|
Nakayama Tadayasu
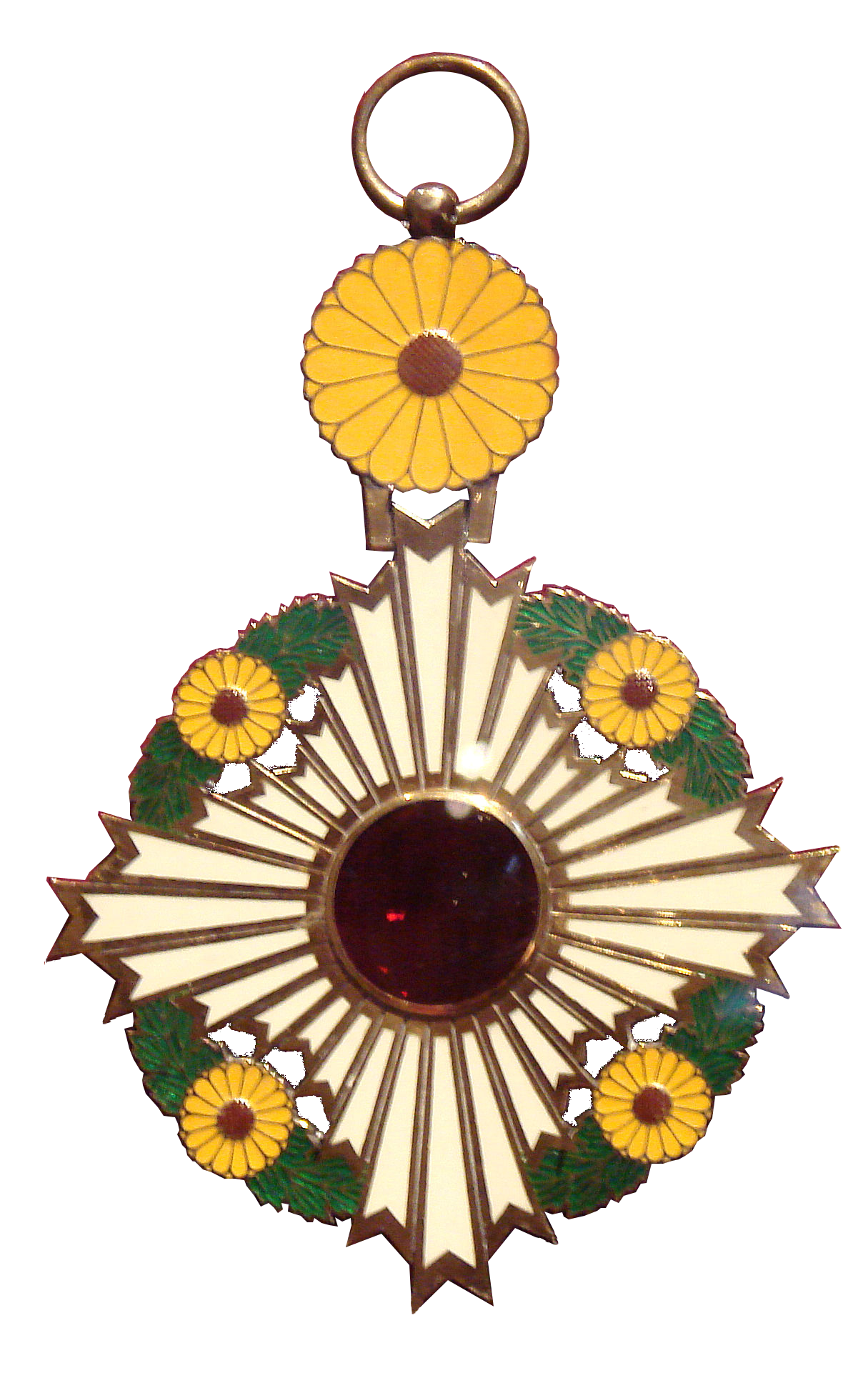
Marquess Nakayama Tadayasu (Japanese 中山 忠能, 17 December 1809 – 12 June 1888) was a Japanese nobleman and courtier of the Edo period and then one of the Kazoku of the post-1867 Empire of Japan. He was the father of Nakayama Yoshiko (1836–1907), mother of the Emperor Meiji, who was born and brought up in Nakayama's household. He had the rare honour of being awarded the Order of the Chrysanthemum while still alive.''The "Japan Gazette" Peerage of Japan'' (Japan Gazette, 1st edition, 1912), p. 57 Early life The second son of Nakayama Tadayori, a member of the Kuge, or court nobility, in 1821, at the age of eleven, Nakayama was named as Provisional Major-General of the Imperial Guard of the Left.Takeda HideakiNakayama Tadayasu (1809–88)at kokugakuin.ac, accessed 24 September 2013 Nakayama married Matsura Aiko (1818–1906), a daughter of Matsura Kiyoshi (1760–1841), ninth ''daimyō'' (feudal ruler) of Hirado and a famous swordsman. Courtier Nakayama received a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakayama Tadayasu
Marquess Nakayama Tadayasu (Japanese 中山 忠能, 17 December 1809 – 12 June 1888) was a Japanese nobleman and courtier of the Edo period and then one of the Kazoku of the post-1867 Empire of Japan. He was the father of Nakayama Yoshiko (1836–1907), mother of the Emperor Meiji, who was born and brought up in Nakayama's household. He had the rare honour of being awarded the Order of the Chrysanthemum while still alive.''The "Japan Gazette" Peerage of Japan'' (Japan Gazette, 1st edition, 1912), p. 57 Early life The second son of Nakayama Tadayori, a member of the Kuge, or court nobility, in 1821, at the age of eleven, Nakayama was named as Provisional Major-General of the Imperial Guard of the Left.Takeda HideakiNakayama Tadayasu (1809–88)at kokugakuin.ac, accessed 24 September 2013 Nakayama married Matsura Aiko (1818–1906), a daughter of Matsura Kiyoshi (1760–1841), ninth ''daimyō'' (feudal ruler) of Hirado and a famous swordsman. Courtier Nakayama received a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yōshū Chikanobu House Of Peers
was a province of Japan, located in Kinai. It overlaps the southern part of modern Kyoto Prefecture on Honshū. Aliases include , the rare , and . It is classified as an upper province in the ''Engishiki''. Yamashiro Province included Kyoto itself, as in 794 AD Yamashiro became the seat of the imperial court, and, during the Muromachi period, was the seat of the Ashikaga shogunate as well. The capital remained in Yamashiro until its de facto move to Tokyo in the 1870s. History "Yamashiro" was formerly written with the characters meaning "mountain" () and "era" (); in the 7th century, there were things built listing the name of the province with the characters for "mountain" and "ridge"/"back" (). On 4 December 794 (8 Shimotsuki, 13th year of Enryaku), at the time of the establishment of Heian-kyō, because Emperor Kanmu made his new capital utilize the surroundings as natural fortification, the character for ''shiro'' was finally changed to "castle" (). Later ''shiro'' from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Kornicki
Peter Francis Kornicki (born 1 May 1950) FBA is an English Japanologist. He is Emeritus Professor of Japanese at Cambridge University and Emeritus Fellow of Robinson College, Cambridge. Kornicki was born at Maidenhead on 1 May 1950, the eldest son of Sq/Ldr Franciszek Kornicki and Patience Ceredwin Kornicka (née Williams). He went to schools in Malta, Aden and Cyprus and was then educated at St George's College, Weybridge. He matriculated at Lincoln College, Oxford, initially to read Classics. He graduated with First Class Honours in Japanese with Korean in 1972. He spent the academic year 1972-3 as a Japanese Ministry of Education foreign student at Tokyo University of Education (now Tsukuba University) and then returned to Oxford and in 1975 received an MSc in Applied Social Studies. He then moved to St Antony's College, Oxford to begin work on a DPhil on Japanese literature of the Meiji period. In 1976 he was awarded a Japan Foundation fellowship for study in Japan and spent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical abilities and consolidated the political system under the Emperor of Japan. The goals of the restored government were expressed by the new emperor in the Charter Oath. The Restoration led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure and spanned both the late Edo period (often called the Bakumatsu) and the beginning of the Meiji era, during which time Japan rapidly Industrialisation, industrialized and adopted Western culture, Western ideas and production methods. Foreign influence The Japanese knew they were behind the Western powers when US Commodore (United States), Commodore Matthew C. Perry came to Japan in 1853 in Black Ships, large warshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto Imperial Palace
The is the former palace of the Emperor of Japan. Since the Meiji Restoration in 1869, the Emperors have resided at the Tokyo Imperial Palace, while the preservation of the Kyoto Imperial Palace was ordered in 1877. Today, the grounds are open to the public, and the Imperial Household Agency hosts public tours of the buildings several times a day. The Kyoto Imperial Palace is the latest of the imperial palaces built at or near its site in the northeastern part of the old capital of Heian-kyō (now known as Kyoto) after the abandonment of the larger original Heian Palace that was located to the west of the current palace during the Heian period. The Palace lost much of its function at the time of the Meiji Restoration, when the capital functions were moved to Tokyo in 1869. However, Emperor Taishō and Shōwa still had their enthronement ceremonies at the palace. Layout The Palace is situated in the , a large rectangular enclosure north to south and east to west. It also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwakura Tomomi
was a Japanese statesman during the Bakumatsu and Meiji period. He was one of the leading figures of the Meiji Restoration, which saw Japan's transition from feudalism to modernity. Born to a noble family, he was adopted by the influential Iwakura family. By 1858 he was an advisor to Emperor Kōmei, but was exiled from the royal court from 1862 to 1867 for his moderation. After release, he became the liaison between the court and the anti-Tokugawa movement. He played a central role in the new Meiji government after 1868. He successfully opposed aggressive policies in Korea in the crisis of 1873, and was nearly assassinated by his enemies. He led the 50-member Iwakura Mission for 18 months in Europe and America, studying modern institutions, technology, and diplomacy. The Mission promoted many key reforms that quickly modernized Japan. He promoted a strong imperial system along Western lines, and played a central role in creating financial institutions for the nation. The 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinmon Incident
The , also known as the , was a rebellion against the Tokugawa shogunate in Japan that took place on August 20 unar calendar: 19th day, 7th month 1864, near the Imperial Palace in Kyoto. History Starting with the Convention of Kanagawa in 1854, within a few years foreign powers forced the shogun dynasty to abandon its isolationist policy ''sakoku''. The rebellion reflected the widespread discontent felt among both pro-imperial/anti-shogunate and anti-foreigner groups, who rebelled under the ''sonnō jōi'' ("revere the emperor, expel the barbarians") slogan. Emperor Kōmei had issued an "Order to expel barbarians". Thus, in March 1863, the '' shishi'' rebels sought to take control of the Emperor to restore the Imperial household to its position of political supremacy. During what was a bloody crushing of the rebellion, the leading Chōshū clan was held responsible for its instigation. To counter the rebels' kidnapping attempt, armies of the Aizu and Satsuma domains (the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakodate
is a city and port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of July 31, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 279,851 with 143,221 households, and a population density of 412.83 persons per km2 (1,069.2 persons per sq. mi.). The total area is . The city is the third biggest in Hokkaido after Sapporo and Asahikawa. History Hakodate was Japan's first city whose port was opened to foreign trade in 1854, as a result of Convention of Kanagawa, and used to be the most important port in northern Japan. Also, the city had been the biggest city in Hokkaido before the Great Hakodate Fire of 1934. Pre-Meiji restoration Hakodate (like much of other parts of Hokkaido), was originally populated by the Ainu. They lived in the Oshima Peninsula. The name "Hakodate" may have originated from an Ainu word, "hak-casi" ("shallow fort"). Another possibility is that it means "box" or "building" in Japanese which refers to the castl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niigata, Niigata
is a city located in the northern part of Niigata Prefecture (). It is the capital and the most populous Cities of Japan, city of Niigata Prefecture, and one of the cities designated by government ordinance of Japan, located in the Chūbu region of Japan. It is the most populous city on the west coast of Honshu, and the second populous city in Chūbu region after Nagoya. It faces the Sea of Japan and Sado, Niigata, Sado Island. , the city had an estimated population of 779,049, and a population density of 1,072 persons per km2. The total area is . Greater Niigata, the Niigata Urban Employment Area, Metropolitan Employment Area, has a GDP of US$43.3 billion as of 2010. It is the only government-designated city on the west coast of Honshu. It has the greatest habitable area of cities in Japan (). It is designated as a reform base for the large scale agriculture under () initiatives. Overview Niigata was one of the cities incorporated by the legislation effective on April 1, 1889 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagasaki, Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan. It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the Nagasaki Region have been recognized and included in the UNESCO World Heritage List. Part of Nagasaki was home to a major Imperial Japanese Navy base during the First Sino-Japanese War and Russo-Japanese War. Near the end of World War II, the American atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki made Nagasaki the second and, to date, last city in the world to experience a nuclear attack (at 11:02 am, August 9, 1945 'Japan Standard Time (UTC+9)'). , the city has an estimated population of 407,624 and a population density of 1,004 people per km2. The total area is . History Nagasaki as a Jesuit port of call The first contact with Portuguese explorers occurred in 1543. An early visitor was Fernão Mendes Pinto, who came from Sagres on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobe
Kobe ( , ; officially , ) is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture Japan. With a population around 1.5 million, Kobe is Japan's seventh-largest city and the third-largest port city after Tokyo and Yokohama. It is located in Kansai region, which makes up the southern side of the main island of Honshū, on the north shore of Osaka Bay. It is part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kyoto. The Kobe city centre is located about west of Osaka and southwest of Kyoto. The earliest written records regarding the region come from the '' Nihon Shoki'', which describes the founding of the Ikuta Shrine by Empress Jingū in AD 201.Ikuta Shrine official website – "History of Ikuta Shrine" (Japanese) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




