|
Keratin Disease
A keratin disease is a genetic disorder of one of the keratin genes. An example is monilethrix. The first to be identified was epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Pathology Examples of keratin disease include: See also * List of cutaneous conditions caused by mutations in keratins There are many different keratin proteins normally expressed in the human integumentary system. Mutations in keratin proteins in the skin can cause disease. Of note, other structural proteins in the epidermis of the skin that are closely rel ... References Cytoskeletal defects {{Genodermatoses-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT17
Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT17'' gene. Keratin 17 is a type I cytokeratin. It is found in nail beds, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and other epidermal appendages. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein lead to PC-K17 (previously known as Jackson-Lawler) type pachyonychia congenita and steatocystoma multiplex. Interactions Keratin 17 has been shown to interact with CCDC85B Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 85B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCDC85B'' gene. Function Hepatitis delta virus (HDV) is a pathogenic human virus whose RNA genome and replication cycle resemble those of plant viroids. .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Pachyonychia Congenita Keratins {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT8
Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 also known as cytokeratin-8 (CK-8) or keratin-8 (K8) is a keratin protein that is encoded in humans by the ''KRT8'' gene. It is often paired with keratin 18. Utility as an immunohistochemical stain Antibodies to CK8 (e.g. CAM 5.2) can be used to differentiate breast cancer, lobular carcinoma of the breast from ductal carcinoma of the breast. CAM 5.2, an antibody that reacts with an epitope found on both CK8 and CK18, is used in immunohistochemistry to demonstrate certain forms of cancer. In normal tissue, it reacts mainly with secretory epithelium, epithelia, but not with squamous epithelium, such as that found in the skin, cervix, and esophagus. However, it also reacts with a range of malignant cells, including those derived from secretory epithelia, but also some squamous carcinomata, such as spindle cell carcinoma. It is considered useful in identifying microscopic metastasis, metastases of breast carcinoma in lymph nodes, and in distinguishing Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Cirrhosis
Familial cirrhosis is a form of liver disease that is inherited and the liver scarring is not caused by any obvious disease process. This type of cirrhosis is a keratin disease. Damage progresses until function becomes impaired. Current cirrhosis treatment is aimed at managing complications as well as chronic poor health related to liver damage. Treatments include abstinence from alcohol, nutritional supplement, identification of any identifiable disease process, management of portal hypertension, and liver transplantation. It is associated with KRT8 and KRT18. See also * Keratin disease A keratin disease is a genetic disorder of one of the keratin genes. An example is monilethrix. The first to be identified was epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Pathology Examples of keratin disease include: See also * List of cutaneous condition ... * Cirrhosis References Further reading * * * External links Congenital disorders of digestive system Cytoskeletal defect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT12
