Prana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
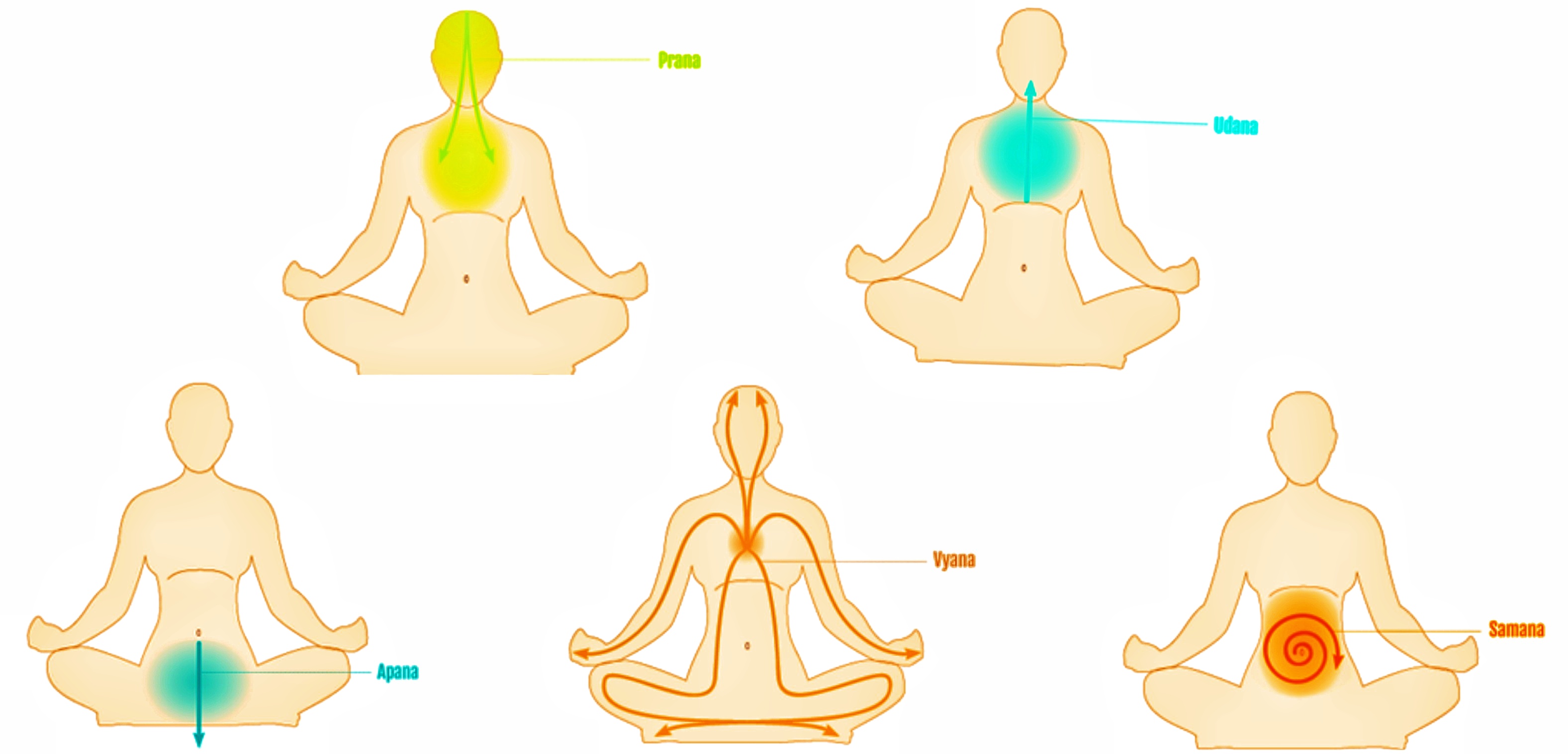 One way of categorizing prāṇa is by means of vāyus. ''Vāyu'' means "wind" or "air" in Sanskrit, and the term is used in a variety of contexts in Hindu philosophy. Prāṇa is considered the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise, as well as one of the five major vāyus. Prāṇa is thus the generic name for all the breaths, including the five major vāyus of prāṇa, apāna, uḍāna, samāna, and vyāna. The ''Nisvasattvasamhita Nayasutra'' describes five minor winds, naming three of these as nāga, dhanamjaya, and kurma; the other two are named in the ''
One way of categorizing prāṇa is by means of vāyus. ''Vāyu'' means "wind" or "air" in Sanskrit, and the term is used in a variety of contexts in Hindu philosophy. Prāṇa is considered the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise, as well as one of the five major vāyus. Prāṇa is thus the generic name for all the breaths, including the five major vāyus of prāṇa, apāna, uḍāna, samāna, and vyāna. The ''Nisvasattvasamhita Nayasutra'' describes five minor winds, naming three of these as nāga, dhanamjaya, and kurma; the other two are named in the ''

Prana - A Overview as per vedic scriptures along with a hymn to Prana from Atharva Veda
Prana – Amazing Secret To Health and Wellbeing as per Yogic Science
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prana Hindu philosophical concepts Vitalism Yoga concepts
yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciou ...
, Indian medicine and Indian martial arts
Indian martial arts refers to the fighting systems of the Indian subcontinent. A variety of terms are used for the English phrases “Indian martial arts”, deriving from ancient sources. While they may seem to imply specific disciplines (e.g. ...
, prana ( sa2, प्राण, ; the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
word for breath, "life force
Life force or lifeforce may refer to:
* Spirit (vital essence), in folk belief, the vital principle or animating force within all living things
* Vitality, ability to live or exist
* Vitalism, the belief in the existence of vital energy
** Energ ...
", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements.
Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five '' vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
, tantra
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the India ...
and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise.
Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya.
Pranayama
Pranayama is the yogic practice of focusing on breath. In Sanskrit, '' prana'' means "vital life force", and ''yama'' means to gain control. In yoga, breath is associated with ''prana'', thus, pranayama is a means to elevate the '' prana'' ''s ...
, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand prana.
Etymology
V. S. Apte
Vaman Shivram Apte (1858 – 9 August 1892) was an Indian lexicographer and a professor of Sanskrit at Pune's Fergusson College
Fergusson College is an autonomous public-private college offering various courses in the streams of arts and s ...
provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural in this sense, there being five such vital airs generally assumed, but three, six, seven, nine, and even ten are also spoken of); energy or vigour; the spirit or soul.
Of these meanings, the concept of "vital air" is used by Bhattacharyya to describe the concept as used in Sanskrit texts dealing with pranayama
Pranayama is the yogic practice of focusing on breath. In Sanskrit, '' prana'' means "vital life force", and ''yama'' means to gain control. In yoga, breath is associated with ''prana'', thus, pranayama is a means to elevate the '' prana'' ''s ...
, the manipulation of the breath. Thomas McEvilley translates ''prāṇa'' as "spirit-energy". The breath
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellu ...
is understood to be its most subtle material form, but is also believed to be present in the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
, and most concentrated in men's semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Sem ...
and women's vaginal fluid.
Early references
The ancient concept of prāṇa is described in many Hindu texts, includingUpanishads
The Upanishads (; sa, उपनिषद् ) are late Vedic Sanskrit texts that supplied the basis of later Hindu philosophy.Wendy Doniger (1990), ''Textual Sources for the Study of Hinduism'', 1st Edition, University of Chicago Press, , ...
and Vedas
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute th ...
. One of the earliest references to prāṇa is from the 3,000-year-old ''Chandogya Upanishad
The ''Chandogya Upanishad'' (Sanskrit: , IAST: ''Chāndogyopaniṣad'') is a Sanskrit text embedded in the Chandogya Brahmana of the Sama Veda of Hinduism.Patrick Olivelle (2014), ''The Early Upanishads'', Oxford University Press; , pp. 166- ...
'', but many other Upanishads use the concept, including the '' Katha'', '' Mundaka'' and '' Prasna Upanishads''. The concept is elaborated upon in great detail in the literature of haṭha yoga, tantra
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the India ...
, and Ayurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
.
The '' Bhagavad Gita'' 4.27 describes the yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciou ...
of self-control as the sacrifice of the actions of the senses and of prāṇa in the fire kindled by knowledge. More generally, the conquest of the senses, the mind, and prāṇa is seen as an essential step on the yogin's path to samadhi
''Samadhi'' ( Pali and sa, समाधि), in Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and yogic schools, is a state of meditative consciousness. In Buddhism, it is the last of the eight elements of the Noble Eightfold Path. In the Ashtanga Yo ...
, or indeed as the goal of yoga. Thus for example the ''Malinivijayottaratantra'' 12.5–7 directs the seeker "who has conquered posture, the mind, prāṇa, the senses, sleep, anger, fear, and anxiety" to practise yoga in a beautiful undisturbed cave.
Prāṇa is typically divided into constituent parts, particularly when concerned with the human body. While not all early sources agree on the names or number of these divisions, the most common list from the ''Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
'', the Upanishads, Ayurvedic and Yogic sources includes five classifications, often subdivided. This list includes ''prāṇa'' (inward moving energy), ''apāna'' (outward moving energy), ''vyāna'' (circulation of energy), ''udāna'' (energy of the head and throat), and ''samāna'' (digestion and assimilation).
Early mention of specific prāṇas often emphasized prāṇa, apāna and vyāna as "the three breaths". This can be seen in the proto-yogic traditions of the Vratyas among others. Texts like the ''Vaikānasasmārta'' utilized the five prāṇas as an internalization of the five sacrificial fires of a panchāgni homa
Homa may refer to:
Places Ethiopia
* Homa (woreda), a district in Oromia Region, Ethiopia
Kenya
* Homa Bay, a town and a bay on the shore of Lake Victoria in Kenya
* Homa Mountain, a volcano near Homa Bay, Kenya
Iran
* Chal Homa, Mar ...
ceremony.
The ''Atharva Veda'' describes prāṇa: 'When they had been watered by Prana, the plants spake in concert: 'thou hast, forsooth, prolonged our life, thou hast made us all fragrant.' (11.4–6) 'The holy (âtharvana) plants, the magic (ângirasa) plants, the divine plants, and those produced by men, spring forth, when thou, O Prâna, quickenest them (11.4–16). 'When Prâna has watered the great earth with rain, then the plants spring forth, and also every sort of herb.' (11.4–17) 'O Prâna, be not turned away from me, thou shall not be other than myself! As the embryo of the waters (fire), thee, O Prâna, do bind to me, that I may live.' (11.4)
Similar concepts
Similar concepts exist in various cultures, including the Latin ''anima'' ("breath", "vital force", "animating principle"), Islamic and Sufic ruh, the Greek pneuma, the Chinese qi, the Polynesian mana, the Amerindian orenda, the German od, and the Hebrew ruah. Prāṇa is also described as subtle energy or life force.Vāyus
 One way of categorizing prāṇa is by means of vāyus. ''Vāyu'' means "wind" or "air" in Sanskrit, and the term is used in a variety of contexts in Hindu philosophy. Prāṇa is considered the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise, as well as one of the five major vāyus. Prāṇa is thus the generic name for all the breaths, including the five major vāyus of prāṇa, apāna, uḍāna, samāna, and vyāna. The ''Nisvasattvasamhita Nayasutra'' describes five minor winds, naming three of these as nāga, dhanamjaya, and kurma; the other two are named in the ''
One way of categorizing prāṇa is by means of vāyus. ''Vāyu'' means "wind" or "air" in Sanskrit, and the term is used in a variety of contexts in Hindu philosophy. Prāṇa is considered the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise, as well as one of the five major vāyus. Prāṇa is thus the generic name for all the breaths, including the five major vāyus of prāṇa, apāna, uḍāna, samāna, and vyāna. The ''Nisvasattvasamhita Nayasutra'' describes five minor winds, naming three of these as nāga, dhanamjaya, and kurma; the other two are named in the ''Skandapurana
The ''Skanda Purana'' (IAST: Skanda Purāṇa) is the largest '' Mukyapurana'', a genre of eighteen Hindu religious texts. The text contains over 81,000 verses, and is of Kaumara literature, titled after Skanda, a son of Shiva and Parvati, w ...
'' (181.46) and '' Sivapurana Vayaviyasamhita'' (37.36) as devadatta and krtaka.
Nadis
Indian philosophy
Indian philosophy refers to philosophical traditions of the Indian subcontinent. A traditional Hindu classification divides āstika and nāstika schools of philosophy, depending on one of three alternate criteria: whether it believes the Veda ...
describes prana flowing in nadis (channels), though the details vary. The ''Brhadaranyaka Upanishad
The ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'' ( sa, बृहदारण्यक उपनिषद्, ) is one of the Principal Upanishads and one of the first Upanishadic scriptures of Hinduism. A key scripture to various schools of Hinduism, the ''B ...
