|
Kshetram
Kshetram (Kshetra) literally means a region. In Hindu mythology, it is referred to as the physical holy location where a temple or a collection of temples, its Temple tank, tank and deities exist. Sacred geography There exist privileged regions and places where energy in the form of terrestrial magnetism rises heavenward. As per Hindu religious mythology, Prana (gravity) pulls life downwards, while apanan (levity) pulls life upwards. Such places are called Tirtha (Hinduism), Tirtha (ways), Kshetra (ways) or pitha (base). Sacred geography can identify sacred places and sometimes explain the importance of those which are already known. The dwelling of gods must be built on such privileged ground (kshetras), and, as a rule, sacred cities arise around them. The temple should be close to a water course or near a lake located to the east or north. For the building of a temple, it should have a lake on the left (north) or in front (east), and not otherwise. If the temple is built on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirtha (Hinduism)
Tirtha (, ) is a Sanskrit word that means "crossing place, ford", and refers to any place, text or person that is holy. It particularly refers to pilgrimage sites and holy places in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. The process or journey associated with ''tirtha'' is called ''tirtha-yatra'', while alternate terms such as ''kshetra'', ''gopitha'' and ''mahalaya'' are used in some Hindu traditions to refer to a "place of pilgrimage". ''Tirtha'' ''Tīrtha'' () literally means "a Ford (crossing), ford, a "crossing place" in the sense of "transition or junction". Tirtha is a spiritual concept in Hinduism, particularly as a "pilgrimage site", states Axel Michaels, that is a holy junction between "worlds that touch and do not touch each other". The word also appears in ancient and medieval Hindu texts to refer to a holy person, or a holy text with something that can be a catalyst for a transition from one state of existence to another. It is, states Knut A. Jacobsen, anything that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theertham
Theertham (Theertha or Tirtha) literally refers to water. In Hindu sacred literature, it is referred to as the physical holy water body associated with a temple or deity. As per Hindu religious belief, water is the principal purification mechanism. While external purification is believed to be through a dip in sacred water bodies, internal purification is through truthfulness. Most Hindu temples are associated with bodies of water, which are called Theertham. In Vishnu temples, devotees are offered a few drops of sacred water called Theertham. Etymology As per Hindu mythology, Hindu temples are usually associated with the trio of Moorthy (image), Stalam (sacred place) and Theertham (a body of water). While most temples are located near rivers or lakes, the temples are usually associated with them. Temple tanks and wells are dug inside or outside the temple for all religious purposes. Also, most temples were centers of social and economic activities, making a waterbody very essen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
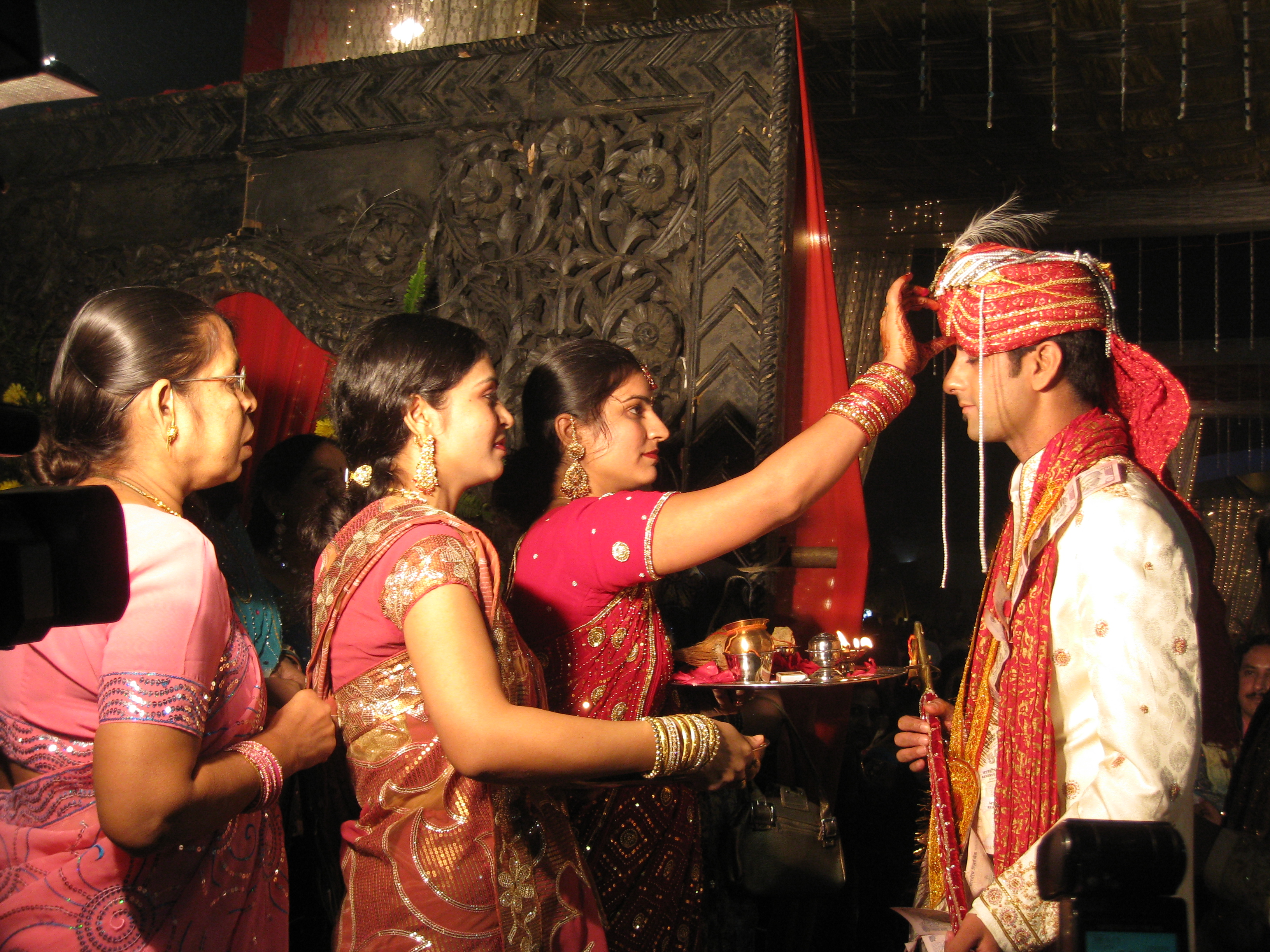
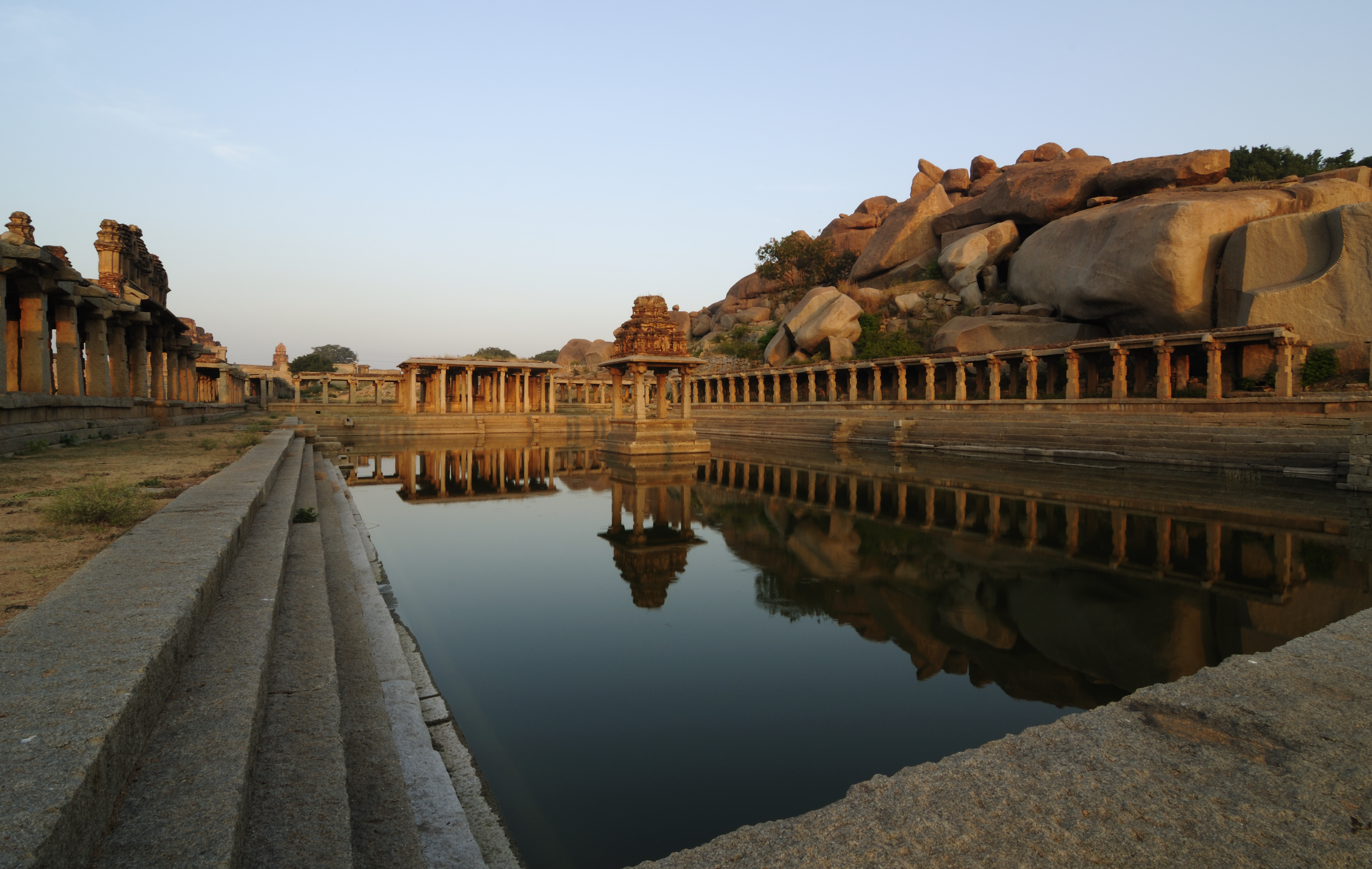
Temple Tank
Temple tanks are water well, wells or reservoirs built as part of the temple complex near Indian temples. They are called pushkarini, kalyani, kunda, sarovara, Theertham, tirtha, talab, pukhuri, ambalakkuḷam, etc. in different languages and regions of India. Some tanks are said to cure various diseases and maladies when bathed in. It is possible that these are cultural remnants of structures such as the Great Bath, Mohenjo-daro, Great Bath of Mohenjo-daro or Dholavira, which was part of the Indus Valley civilization. Some are stepwells with many steps at the sides. Tank design Since ancient times, the design of water storage has been important in India's temple architecture, especially in western India where dry and monsoon seasons alternate. Temple tank design became an art form in itself. An example of the art of tank design is the large, geometrically spectacular Stepped Tank at the Royal Center at the ruins of Vijayanagara, the capital of the Vijayanagara Empire, surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
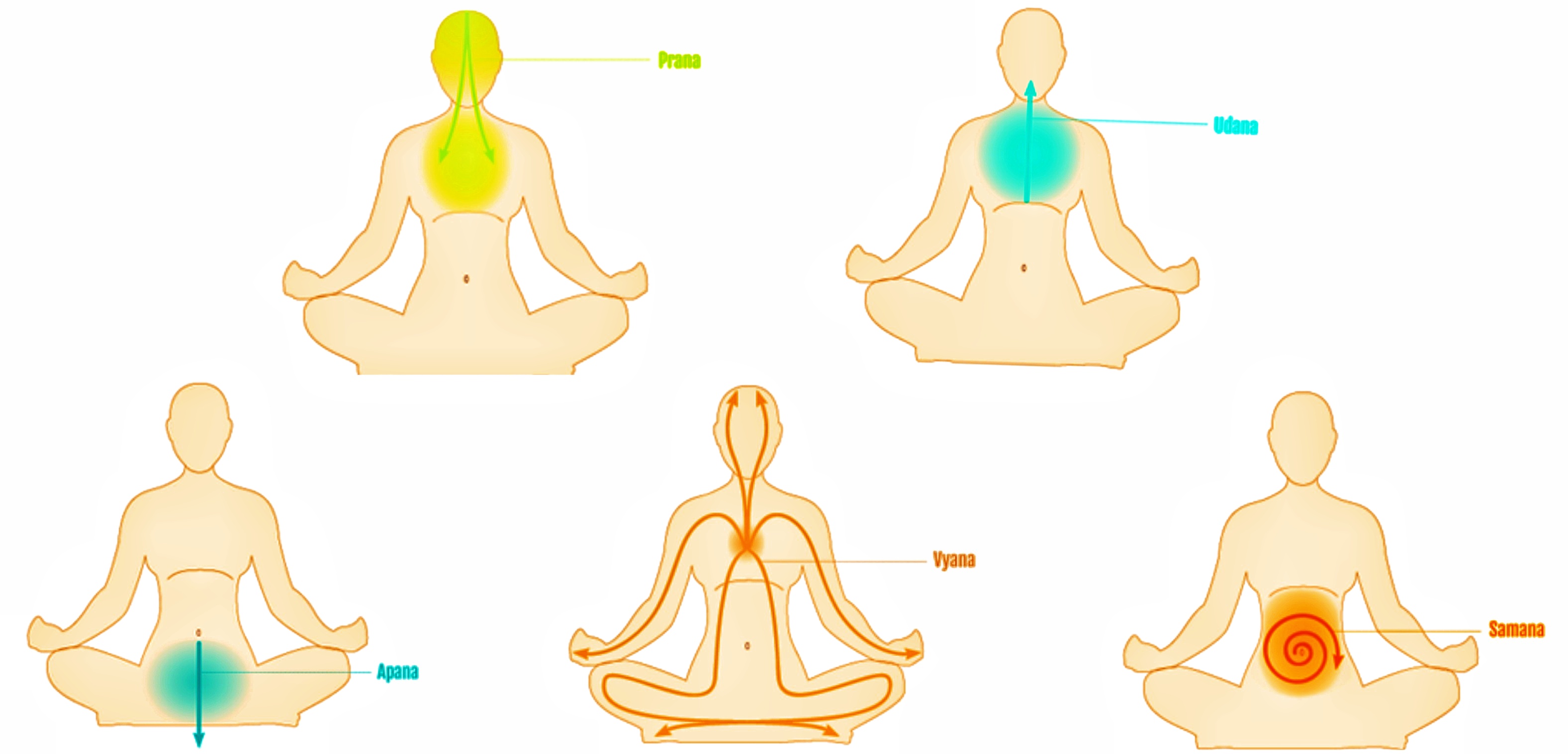
Prana
In yoga, Ayurveda, and Indian martial arts, prana (, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five '' vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand conscious awareness of prana. Etymology V.S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and world, its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other Astronomical object, celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word Geography (Ptolemy), γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
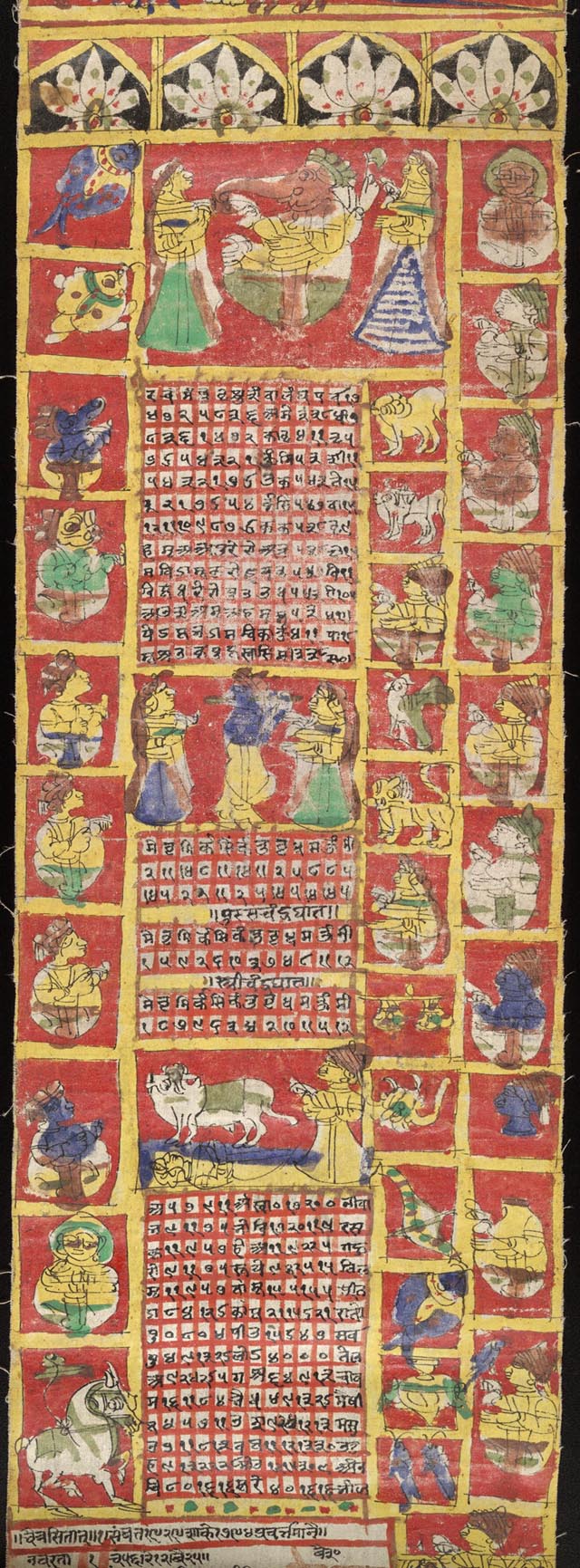
Hindu Calendar
The Hindu calendar, also called Panchangam, Panchanga (), is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a similar underlying concept for timekeeping based on sidereal year for solar cycle, solar cycle and adjustment of lunar cycles in every three years, but differ in their relative emphasis to moon cycle or the sun cycle and the names of months and when they consider the New Year to start. Of the various regional calendars, the most studied and known Hindu calendars are the Shaka era, Shalivahana Shaka (Based on the Shalivahana, King Shalivahana, also the Indian national calendar) found in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region of Southern India and the Vikram Samvat (Bikrami) found in Nepal and the North and Central regions of India – both of which emphasize the lunar cycle. Their new year starts in spring. In regions such as Tamil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Deities
Hindu deities are the gods and goddesses in Hinduism. Deities in Hinduism are as diverse as its traditions, and a Hindu can choose to be polytheistic, pantheistic, monotheistic, monistic, even agnostic, atheistic, or humanist. Julius J. Lipner (2009), Hindus: Their Religious Beliefs and Practices, 2nd edition, Routledge, , p. 8; Quote: "(...) one need not be religious in the minimal sense described to be accepted as a Hindu by Hindus, or describe oneself perfectly validly as Hindu. One may be polytheistic or monotheistic, monistic or pantheistic, even an agnostic, humanist or atheist, and still be considered a Hindu." The terms and epithets for deities within the diverse traditions of Hinduism vary, and include Deva, Devi, Ishvara, Ishvari, Bhagavān and Bhagavati. The deities of Hinduism have evolved from the Vedic era (2nd millennium BCE) through the medieval era (1st millennium CE), regionally within Nepal, Pakistan, India and in Southeast Asia, and across Hinduism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Denominations
Hindu denominations, ''sampradayas'', traditions, movements, and sects are traditions and sub-traditions within Hinduism centered on one or more gods or goddesses, such as Vishnu, Shiva, Shakti and so on. The term ''sampradaya'' is used for branches with a particular founder-guru with a particular philosophy. Hinduism has no central doctrinal authority and many practising Hindus do not claim to belong to any particular denomination or tradition. Four major traditions are, however, used in scholarly studies: ''Vaishnavism'', ''Shaivism'', ''Shaktism'' and ''Smartism''.Lance Nelson (2007), An Introductory Dictionary of Theology and Religious Studies (Editors: Orlando O. Espín, James B. Nickoloff), Liturgical Press, , pages 562–563 These are sometimes referred to as the denominations of Hinduism, and they differ in the primary deity at the centre of each tradition.SS Kumar (2010), Bhakti — the Yoga of Love, LIT Verlag Münster, , pp. 35–36. A notable feature of Hindu denom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Mythology
Hindu mythology refers to the collection of myths associated with Hinduism, derived from various Hindu texts and traditions. These myths are found in sacred texts such as the Vedas, the Itihasas (the ''Mahabharata'' and the ''Ramayana''), and the Puranas. They also appear in regional and ethnolinguistic texts, including the Bengali ''Mangal Kavya'' and the Tamil '' Periya Puranam'' and ''Divya Prabandham''. Additionally, Hindu myths are also found in widely translated fables like the ''Panchatantra'' and the '' Hitopadesha'', as well as in Southeast Asian texts influenced by Hindu traditions. Meaning of "myth" Myth is a genre of folklore or theology consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. For folklorists, historians, philosophers or theologians this is very different from the use of "myth" simply indicating that something is not true. Instead, the truth value of a myth is not a def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism By Country
Hinduism has approximately 1.2 billion adherents worldwide (15% of the world's population). Hinduism is the third largest religion in the world behind Christianity (32.8%) and Islam (23.3%).Table: Religious Composition (%) by Country Global Religious Composition, Pew Research Center (2012) Most Hindus live in Asian countries, and the majority of and are Hindus, and a significant number in |