Keratin 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT12 gene. Keratin 12 is keratin found expressed in corneal epithelia. Mutations in the gene encoding this protein lead to Meesmann corneal dystrophy Meesmann corneal dystrophy (MECD) is a rare hereditary autosomal dominant disease that is characterized as a type of corneal dystrophy and a keratin disease. MECD is characterized by the formation of microcysts in the outermost layer of the cornea, .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * Keratins {{Gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT3
Keratin 3 also known as ''cytokeratin 3'' is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT3'' gene. Keratin 3 is a type II cytokeratin. It is specifically found in the corneal epithelium together with keratin 12. Mutations in the KRT3 encoding this protein have been associated with Meesmanns Corneal Dystrophy Meesmann corneal dystrophy (MECD) is a rare hereditary autosomal dominant disease that is characterized as a type of corneal dystrophy and a keratin disease. MECD is characterized by the formation of microcysts in the outermost layer of the cornea, .... References Keratins {{Gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meesman Juvenile Epithelial Corneal Dystrophy
Meesmann corneal dystrophy (MECD) is a rare hereditary autosomal dominant disease that is characterized as a type of corneal dystrophy and a keratin disease. MECD is characterized by the formation of microcysts in the outermost layer of the cornea, known as the anterior corneal epithelium. The anterior corneal epithelium also becomes fragile. This usually affects both eyes rather than a single eye and worsens over time. There are two phenotypes, Meesmann corneal dystrophy 1 (MECD1) and Meesmann corneal dystrophy 2 (MECD2), which affect the genes KRT3 and KRT12, respectively. A heterozygous mutation in either of these genes will lead to a single phenotype. Many with Meesmann corneal dystrophy are asymptomatic or experience mild symptoms. It is named after the German ophthalmologist Alois Meesmann (1888-1969). It is often considered as the "Meesmann-Wilke syndrome", after the joint contribution of Meesmann and Wilke in 1939.A. Meesmann, F. Wilke. Klinische und anatomische Untersuchu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT86
Keratin, type II cuticular Hb6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT86'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. As a type II hair keratin, it is a basic protein which heterodimerizes with type I keratins to form hair and nails. The type II hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q13 and are grouped into two distinct subfamilies based on structure similarity. One subfamily, consisting of KRTHB1, KRTHB3, and KRTHB6, is highly related. The other less-related subfamily includes KRTHB2, KRTHB4, and KRTHB5. All hair keratins are expressed in the hair follicle; this hair keratin, as well as KRTHB1 and KRTHB3, is found primarily in the hair cortex. Mutations in this gene a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT83
Keratin 83, also known as KRT83, is a protein which humans is encoded by the ''KRT83'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. As a type II hair keratin, it is a basic protein which heterodimerizes with type I keratins to form hair and nails. The type II hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q13 and are grouped into two distinct subfamilies based on structure similarity. One subfamily, consisting of KRTHB1 (KRT81), KRTHB3 (KRT83, this protein), and KRTHB6 (KRT86), is highly related. The other less-related subfamily includes KRTHB2 (KRT82), KRTHB4 (KRT84), and KRTHB5 (KRT85). All hair keratins are expressed in the hair follicle; this hair keratin, as well as KRTHB1 and KRTHB6, is found primarily in the hair cortex. Clinical significance Mutations in the ''KRT83'' gene have been associated with monilethrix Monilethrix (also referred to as beaded hair) is a rare autosomal dominant hair disease that results in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KRT81
Keratin, type II cuticular Hb1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KRT81'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. As a type II hair keratin, it is a basic protein which heterodimerizes with type I keratins to form hair and nails. The type II hair keratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q13 and are grouped into two distinct subfamilies based on structure similarity. One subfamily, consisting of KRTHB1, KRTHB3, and KRTHB6, is highly related. The other less-related subfamily includes KRTHB2, KRTHB4, and KRTHB5. All hair keratins are expressed in the hair follicle; this hair keratin, as well as KRTHB3 and KRTHB6, is found primarily in the hair cortex. Mutations in this gene a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monilethrix
Monilethrix (also referred to as beaded hair) is a rare autosomal dominant hair disease that results in short, fragile, broken hair that appears beaded. It comes from the Latin word for necklace (''monile'') and the Greek word for hair (''thrix''). Hair becomes brittle, and breaks off at the thinner parts between the beads. It appears as a thinning or baldness of hair and was first described in 1897 by Walter Smith Signs and symptoms Some indicators of monilethrix are small bumps on the skin, mainly on the scalp, neck and arms. In most cases, firm, dark papules, covered with dark scales and crusts appears on the skin, especially the scalp. The affected individual would have beaded hair strands. The possible areas for the hair loss are the eyebrows, eyelashes, limbs, and pubic region. Hair strands are usually dull, dry, and brittle. The strands are prone to mild to severe breakage, causing onset alopecia, especially during pregnancy. Fingernail and toenails tend to appear abnorma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
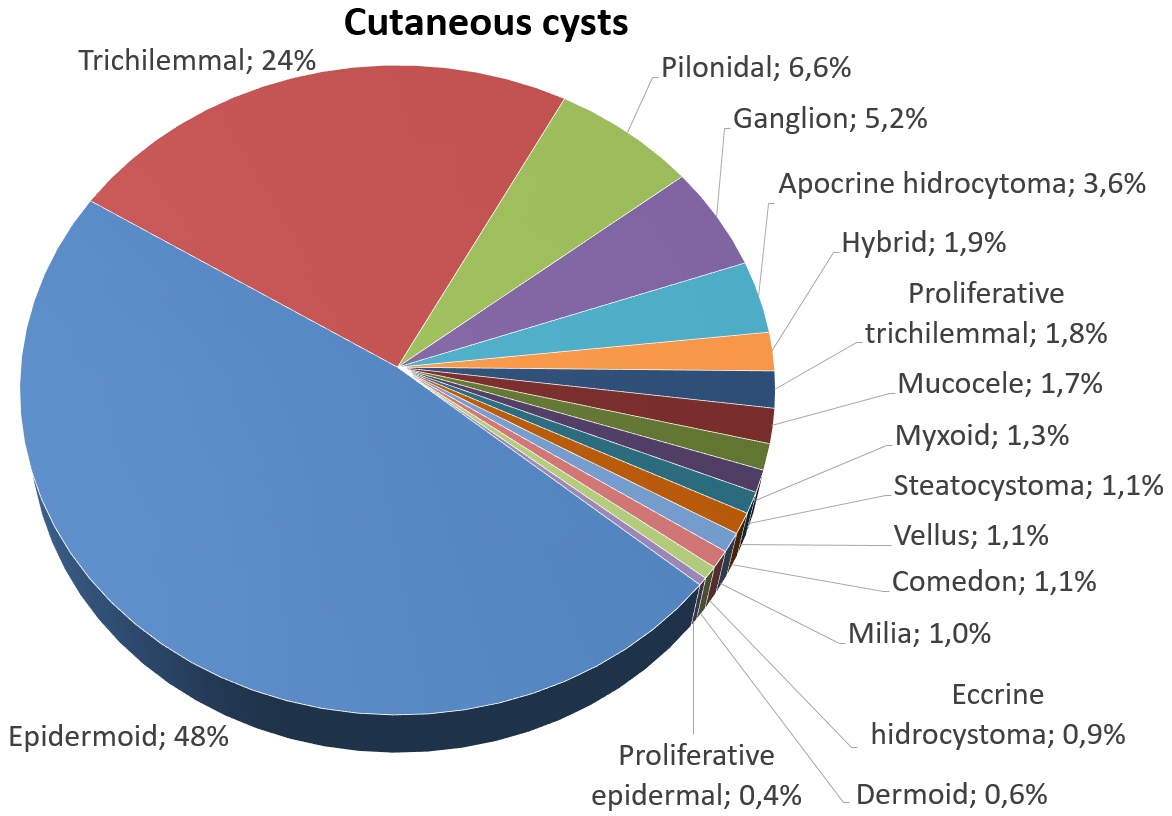
Steatocystoma Multiplex
Steatocystoma multiplex, is a benign, autosomal dominant congenital condition resulting in multiple cysts on a person's body. Steatocystoma simplex is the solitary counterpart to steatocystoma multiplex. In steatocystoma multiplex, the tendency to develop cysts is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, so one parent can be expected to also have steatocystoma multiplex. It may also occur sporadically. Both males and females may be affected. The onset at puberty is presumably due to hormonal stimulus of the pilosebaceous unit. They most often arise on the chest and may also occur on the abdomen, upper arms, armpits and face. In some cases cysts may develop all over the body. The cysts are mostly small (2–20 mm) but they may be several centimetres in diameter. They tend to be soft to firm semi-translucent bumps, and contain an oily, yellow liquid. Sometimes a small central punctum can be identified and they may contain one or more hairs (eruptive vellus hair cysts). They may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |