|
Kleisma As Thirds Versus One Twelfth On F-sharp
In music theory and musical tuning, tuning, the kleisma (κλείσμα), or semicomma majeur, is a minute and barely perceptible comma (music), comma type interval (music), interval important to musical musical temperament, temperaments. It is the difference between six just intonation, justly tuned minor thirds (each with a frequency ratio of 6/5) and one justly tuned ''tritave'' or ''perfect twelfth'' (with a frequency ratio of 3/1, formed by a 2/1 octave plus a 3/2 perfect fifth). It is equal to a frequency ratio of 15625/15552 = 2−6 3−5 56, or approximately 8.1 cent (music), cents (). It can be also defined as the difference between five justly tuned minor thirds and one justly tuned major tenth (of size 5/2, formed by a 2/1 octave plus a 5/4 major third) or as the difference between a chromatic semitone (25/24) and a greater diesis (648/625). The interval was named by Shohé Tanaka after the Greek for "closure",Just Intonation Network (1993). ''1/1: The Quarterly Journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleisma As Thirds Versus One Twelfth On F-sharp
In music theory and musical tuning, tuning, the kleisma (κλείσμα), or semicomma majeur, is a minute and barely perceptible comma (music), comma type interval (music), interval important to musical musical temperament, temperaments. It is the difference between six just intonation, justly tuned minor thirds (each with a frequency ratio of 6/5) and one justly tuned ''tritave'' or ''perfect twelfth'' (with a frequency ratio of 3/1, formed by a 2/1 octave plus a 3/2 perfect fifth). It is equal to a frequency ratio of 15625/15552 = 2−6 3−5 56, or approximately 8.1 cent (music), cents (). It can be also defined as the difference between five justly tuned minor thirds and one justly tuned major tenth (of size 5/2, formed by a 2/1 octave plus a 5/4 major third) or as the difference between a chromatic semitone (25/24) and a greater diesis (648/625). The interval was named by Shohé Tanaka after the Greek for "closure",Just Intonation Network (1993). ''1/1: The Quarterly Journa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Semitone
In modern Western tonal music theory an augmented unison or augmented prime is the interval between two notes on the same staff position, or denoted by the same note letter, whose alterations cause them, in ordinary equal temperament, to be one semitone apart. In other words, it is a unison where one note has been altered by a half-step, such as B and B or C and C. The interval is often described as a chromatic semitone. The term, in its French form ''unisson superflu'', appears to have been coined by Jean-Philippe Rameau in 1722, who also called this interval a minor semitone (''semiton mineur'').Gene Henry Anderson, "Musical Terminology in J.-P. Rameau's ''Traité de l'harmonie'': A Study and Glossary Based on an Index". PhD diss. (Iowa City: University of Iowa, 1981): 196. Historically, this interval, like the tritone, is described as being "mi contra fa", and therefore is the "diabolus in musica" (the Devil in music). In 12-tone equal temperament, it is the enharmonic equiva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohlen–Pierce Scale
The Bohlen–Pierce scale (BP scale) is a musical tuning and scale, first described in the 1970s, that offers an alternative to the octave-repeating scales typical in Western and other musics, specifically the equal-tempered diatonic scale. The interval 3:1 (often called by a new name, ''tritave'') serves as the fundamental harmonic ratio, replacing the diatonic scale's 2:1 (the octave) with a perfect twelfth (an octave higher than a perfect fifth). For any pitch that is part of the BP scale, all pitches one or more tritaves higher or lower are part of the system as well, and are considered equivalent. The BP scale divides the tritave into 13 steps, either equal tempered (the most popular form), or in a justly tuned version. Compared with octave-repeating scales, the BP scale's intervals are more consonant with certain types of acoustic spectra. The scale was independently described by Heinz Bohlen, Kees van Prooijen and John R. Pierce. Pierce, who, with Max Mathews and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Philippe Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; – ) was a French composer and music theory, music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of French opera and