|
Knoetschkesuchus
''Knoetschkesuchus'' is a genus of small atoposaurid crocodylomorph from the Late Jurassic of Germany and Portugal. Two species are known: the German species ''K. langenbergensis'', described by Schwarz and colleagues in 2017 based on two partial skeletons and various isolated bones; and the Portuguese species ''K. guimarotae'', named from over 400 specimens including several partial skeletons. ''Knoetschkesuchus'' was a small and short-snouted crocodilian, measuring about in length, that primarily fed on small prey, including invertebrates, amphibians, and mammals. This specialization towards small prey ecologically separated ''Knoetschkesuchus'' from most of the other diverse crocodilians that it lived with in the island ecosystem of Jurassic Europe. Both species were formerly recognized as belonging to ''Theriosuchus''; ''K. guimarotae'' was initially named as ''T. guimarotae'', and specimens of ''K. langenbergensis'' were initially referred to ''T. pusillus'' upon their dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theriosuchus
''Theriosuchus'' is an extinct genus of atoposaurid neosuchian from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Europe (Hungary & southern England), Southeast Asia (Thailand) and western North America (Wyoming), with fragmentary records from Middle Jurassic and Early Cretaceous sites in China, Morocco, and Scotland. Taxonomy Three valid species are currently recognized: ''Theriosuchus pusillus'' from southern England, ''T. grandinaris'' from Thailand, and ''T. morrisonensis'' from the Morrison Formation of North America. ''Theriosuchus'' was previously assigned to Atoposauridae, but a 2016 cladistic analysis recovered it as a neosuchian more closely related to members of the family Paralligatoridae than to atoposaurids. Two species previously assigned to this genus, ''Theriosuchus ibericus'' and ''T. symplesiodon'', have been reassigned to the new genus ''Sabresuchus''. On the other hand, ''Theriosuchus guimarotae'' from Portugal has been reassigned to ''Knoetschkesuchus ''Knoets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoposauridae
Atoposauridae is a Family (biology), family of crocodile-line archosaurs belonging to Neosuchia. The majority of the family are known from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous marine deposits in France, Portugal, and Bavaria in southern Germany. The discovery of the genus ''Aprosuchus'', however, extends the duration of the lineage to the end of the Cretaceous in Romania. Classification Phylogeny Cladogram modified from Buscalioni and Sanz (1988) and Buscalioni and Sanz (1990): References Late Jurassic crocodylomorphs Taxa named by Paul Gervais Prehistoric reptile families {{paleo-archosaur-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
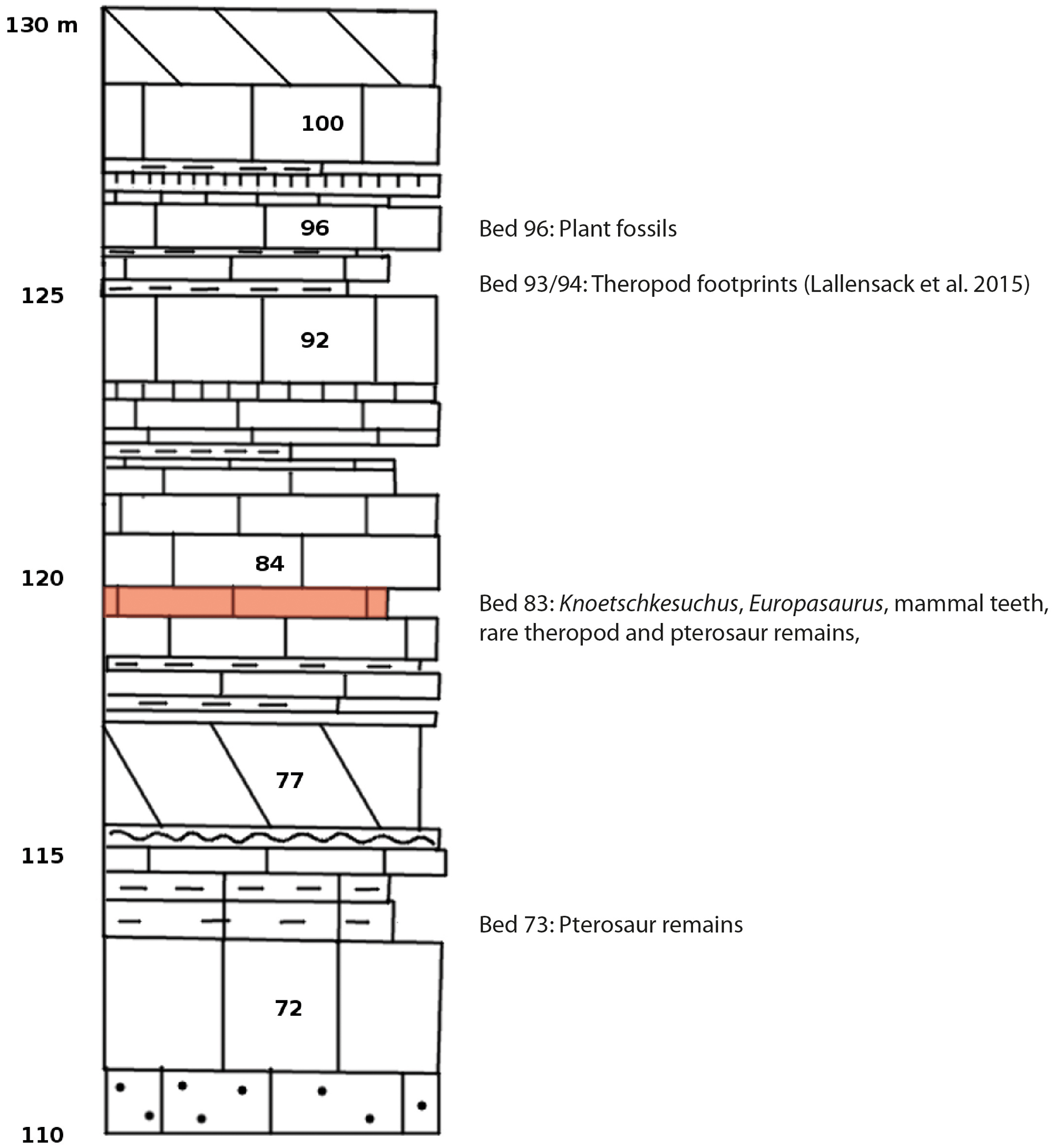
Süntel Formation
The Süntel Formation, previously known as the Kimmeridge Formation (German language, German: ''"Mittlerer Kimmeridge"''; Middle Kimmeridge),Lallensack et al., 2015, p.4 is a geological formation in Germany. It is Late Jurassic in age, spanning the early to late Kimmeridgian stage. It predominantly consists of limestone deposited in shallow marine Carbonate platform, carbonate ramp conditions. Description The formation is part of the Lower Saxony Basin that borders the Süntel massif of the Lower Saxon Hills, part of the larger Harz Mountains. The formation is described as alternations of glauconitic marl, limestone and sandstone.Bai et al., 2017 Paleontological significance The formation is known for its fossils, with the Langenberg quarry, Langenberg Quarry having provided fossils of numerous vertebrates. Dinosaurs Turtles Squamates Pterosaurs Crocodyliformes Mammaliaforms Ichnofossils See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylomorpha
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction. During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, crocodylomorphs were far more diverse than they are now. Triassic forms were small, lightly built, active terrestrial animals. The earliest and most primitive crocodylomorphs are represented by " sphenosuchians", a paraphyletic assemblage containing small-bodied forms with elongated limbs that walked upright, which represents the ancestral morphology of Crocodylomorpha. These forms persisted until the end of the Jurassic. During the Jurassic, Crocodylomorphs morphologically diversified into numerous niches, including into the aquatic and marine realms. Evolutionary history When their extinct species and stem group are examined, the crocodylian lineage (clade Pseudosuchia, formerly Crurotarsi) proves to have been a very diverse and adaptive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the district of Goslar and located on the northwestern slopes of the Harz mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar and the Mines of Rammelsberg are UNESCO World Heritage Sites for their millenium-long testimony to the history of ore mining and their political importance for the Holy Roman Empire and Hanseatic League. Each year Goslar awards the Kaiserring to an international artist, called the "Nobel Prize" of the art world. Geography Goslar is situated in the middle of the upper half of Germany, about south of Brunswick and about southeast of the state capital, Hanover. The Schalke mountain is the highest elevation within the municipal boundaries at . The lowest point of is near the Oker river. Geographically, Goslar forms the boundary between the Hildesheim Börde which is part of the Northern German Plain, and the Harz range, which is the highest, norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, albeit in declining numbers. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-enclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Lüneburg, Osnabrück, Oldenburg, Hildesheim, Salzgitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimmeridgian
In the geologic timescale, the Kimmeridgian is an age in the Late Jurassic Epoch and a stage in the Upper Jurassic Series. It spans the time between 157.3 ± 1.0 Ma and 152.1 ± 0.9 Ma (million years ago). The Kimmeridgian follows the Oxfordian and precedes the Tithonian. Stratigraphic definition The Kimmeridgian Stage takes its name from the village of Kimmeridge on the Dorset coast, England. The name was introduced into the literature by French geologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1842. The Kimmeridge Clay Formation takes its name from the same type location (although this formation extends from the Kimmeridgian stage of the Upper Jurassic into the Lower Cretaceous). It is the source for about 95% of the petroleum in the North Sea. Historically, the term Kimmeridgian has been used in two different ways. The base of the interval is the same but the top was defined by British stratigraphers as the base of the Portlandian (''sensu anglico'') whereas in France the top was defined as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rehburg-Loccum
Rehburg-Loccum () is a town 50 km north west of Hanover in the district of Nienburg in Lower Saxony, Germany. Geography Geographical location Rehburg-Loccum borders the Steinhude Lake. The closest cities are Wunstorf and Neustadt in the district of Hanover, Petershagen/Weser in the district of Minden-Lübbecke/North Rhine-Westphalia, Landesbergen in the district of Nienburg, and Niedernwöhren and Sachsenhagen in the district of Schaumburg. Division of the town Rehburg-Loccum was founded in 1974 out of the city Rehburg and the neighbouring villages Loccum, Münchehagen, Bad Rehburg, and Winzlar as a consequence of a community restructuring legislation enacted by the federal state government of Lower-Saxony. The Steinhude Lake Nature Reserve spans part of the city area. Education The city council runs kindergartens in most parts of the city. There is one primary school each in Münchehagen and Rehburg. A secondary school is located in Loccum. The regional public libra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German word ''Hardt'' or ''Hart'' (hill forest). The name ''Hercynia'' derives from a Celtic name and could refer to other mountain forests, but has also been applied to the geology of the Harz. The Brocken is the highest summit in the Harz with an elevation of above sea level. The Wurmberg () is the highest peak located entirely within the state of Lower Saxony. Geography Location and extent The Harz has a length of , stretching from the town of Seesen in the northwest to Eisleben in the east, and a width of . It occupies an area of , and is divided into the Upper Harz (''Oberharz'') in the northwest, which is up to 800 m high, apart from the 1,100 m high Brocken massif, and the Lower Harz (''Unterharz'') in the east which is up to aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |