|
Kynamro
Mipomersen (INN; trade name Kynamro) is a drug used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by subcutaneous injection. There is a serious risk of liver damage from this drug and it can only be prescribed in the context of a risk management plan. Indications Kynamro is used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by injection. It cannot be freely prescribed; instead every person put on mipomersen is enrolled in a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) program approved by the FDA. Pregnancy and lactation Mipomersen is pregnancy category B; women who are pregnant or intending to become pregnant should only use this drug if needed. It is unknown if it is secreted in human breast milk, but it was found to be secreted in the breast milk of rats. Contraindications The drug is contraindicated in people with moderate to severe liver impairment, active liver diseases, and unexplained high levels of transaminase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mipomersen
Mipomersen (INN; trade name Kynamro) is a drug used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by subcutaneous injection. There is a serious risk of liver damage from this drug and it can only be prescribed in the context of a risk management plan. Indications Kynamro is used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by injection. It cannot be freely prescribed; instead every person put on mipomersen is enrolled in a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) program approved by the FDA. Pregnancy and lactation Mipomersen is pregnancy category B; women who are pregnant or intending to become pregnant should only use this drug if needed. It is unknown if it is secreted in human breast milk, but it was found to be secreted in the breast milk of rats. Contraindications The drug is contraindicated in people with moderate to severe liver impairment, active liver diseases, and unexplained high levels of transaminas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mipomersen Sodium
Mipomersen (INN; trade name Kynamro) is a drug used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by subcutaneous injection. There is a serious risk of liver damage from this drug and it can only be prescribed in the context of a risk management plan. Indications Kynamro is used to treat homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and is administered by injection. It cannot be freely prescribed; instead every person put on mipomersen is enrolled in a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) program approved by the FDA. Pregnancy and lactation Mipomersen is pregnancy category B; women who are pregnant or intending to become pregnant should only use this drug if needed. It is unknown if it is secreted in human breast milk, but it was found to be secreted in the breast milk of rats. Contraindications The drug is contraindicated in people with moderate to severe liver impairment, active liver diseases, and unexplained high levels of transaminase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL cholesterol), in the blood and early cardiovascular disease. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver. Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH (such as dietary modification and statin tablets). Nevertheless, treatment (including higher statin doses) is usually effective. FH is classified as a type 2 familial dyslipidemia. There are five types of familial dyslipidemia (not including subtypes), and each are classified from both the altered lipid profile and by the genetic abnormality. For example, high LDL (often due to LDL receptor defect) is type 2. Others include defects in chylomicro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiophosphate
Thiophosphates (or phosphorothioates, PS) are chemical compounds and anions with the general chemical formula (''x'' = 0, 1, 2, or 3) and related derivatives where organic groups are attached to one or more O or S. Thiophosphates feature tetrahedral phosphorus(V) centers. Organic Organothiophosphates are a subclass of organophosphorus compounds that are structurally related to the inorganic thiophosphates. Common members have formulas of the type (RO)3−''x''R''x''PS and related compounds where RO is replaced by RS. Many of these compounds are used as insecticides, some have medical applications, and some have been used as oil additives.J. Svara, N. Weferling, T. Hofmann "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2006. Oligonucleotide phosphorothioates (OPS) are modified oligonucleotides where one of the oxygen atoms in the phosphate moiety is replaced by sulfur. They are the basis of antisense therapy, e.g., the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, collectively referred to as the cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected here are for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot effect. Compared with other routes of administration, it is slower than intramuscular injections but still faster than intradermal injections. Subcutaneous infusion (as opp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Low-density Lipoprotein