is also considered the leading French composer of his time for the harpsichord, alongside François Couperin. Little is known about Rameau's early years. It was not until the 1720s that he won fame as a major theorist of music with his ''Treatise on Harmony'' (1722) and also in the following years as a composer of masterpieces for the harpsichord, which circulated throughout Europe. He was almost 50 before he embarked on the operatic career on which his reputation chiefly rests today. His debut, ''Hippolyte et Aricie'' (1733), caused a great stir and was fiercely attacked by the supporters of Lully's style of music for its revolutionary use of harmony. Nevertheless, Rameau's pre-eminence in the field of French opera was soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
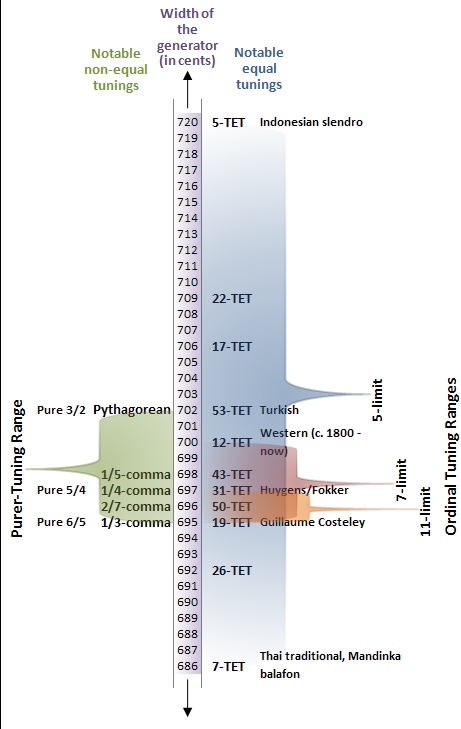
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or tuning system, which approximates just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into equal steps. This means the ratio of the frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same, which gives an equal perceived step size as pitch is perceived roughly as the logarithm of frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been twelve-tone equal temperament (also known as 12 equal temperament, 12-TET or 12-ET; informally abbreviated to twelve equal), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the 12th root of 2 ( ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western countries the term ''equal temperament'', without qualification, generally means 12-TET. In modern times, 12-TET is usually tuned relative to a standard pitch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
72 Equal Temperament
In music, 72 equal temperament, called twelfth-tone, 72-TET, 72- EDO, or 72-ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into twelfth-tones, or in other words 72 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or cents, which divides the 100 cent " halftone" into 6 equal parts (100 ÷ = 6) and is thus a "twelfth-tone" (). Since 72 is divisible by 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, and 72, 72-EDO includes all those equal temperaments. Since it contains so many temperaments, 72-EDO contains at the same time tempered semitones, third-tones, quartertones and sixth-tones, which makes it a very versatile temperament. This division of the octave has attracted much attention from tuning theorists, since on the one hand it subdivides the standard 12 equal temperament and on the other hand it accurately represents overtones up to the twelfth partial tone, and hence can be used for 11-limit music. It was theoreticized in the form of twelf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
34 Equal Temperament
In musical theory, 34 equal temperament, also referred to as 34-TET, 34- EDO or 34-ET, is the tempered tuning derived by dividing the octave into 34 equal-sized steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 35.29 cents . History and use Unlike divisions of the octave into 19, 31 or 53 steps, which can be considered as being derived from ancient Greek intervals (the greater and lesser diesis and the syntonic comma), division into 34 steps did not arise 'naturally' out of older music theory, although Cyriakus Schneegass proposed a meantone system with 34 divisions based in effect on half a chromatic semitone (the difference between a major third and a minor third, 25:24 or 70.67 cents). Wider interest in the tuning was not seen until modern times, when the computer made possible a systematic search of all possible equal temperaments. While Barbour discusses it,''Tuning and Temperament'', Michigan State College Press, 1951 the first recognition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19 Equal Temperament
In music, 19 Tone Equal Temperament, called 19 TET, 19 EDO ("Equal Division of the Octave"), or 19 ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 19 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of , or 63.16 cents (). The fact that traditional western music maps unambiguously onto this scale (unless it presupposes 12-EDO enharmonic equivalences) makes it easier to perform such music in this tuning than in many other tunings. 19 EDO is the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the tempered perfect fifth is equal to 694.737 cents, as shown in Figure 1 (look for the label "19 TET"). On an isomorphic keyboard, the fingering of music composed in 19 EDO is precisely the same as it is in any other syntonic tuning (such as 12 EDO), so long as the notes are "spelled properly" – that is, with no assumption that the sharp below matches the flat immediately above it ( enharmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
53 Equal Temperament
In music, 53 equal temperament, called 53 TET, 53 EDO, or 53 ET, is the tempered scale derived by dividing the octave into 53 equal steps (equal frequency ratios). Each step represents a frequency ratio of 2, or 22.6415 cents (), an interval sometimes called the Holdrian comma. 53-TET is a tuning of equal temperament in which the tempered perfect fifth is 701.89 cents wide, as shown in Figure 1. The 53-TET tuning equates to the unison, or ''tempers out'', the intervals , known as the schisma, and , known as the kleisma. These are both 5 limit intervals, involving only the primes 2, 3 and 5 in their factorization, and the fact that 53 ET tempers out both characterizes it completely as a 5 limit temperament: it is the only regular temperament tempering out both of these intervals, or commas, a fact which seems to have first been recognized by Japanese music theorist Shohé Tanaka. Because it tempers these out, 53-TET can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unison
In music, unison is two or more musical parts that sound either the same pitch or pitches separated by intervals of one or more octaves, usually at the same time. ''Rhythmic unison'' is another term for homorhythm. Definition Unison or perfect unison (also called a prime, or perfect prime)Benward & Saker (2003), p. 53. may refer to the (pseudo-) interval formed by a tone and its duplication (in German, ''Unisono'', ''Einklang'', or ''Prime''), for example C–C, as differentiated from the second, C–D, etc. In the unison the two pitches have the ratio of 1:1 or 0 half steps and zero cents. Although two tones in unison are considered to be the same pitch, they are still perceivable as coming from separate sources, whether played on instruments of a different type: ; or of the same type: . This is because a pair of tones in unison come from different locations or can have different "colors" (timbres), i.e. come from different musical instruments or human voices. Voices wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shohé Tanaka
was a Japanese physicist, music theorist, and inventor. He graduated from Tokyo University in 1882 as a science student. On an imperial scholarship, he was sent to Germany for doctoral studies in 1884, together with Mori Ōgai. His dissertation concerned just intonation and practical means to its implementation. Tanaka was an early advocate of 53 equal temperament as a means of closely approximating 5-limit just intonation. He was the first to obtain a clear understanding of the temperament, noticing that it tempered out both the schisma, 32805/32768, but also the kleisma (), an interval of size 15625/15552 = 2−6 3−5 56, which is the interval by which five just minor thirds of size 6/5 exactly differs from a just tenth of size 5/2 exactly. Tanaka was the first to take practical note of this interval and gave it its name. Tanaka realized that the 53 equal temperament was completely characterized as a five limit temperament by the fact that it tempers out both the schisma and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Diesis
In classical music from Western culture, a diesis ( , plural dieses ( , "difference"; Ancient Greek, Greek: δίεσις "leak" or "escape"Benson, Dave (2006). ''Music: A Mathematical Offering'', p.171. . Based on the technique of playing the aulos, where pitch is raised a small amount by slightly raising the finger on the lowest closed hole, letting a small amount of air "escape".) is either an accidental (music), accidental (see sharp (music), sharp), or a very small interval (music), musical interval, usually defined as the difference between an octave (in the interval ratio, ratio 2:1) and three just intonation, justly tuned major thirds (tuned in the ratio sesquiquartum, 5:4), equal to 128:125 or about 41.06 Cent (music), cents. In 12-tone equal temperament (on a piano for example) three major thirds in a row equal an octave, but three justly-tuned major thirds fall quite a bit narrow of an octave, and the diesis describes the amount by which they are short. For instance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_-_001.jpg)