'' (2.I.19) mentions 72,000 nadis in the human body, running out from the heart, whereas the '' Katha Upanishad'' (6.16) says that 101 channels radiate from the heart. The ''Vinashikhatantra'' (140–146) explains the most common model, namely that the three most important nadis are the Ida on the left, the Pingala on the right, and the Sushumna in the centre connecting the base chakra to the crown chakra, enabling prana to flow throughout the subtle body.
When the mind is agitated due to our interactions with the world at large, the physical body also follows in its wake. These agitations cause violent fluctuations in the flow of prana in the nadis.
Pranayama
Prāṇāyāma is a common term for various techniques for accumulating, expanding and working with prana. Pranayama is one of the eight limbs of yoga and is a practice of specific and often intricate breath control techniques. The dynamics and laws of Prana were understood through systematic practice of Pranayama to gain mastery over Prana. Many pranayama techniques are designed to cleanse the nadis, allowing for greater movement of prana. Other techniques may be utilized to arrest the breath forsamadhi
''Samadhi'' ( Pali and sa, समाधि), in Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and yogic schools, is a state of meditative consciousness. In Buddhism, it is the last of the eight elements of the Noble Eightfold Path. In the Ashtanga Yo ...
or to bring awareness to specific areas in the practitioner's subtle or physical body. In Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
, it is utilized to generate inner heat in the practice of tummo
In Tibetan Buddhism, ''tummo'' (; sa, चण्डाली, caṇḍālī) is the fierce goddess of heat and passion. Tummo is found in the Mahasiddha Krishnacarya and the '' Hevajra Tantra'' texts.
Tummo is also a tantric practice for in ...
.
In Ayurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
and therapeutic yoga, pranayama is utilized for many tasks, including to affect mood and aid in digestion. A. G. Mohan
A. G. Mohan (born 1945) is an Indian yoga teacher, author, and co-founder of Svastha Yoga & Ayurveda. Mohan was a longtime disciple of Tirumalai Krishnamacharya (1888-1989), the "father of modern yoga".
Mohan co-founded with T.K.V. Desikachar ...
stated that the physical goals of pranayama may be to recover from illness or the maintenance of health, while its mental goals are: "to remove mental disturbances and make the mind focused for meditation".
According to the scholar-practitioner of yoga Theos Bernard, the ultimate aim of pranayama is the suspension of breathing, "causing the mind to swoon".
Swami Yogananda
Swami Yogananda ( bn, স্বামী যোগানন্দ, translit=Sbāmī Yōgānanda) was a disciple of Ramakrishna, the 19th-century mystic. He took his formal initiation from Sarada Devi, the "holy mother" of Ramakrishna Order ...
writes, "The real meaning of Pranayama, according to Patanjali, the founder of Yoga philosophy, is the gradual cessation of breathing, the discontinuance of inhalation and exhalation".
See also
*Chaitanya (consciousness)
Chaitanya () refers variously to 'awareness', 'consciousness', 'Conscious Self', 'intelligence' or 'Pure Consciousness'. It can also mean energy or enthusiasm.
Etymology
It is derived from cetanā (), which refers to living things or conscio ...
* Chakra
Chakras (, ; sa , text=चक्र , translit=cakra , translit-std=IAST , lit=wheel, circle; pi, cakka) are various focal points used in a variety of ancient meditation practices, collectively denominated as Tantra, or the esoteric or ...
* Scientific skepticism
* Qi Men Dun Jia
Qimen Dunjia is an ancient form of divination from China. It is still in use in Mainland China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Macau, Malaysia, Singapore and the Chinese diaspora in Southeast Asia. It is one of the Three Styles () of Chinese divination, wit ...
* Vijñāna
* Yoga Sutra
The ''Yoga Sutras of Patañjali'' is a collection of Sanskrit sutras (aphorisms) on the theory and practice of yoga – 195 sutras (according to Vyāsa and Krishnamacharya) and 196 sutras (according to others, including BKS Iyengar). The ...
References
Sources
* *External links
Prana - A Overview as per vedic scriptures along with a hymn to Prana from Atharva Veda
Prana – Amazing Secret To Health and Wellbeing as per Yogic Science
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prana Hindu philosophical concepts Vitalism Yoga concepts