|
Kurdish Historical Sites
This article briefly introduces a list of better known Kurdish historical sites (Kurdish: Asewari mêjûyi Kurdan). Apart from Kurdish historical sites within Kurdistan, non-Kurdish sites within Kurdistan, and Kurdish sites outside of Kurdistan are also included. Sites in Iran and Iranian Kurdistan * Dimdim Castle, West Azarbaijan Province Sites in Iraqi Kurdistan *Pira Delal * Tomb of the Prophet Hazkiel, Amadiya, Iraqi Kurdistan, The tomb is Considered holy to Muslims, Christians and Jews. * Lalish Temple, Located in Nineveh, Iraq, the temple is considered a sacred place of worship for the Yezidi Kurds, According to Historians and archaeologists The site and temple is believed to date back to approximately 4,000 years *Xarab-I Kilashin, ancient city rediscovered in 2017 near the Grand Zab River in Iraqi Kurdistan * Hawler Citadel, Erbil is first mentioned in literary sources by the Sumerians around 2300 B.C, According to Giovanni Pettinato, author of several publications ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish languages, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros Mountains, Zagros and the eastern Taurus Mountains, Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey (Turkish Kurdistan, Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Iraqi Kurdistan, Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran (Iranian Kurdistan, Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria (Syrian Kurdistan, Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern South Caucasus, Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalism, Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menüçehr Mosque
Menucihr Mosque () is a mosque in the medieval city of Ani in Kars Province, Turkey. It was built between 1072 and 1086 by Ebu’l Manuçehr Bey of the Kurdish Shaddadid dynasty. Restoration of the mosque started in june 2020. See also * Spread of Islam among Kurds *Seljuk architecture Seljuk architecture comprises the building traditions that developed under the Seljuk dynasty, when it ruled most of the Middle East and Anatolia during the 11th to 13th centuries. The Great Seljuk Empire (11th-12th centuries) contributed signif ... References {{Mosques in Turkey Mosques in Turkey Religious buildings and structures completed in 1086 Shaddadids Buildings and structures in Kars Province 11th-century mosques Seljuk architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayyubid Dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurds, Kurdish origin, Saladin had originally served Nur ad-Din (died 1174), Nur ad-Din of Syria, leading Nur ad-Din's army in battle against the Crusaders in Fatimid Egypt, where he was made Vizier. Following Nur ad-Din's death, Saladin was proclaimed as the first Sultan of Egypt, and rapidly expanded the new sultanate beyond the frontiers of Egypt to encompass most of the Levant (including the former territories of Nur ad-Din), in addition to Hijaz, Yemen, northern Nubia, Tripolitania, Tarabulus, Cyrenaica, southern Anatolia, and northern Iraq, the homeland of his Kurdish family. By virtue of his sultanate including Hijaz, the location of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina, he was the first ruler to be hailed as the Cus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citadel Of Aleppo
The Citadel of Aleppo ( ar, قلعة حلب, Qalʿat Ḥalab) is a large medieval fortified palace in the centre of the old city of Aleppo, northern Syria. It is considered to be one of the oldest and largest castles in the world. Usage of the Citadel hill dates back at least to the middle of the 3rd millennium BC. Occupied by many civilizations over timeincluding the Armenians, Greeks, Byzantines, Ayyubids, Mamluks and Ottomans the majority of the construction as it stands today is thought to originate from the Ayyubid period. An extensive conservation work took place in the 2000s by the Aga Khan Trust for Culture, in collaboration with Aleppo Archeological Society. Dominating the city, the Citadel is part of the Ancient City of Aleppo, an UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1986. During the 2010s, the Citadel received significant damage during the lengthy Battle of Aleppo. It was reopened to the public in early 2018 with repairs to damaged parts underway. History The rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
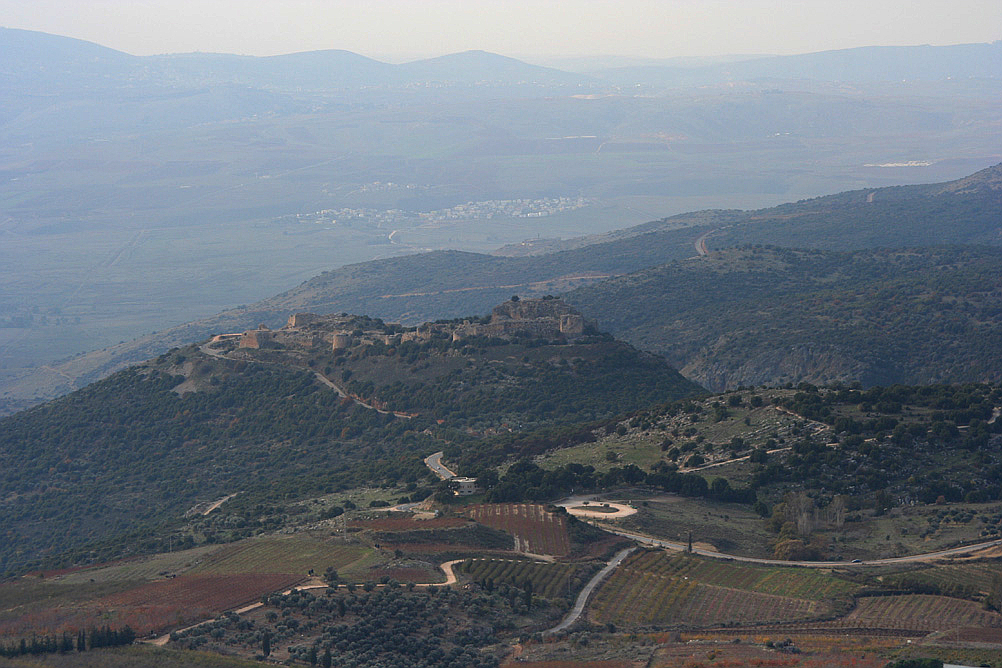
Nimrod Castle
The Nimrod Fortress or Nimrod Castle ( ar, قلعة الصبيبة ''Qal'at al-Subeiba'', "Castle of the Large Cliff", later ''Qal'at Namrud'', "Nimrod's Castle"; he, מבצר נמרוד, ''Mivtzar Nimrod'', "Nimrod's Fortress") is a castle built by the Ayyubids and hugely enlarged by the Mamluks, situated on the southern slopes of Mount Hermon, on a ridge rising about 800 m (2600 feet) above sea level. It overlooks the Golan Heights and was built with the purpose of guarding a major access route to Damascus against armies coming from the west. Alternative forms and spellings include: ''Kal'at'' instead of '' Qal'at'', the prefix ''as-'' instead of ''al-'', and ''Subayba'', ''Subaybah'' and ''Subeibeh'' in place of ''Subeiba''. The area is under Israeli occupation and administration since 1967 together with the adjacent Golan Heights. The international community sees the area as Syrian territory. History According to geological observations and archaeological findings, the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citadel Of Damascus
The Citadel of Damascus ( ar, قلعة دمشق, Qalʿat Dimašq) is a large medieval fortified palace and citadel in Damascus, Syria. It is part of the Ancient City of Damascus, which was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979. The location of the current citadel was first fortified in 1076 by the Turkman warlord Atsiz bin Uvak, although it is possible but not proven that a citadel stood on this place in the Hellenistic and Roman periods. After the assassination of Atsiz bin Uvak, the project was finished by the Seljuq ruler Tutush I. The emirs of the subsequent Burid and Zengid dynasties carried out modifications and added new structures to it. During this period, the citadel and the city were besieged several times by Crusader and Muslim armies. In 1174, the citadel was captured by Saladin, the Ayyubid sultan of Egypt, who made it his residence and had the defences and residential buildings modified. Saladin's brother Al-Adil rebuilt the citadel completely between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Adil I
Al-Adil I ( ar, العادل, in full al-Malik al-Adil Sayf ad-Din Abu-Bakr Ahmed ibn Najm ad-Din Ayyub, ar, الملك العادل سيف الدين أبو بكر بن أيوب, "Ahmed, son of Najm ad-Din Ayyub, father of Bakr, the Just King, Sword of the Faith"; 1145 – 31 August 1218) was the fourth Sultan of Egypt and Syria, and brother of Saladin, who founded both the Sultanate of Egypt, and the Ayyubid dynasty. He was known to the Crusaders as Saphadin (derived from his ''laqab'' or honorific title Sayf ad-Din, meaning "Sword of Faith"), a name by which he is still known in the Western world. A gifted and effective administrator and organizer, Al-Adil provided crucial military and civilian support for the great campaigns of Saladin (an early example of a great minister of war). He was also a capable general and strategist in his own right, and was instrumental in the transformation of the decayed Fatimid Caliphate of Cairo into the Ayyubid Sultanate of Egypt. Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Adiliyah Madrasa
Al-Adiliyah Madrasa () is a 13th-century madrasah located in Damascus, Syria.Al-Adiliyah Madrasa Archnet Digital Library. Modern day In 1919 CE, the National Museum was assembled inside this school. It holds now the Arabic Language Academy in Damascus./ref> See also * * |
Al-Ashraf Qansuh Al-Ghuri
Al-Ashraf Qansuh al-Ghuri ( ar, الأشرف قانصوه الغوري) or Qansuh II al-Ghawri (c. 1441/1446 – 24 August 1516) was the second-to-last of the Mamluk Sultans. One of the last and most powerful of the Burji dynasty, he reigned from 1501 to 1516. Early life Qansuh, born between 1441 and 1446, was bought by Qaitbay, and educated at the al-Ghuri military school in Cairo, from which he gained his nickname "al-Ghuri".Behrens-Abouseif, Doris. "Cairo of the Mamluks". Cairo:AUC Press, 2008. p 295 Consequently, he held several official positions in Upper Egypt, Aleppo, Tarsus and Malatya. Later on, a revolt against Tuman bay by the conspiring emirs, led to the appointment of Qansuh as Sultan against his will, because he feared to be deposed by execution like his predecessors. Consolidation of power The reign began as usual with the removal of all Tuman bay's adherents. As dangerous to the throne, they were laid hold of, imprisoned or exiled and their property esche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab Al-Ahmar
Bab al-Ahmar ( ar, بَاب الْأَحْمَر, Bāb al-ʾAḥmar) meaning the ''Red Gate'', was one of the nine historical gates of the Ancient City of Aleppo, Syria. The name was derived from the village of al-Hamr ( ar, الحمر) as the gate was leading to the village at the eastern suburbs of ancient Aleppo. History The gate was built in the eastern part of old Aleppo in the first half of the 13th century, during the reign of the Ayyubid emir of Aleppo al-Aziz Muhammad. It was renovated during the rule of the Mamluk sultan Al-Ashraf Qansuh al-Ghawri at the beginning of the 16th century. The gate was completely ruined in the 1830s by Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt during his campaign in Syria against the Ottomans between 1831–1833. in 1834, the stones of the gate were used to build the Ibrahim Pasha military barracks (the current Aleppo Citadel Museum) in the Citadel of Aleppo The Citadel of Aleppo ( ar, قلعة حلب, Qalʿat Ḥalab) is a large medieval fortifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirdasid Dynasty
The Mirdasid dynasty ( ar, المرداسيون, al-Mirdāsiyyīn), also called the Banu Mirdas, was an Arab dynasty which ruled an Aleppo-based emirate in northern Syria and the western Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) more or less continuously from 1024 until 1080. History Dominance of the Kilab in northern Syria The Mirdasids were a family of the Bedouin (nomadic Arab) tribe of Banu Kilab. The Kilab's ancestral home was in central Arabia and its tribesmen first established themselves in northern Syria and the western Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia) in the years after the 630s–Muslim conquest. A second major wave of Kilabi tribesmen migrated to northern Syria from Arabia in the 9th century. The political vacuum and frequent revolts throughout the region during that period paved the way for the Kilab to strengthen their influence, becoming the predominant tribe in the region north of the Palmyrene steppe and west of the Euphrates River by the early to mid-10th century. A thir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
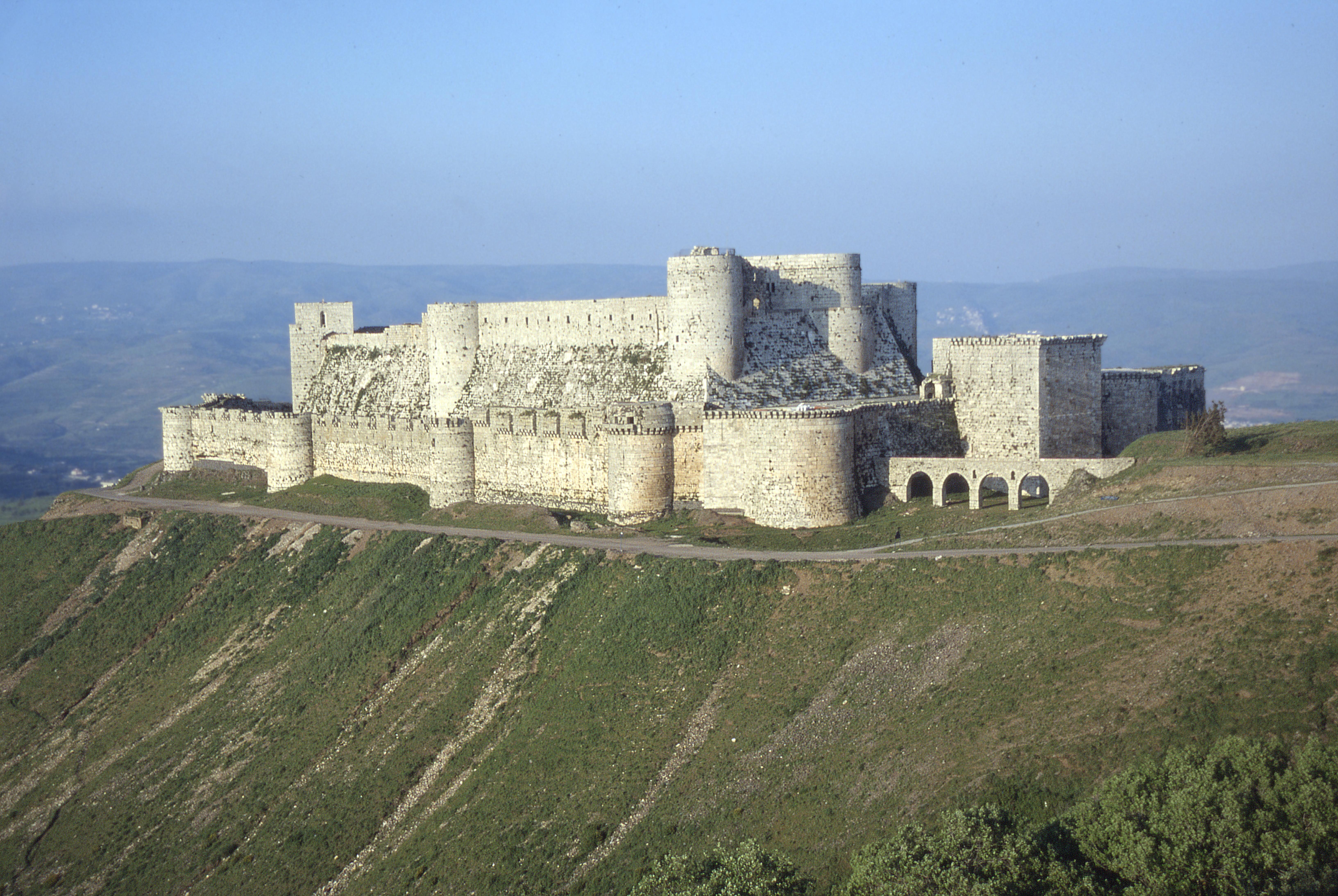
Krak Des Chevaliers
Krak des Chevaliers, ar, قلعة الحصن, Qalʿat al-Ḥiṣn also called Hisn al-Akrad ( ar, حصن الأكراد, Ḥiṣn al-Akrād, rtl=yes, ) and formerly Crac de l'Ospital; Krak des Chevaliers or Crac des Chevaliers (), is a medieval castle in Syria and one of the most important preserved medieval castles in the world. The site was first inhabited in the 11th century by Kurds, Kurdish troops garrisoned there by the Mirdasid dynasty, Mirdasids. In 1142 it was given by Raymond II of Tripoli, Raymond II, County of Tripoli, Count of Tripoli, to the order of the Knights Hospitaller. It remained in their possession until it fell in 1271. The Hospitallers began rebuilding the castle in the 1140s and were finished by 1170 when an earthquake damaged the castle. The order controlled a number of castles along the border of the County of Tripoli, a Crusader state, state founded after the First Crusade. Krak des Chevaliers was among the most important, and acted as a center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |