|
Kenosha Streetcar
Streetcars were part of the public transit service in Kenosha, Wisconsin in the first third of the 20th century, and returned to this role in 2000. Kenosha Electric Railway The first Kenosha Electric Railway (KERy) was a street railway serving the city of Kenosha, Wisconsin, United States, from February 3, 1903, through February 14, 1932. Throughout these 29 years of service, the system operated Birney Safety Cars. Although it had several owners, the original name was used throughout its history and is still attached to the current streetcar line in Kenosha. In 1932 the Kenosha system was converted to electric trolley buses, making Kenosha an early user of these vehicles for all transit operations (both Ipswich and Darlington in the UK converted entirely to trolley buses in 1926). Kenosha also utilized color-coding for transit routes, a more common practice in horsecar days but used by Glasgow on its electric cars from the beginning. Modern streetcar line At the turn of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenosha, Wisconsin
Kenosha () is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the seat of Kenosha County. Per the 2020 census, the population was 99,986 which made it the fourth-largest city in Wisconsin. Situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan, Kenosha is part of the greater Chicago metropolitan area (Chicagoland) as defined by the U.S. Census Bureau. It also has longstanding connections to the Racine and Milwaukee areas to the north. Interstate 94 connects Kenosha to the Chicago and Milwaukee metro areas, and Kenosha itself is situated about halfway between each city. Kenosha was once a center of industrial activity; it was home to large automotive factories which fueled its economy. Like some other Rust Belt cities, Kenosha lost these factories in the late 20th century, causing it to gradually transition into a services-based economy. In recent years, the city and surrounding county have benefited from increased job growth, and the city has worked on repairing roads and other infr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Tracks
A railway track (British English and UIC terminology) or railroad track (American English), also known as permanent way or simply track, is the structure on a railway or railroad consisting of the rails, fasteners, railroad ties (sleepers, British English) and ballast (or slab track), plus the underlying subgrade. It enables trains to move by providing a dependable surface for their wheels to roll upon. Early tracks were constructed with wooden or cast iron rails, and wooden or stone sleepers; since the 1870s, rails have almost universally been made from steel. Historical development The first railway in Britain was the Wollaton Wagonway, built in 1603 between Wollaton and Strelley in Nottinghamshire. It used wooden rails and was the first of around 50 wooden-railed tramways built over the next 164 years. These early wooden tramways typically used rails of oak or beech, attached to wooden sleepers with iron or wooden nails. Gravel or small stones were packed around the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Municipal Railway
The San Francisco Municipal Railway (SF Muni or Muni), is the public transit system for the City and County of San Francisco. It operates a system of bus routes (including trolleybuses), the Muni Metro light rail system, three historic cable car lines, and two historic streetcar lines. Previously an independent agency, the San Francisco Municipal Railway merged with two other agencies in 1999 to become the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA). In 2018, Muni served with an operating budget of about $1.2 billion. Muni is the seventh-highest-ridership transit system in the United States, with rides in , and the second-highest in California after the Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Operations Most bus lines are scheduled to operate every five to fifteen minutes during peak hours, every five to twenty minutes middays, about every ten to twenty minutes from 9 pm to midnight, and roughly every half-hour for the late night "owl" ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cincinnati Street Railways
Cincinnati Street Railway (CSR) was the public transit operator in Cincinnati, Ohio, from 1859 to 1952. The company ceased streetcar operations and was renamed Cincinnati Transit Company. The company was founded in 1859 and was one of several operators. The Cincinnati Consolidated Railway merged with CSR in 1880: * Passenger Railroad of Cincinnati 1859-1873 - merged with CCR * Route Nine Street Railroad 1859-1873 - merged with CCR * Pendleton Street Railroad 1860-1873 - merged with East and West Street Railroad Company and finally with CCR in 1873 * Cincinnati, Walnut Hills, Avondale and Pleasant Ridge Street Railway 1874-1880 - merged with CSR * Storrs and Sedamsvill Street Railroad 1878-1880 * Cincinnati and Clifton Incline Plane Railroad 1876-1880 * Rees McDuffie 1884-1885 * Cumminsville Street Passenger Railroad ?-1889 * Walnut Hills and Cincinnati Street Railway 1872-1880 * Mount Adams and Eden Park Incline Railway 1876-1881 * Mount Auburn Cable Railway 1887-1896 * Mount Aub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnstown Traction Company
Johnstown Traction Company (JTC) was a public transit system in Johnstown, Pennsylvania, United States. For most of its existence it was primarily a street-railway system, but in later years also operated rubber-tired vehicles. JTC operated trolley (tram) service in Johnstown from February 23, 1910 to June 11, 1960. Johnstown was one of the last small cities to abandon trolley service in the United States. Middleton, William D. (1967). ''The Time of the Trolley'', p. 190. Milwaukee: Kalmbach Publishing. . It was also the smallest city to acquire a fleet of PCC cars and acquired trackless trolleys at a late date compared to larger transit properties. Many of the 1920s-era cars went directly to museums; however, none of the 17 PCC streetcars were saved. Efforts to sell the 16 then-surviving PCC cars intact were unsuccessful, and in 1962 they were scrapped, but many of their components were salvaged and sold to the Brussels, Belgium tram system, reused in the last series of sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
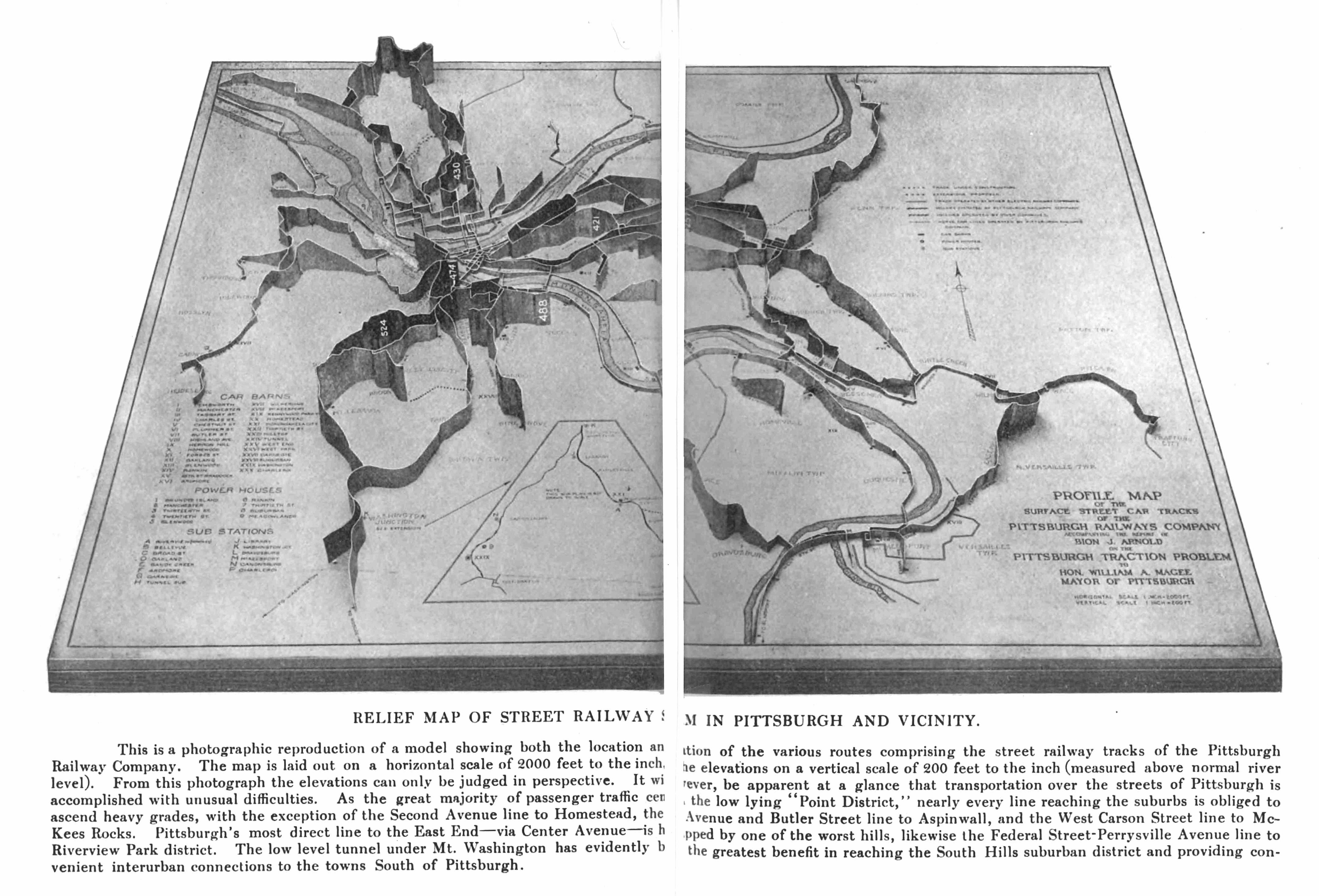
Pittsburgh Railways Company
Pittsburgh Railways was one of the predecessors of Pittsburgh Regional Transit. It had 666 PCC cars, the third largest fleet in North America (after Toronto (745) and Chicago (683)). It had 68 streetcar routes, of which only three (until April 5, 2010, the 42 series, the 47 series, and 52) are used by the Port Authority as light rail routes. With the Port Authority's Transit Development Plan, many route names will be changed to its original, such as the 41D Brookline becoming the 39 Brookline. Many of the streetcar routes have been remembered in the route names of many Port Authority buses (e.g. 71 series). History 1895 to 1905 was a time of consolidation for the numerous street railways serving Pittsburgh. On July 24, 1895 the Consolidated Traction Company (CTC) was chartered and the following year acquired the Central Traction Company, Citizens Traction Company, Duquesne Traction Company and Pittsburgh Traction Company and converted them to electric operation. On July 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Surface Lines
The Chicago Surface Lines (CSL) was operator of the street railway system of Chicago, Illinois, from 1913 to 1947. The firm is a predecessor of today's publicly owned operator, the Chicago Transit Authority. History The first streetcars in Chicago were horse cars run by the Chicago City Railway Company and the North Chicago City Railway Company around 1858-1861. This method was slow and expensive, and the companies began substituting cable cars in the 1880s. Chicago City Railway was the first in (1881), and with the addition of the Chicago Passenger Railway (1883) and the West Chicago Street Railroad Company (1887), Chicago had the largest cable railway system in the world. The north and west side cable car systems were constructed by an investment syndicate under the direction of Charles Yerkes. It was also in the 1880s that electric-powered " trolleys" first became practical. The Chicago companies hesitated at first to install these faster and more efficient systems beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Car And Foundry Company
Canadian Car and Foundry (CC&F), also variously known as "Canadian Car & Foundry" or more familiarly as "Can Car", was a manufacturer of buses, railway rolling stock, forestry equipment, and later aircraft for the Canadian market. CC&F history goes back to 1897, but the main company was established in 1909 from an amalgamation of several companies and later became part of Hawker Siddeley Canada through the purchase by A.V. Roe Canada in 1957. Today the remaining factories are part of Alstom after its acquisition of Bombardier Transportation completed in 2021. Press release from Alstom on the acquisition of Bombardier Transportation History Canadian Car & Foundry (CC&F) was established in 1909 in Montreal as the result of an amalgamation of three companies: * Rhodes Curry Company of Amherst, NS - founded 1891 * Canada Car Company of Turcot, QC - founded 1905 * Dominion Car and Foundry of Montreal, QC In 1911 the CC&F Board of Directors recognized that the company could improve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto Transit Commission
The Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) is the public transport agency that operates bus, subway, streetcar, and paratransit services in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, some of which run into the Peel Region and York Region. It is the oldest and largest of the urban transit service providers in the Greater Toronto Area, with numerous connections to systems serving its surrounding municipalities. Established as the Toronto Transportation Commission in 1921, the TTC owns and operates Toronto subway, four rapid transit lines with List of Toronto subway stations, 75 stations, over 150 List of Toronto Transit Commission bus routes, bus routes, and 9 Toronto streetcar system, streetcar lines. In , the system had a ridership of , or about per weekday as of . The TTC is the most heavily used Public transport in Canada, urban mass transit system in Canada and the third largest in North America, after the New York City Transit Authority and Mexico City Metro. History Public transportatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
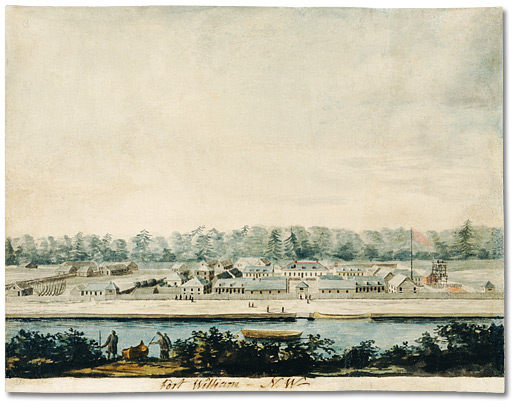
Fort William, Ontario
Fort William was a city in Ontario, Canada, located on the Kaministiquia River, at its entrance to Lake Superior. It amalgamated with Port Arthur and the townships of Neebing and McIntyre to form the city of Thunder Bay in January 1970. Since then it has been the largest city in Northwestern Ontario. The city's Latin motto was ''A posse ad esse'' (''From a possibility to an actuality''), featured on its coat of arms designed in 1900 by town officials, "On one side of the shield stands an Indian dressed in the paint and feathers of the early days; on the other side is a French voyageur; the center contains a grain elevator, a steamship and a locomotive, while the beaver surmounts the whole." History Fur trade era Fort William and Grand Portage were the two starting points for the canoe route from the Great Lakes to Western Canada. For details of the route inland see Kaministiquia River. French period (Fort Kaministiquia) Kamanistigouian, as a place, is first mentioned in a decr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure, for instance there are 55,000 substations in the United States. Substations may be owned and operated by an electrical utility, or may be owned by a large industrial or commercial customer. Generally substations are unattended, relying on SCADA for remote supervision and control. The word ''substation'' comes from the days before the distribution system became a grid. As central generation stations became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid State (electronics)
Solid-state electronics means semiconductor electronics: electronic equipment using semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used as an adjective for devices in which semiconductor electronics that have no moving parts replace devices with moving parts, such as the solid-state relay in which transistor switches are used in place of a moving-arm electromechanical relay, or the solid-state drive (SSD) a type of semiconductor memory used in computers to replace hard disk drives, which store data on a rotating disk. History The term "solid-state" became popular at the beginning of the semiconductor era in the 1960s to distinguish this new technology based on the transistor, in which the electronic action of devices occurred in a solid state, from previous electronic equipment that used vacuum tubes, in which the electronic action occurred in a gaseous state. A semiconductor device works by controlling an electric current c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)