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins ( chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. VLDL is assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL is converted in the bloodstream to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). VLDL particles have a diameter of 30–80 nm. VLDL transports endogenous products, whereas chylomicrons transport exogenous (dietary) products. In the early 2010s both the lipid composition and protein composition of this lipoprotein were characterised in great detail. Function Very-low-density lipoproteins transport endogenous triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and cholesteryl esters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, or more precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of a hydroxy group. Discovered in 1929 by Phoebus Levene, deoxyribose is most notable for its presence in DNA. Since the pentose sugars arabinose and ribose only differ by the stereochemistry at C2′, 2-deoxyribose and 2-deoxyarabinose are equivalent, although the latter term is rarely used because ribose, not arabinose, is the precursor to deoxyribose. Structure Several isomers exist with the formula H−(C=O)−(CH2)−(CHOH)3−H, but in deoxyribose all the hydroxyl groups are on the same side in the Fischer projection. The term "2-deoxyribose" may refer to either of two enantiomers: the biologically important -2-deoxyribose and to the rarely encountered mirror image -2-deoxyribose.C Bernelot-Moens and B Demple (1989), ''Multiple DNA repair activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleic Acid
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (''mRNA'') to convey genetic information (using the nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiester
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is dominated by their prevalence in DNA and RNA, but phosphodiesters occur in other biomolecules, e.g. acyl carrier proteins. Phosphodiester bonds make up the backbones of DNA and RNA. The phosphate is attached to the 5' carbon. The 3' carbon of one sugar is bonded to the 5' phosphate of the adjacent sugar. Specifically, the phosphodiester bond links the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another (hence the name, 3', 5' phosphodiester linkage). These saccharide groups are derived from deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. Phosphodiesters are negatively charged at pH 7. Repulsion between these negative charges influences the conformation of the polynucleic acids. The negative charge attracts histones, metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
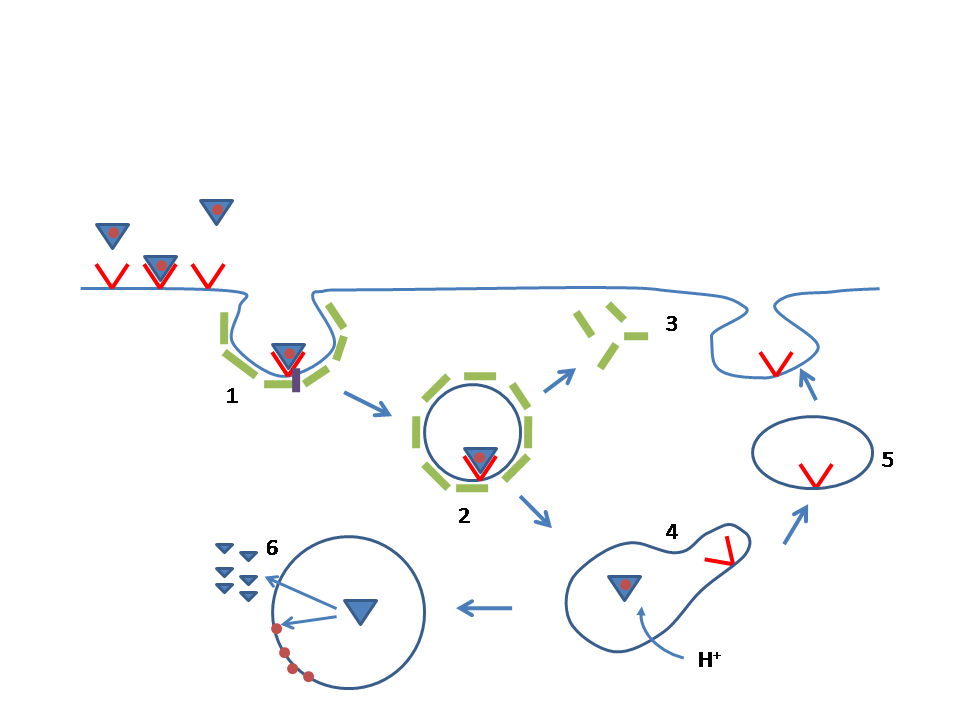
Antisense Oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small bits of nucleic acids can be manufactured as single-stranded molecules with any user-specified sequence, and so are vital for artificial gene synthesis, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, molecular cloning and as molecular probes. In nature, oligonucleotides are usually found as small RNA molecules that function in the regulation of gene expression (e.g. microRNA), or are degradation intermediates derived from the breakdown of larger nucleic acid molecules. Oligonucleotides are characterized by the sequence of nucleotide residues that make up the entire molecule. The length of the oligonucleotide is usually denoted by "-mer" (from Greek ''meros'', "part"). For example, an oligonucleotide of six nucleotides (nt) is a hexamer, while one of 25 nt wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5′ to 3′ exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3′ to 5′ exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3′ to 5′ exonuclease. In both archaea and eukaryotes, one of the main routes of RNA degradation is performed by the multi-protein exosome complex, which consists largely of 3′ to 5′ exoribonucleases. Significance to polymerase RNA polymerase II is known to be in effect during transcriptional termination; it works with a 5' exonuclease (human gene Xrn2) to degrade the newly formed tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |