokutai'' or "national polity" which hence became the constitutional justification for imperial authority. During the 1880s, Itō emerged as the most p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwakura Tomomi
was a Japanese statesman during the Bakumatsu and Meiji period. He was one of the leading figures of the Meiji Restoration, which saw Japan's transition from feudalism to modernity. Born to a noble family, he was adopted by the influential Iwakura family. By 1858 he was an advisor to Emperor Kōmei, but was exiled from the royal court from 1862 to 1867 for his moderation. After release, he became the liaison between the court and the anti-Tokugawa movement. He played a central role in the new Meiji government after 1868. He successfully opposed aggressive policies in Korea in the crisis of 1873, and was nearly assassinated by his enemies. He led the 50-member Iwakura Mission for 18 months in Europe and America, studying modern institutions, technology, and diplomacy. The Mission promoted many key reforms that quickly modernized Japan. He promoted a strong imperial system along Western lines, and played a central role in creating financial institutions for the nation. The 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories. Under the slogans of and following the Boshin War and restoration of power to the Emperor from the Shogun, Japan underwent a period of industrialization and militarization, the Meiji Restoration, which is often regarded as the fastest modernisation of any country to date. All of these aspects contributed to Japan's emergence as a great power and the establishment of a colonial empire following the First Sino-Japanese War, the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War, and World War I. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s, including the Great Depression, led to the rise of militarism, nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks. Peerages include: Australia * Australian peers Belgium * Belgian nobility Canada * British peerage titles granted to Canadian subjects of the Crown * Canadian nobility in the aristocracy of France China * Chinese nobility France * Peerage of France * List of French peerages * Peerage of Jerusalem Japan * Peerage of the Empire of Japan * House of Peers (Japan) Portugal * Chamber of Most Worthy Peers Spain * Chamber of Peers (Spain) * List of dukes in the peerage of Spain * List of viscounts in the peerage of Spain * List of barons in the peerage of Spain * List of lords in the peerage of Spain United Kingdom Great Britain and Ireland * Peerages in the United Kingdom ** Hereditary peer, holders of titles which can be inherited by an heir ** Life peer, members of the peerage of the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Japan
The Constitution of Japan (Shinjitai: , Kyūjitai: , Hepburn: ) is the constitution of Japan and the supreme law in the state. Written primarily by American civilian officials working under the Allied occupation of Japan, the constitution replaced the Meiji Constitution of 1890 when it came into effect on 3 May 1947. The constitution provides for a parliamentary system of government and guarantees certain fundamental rights. In contrast to the Meiji Constitution, which invested the Emperor of Japan with supreme political power, under the new charter the Emperor was reduced to "the symbol of the State and of the unity of the people" and exercises only a ceremonial role acting under the sovereignty of the people. The constitution, also known as the MacArthur Constitution, , or the , was drafted under the supervision of Douglas MacArthur, the Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers, during the Allied occupation of Japan after World War II. Japanese scholars reviewed and modi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, literally "the one who takes the first lace/position), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the '' princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus established the formal position of monarch on the basis of principate, not dominion. He also tasked his grandsons as summer rulers of the city when most of the government were on holiday in the country or attending religious rituals, and, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kuge Families
List of Kuge families include the high level bureaucrats and nobles (''kuge'') in the Japanese Imperial court. This list is based on the lineage of the family (the clan from which the family derives, such as the Fujiwara, Minamoto, or Taira) and the ''kakaku'' (, rank). The ''kuge'' along with the ''daimyō'' made up the nobility (''kazoku'') of post-Meiji Restoration Japan. The ''kazoku'' was abolished shortly after World War II. The ''kakaku'' consists of six ranks, from highest to lowest, they are Sekke (摂家), (清華家), (大臣家), (羽林家), (名家), and (半家). Fujiwara clan Originally, the Fujiwara four families (藤原四家) were branches established by the four sons of Fujiwara no Fuhito: Nanke, Hokke, Shikike, and Kyōke. Brinkley, Frank and Dairoku Kikuchi. (1915). ''A History of the Japanese People from the Earliest Times to the End of the Meiji Era,'' ; excerpt, "Muchimaro's home, being in the south (''nan'') of the capital, was called ''Nan-ke'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
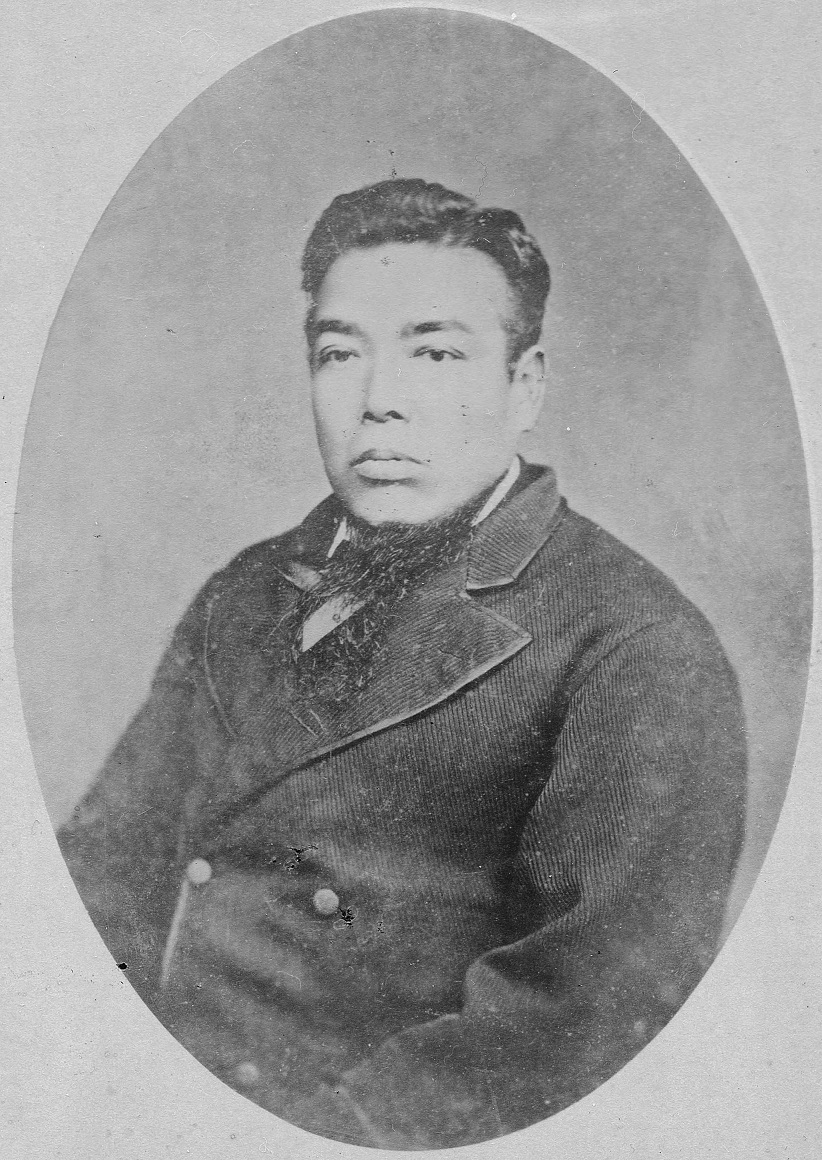
Michitsune Koga 01
was a Japanese samurai of the Satsuma Domain during the Late Tokugawa shogunate. After the Meiji Restoration he served in the Home Ministry as a bureaucrat and viscount. He is also commonly known as Yahei or Yahée (弥兵衞 ''Yahee''). His second daughter Mineko was married to Ōkubo Toshimichi's second son Makino Nobuaki. He had two sons, his first son Yatarō Mishima was an eighth-generation custodian of the Bank of Japan, while his second son Yahiko Mishima was a track and field athlete who competed in the 1912 Summer Olympics. His grandson Michiharu Mishima served as the fourth Chief Scout of the Scout Association of Japan. Ordinance of Yamagata In 1874, Mishima became the Ordinance of Sakata Prefecture. The focus of this new post soon turned to countermeasures aimed at an agrarian-sector demonstration known as the Wappa Rebellion. This was a peasant protest opposed to a failure on the part of the ordinance and government officials, who had come from being lords and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |