|
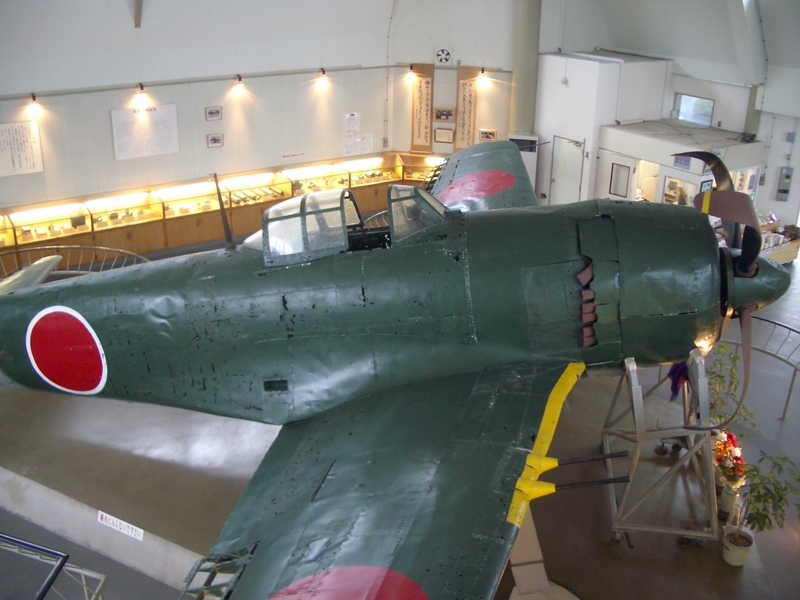
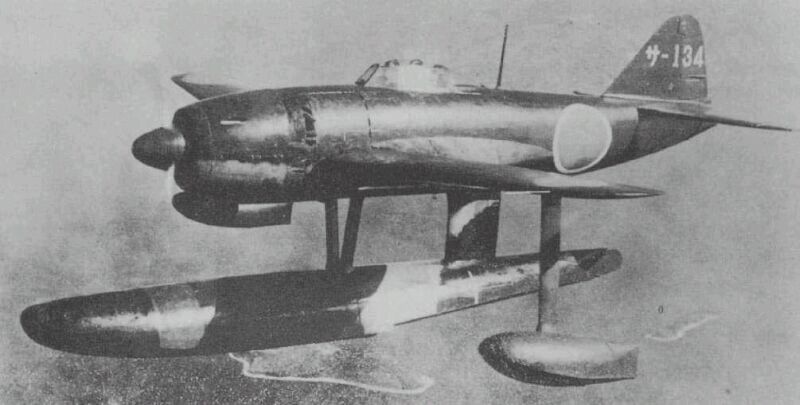
Kawanishi N1K-J
The Kawanishi N1K is an Imperial Japanese Navy fighter aircraft which was developed in two forms: the N1K ''Kyōfū'' (, "Strong Wind", Allied reporting name Rex), a floatplane designed to support forward offensive operations where no airstrips were available, and the N1K-J ''Shiden'' (, "Violet Lightning", reporting name George), a land-based version of the N1K. The N1K-J was considered by both its pilots and opponents to be one of the finest land-based fighters flown by the Japanese during World War II. An improved variant, the N1K2-J "Shiden-Kai" (紫電改) first flew on 1 January 1944. The ''Shiden Kai'' possessed heavy armament, as well as surprisingly good maneuverability, due to a mercury switch that automatically extended the flaps during turns. These "combat" flaps created more lift, thereby allowing tighter turns. Unlike the Mitsubishi A6M Zero, the ''Shiden Kai'' could compete against the best late-war Allied fighters, such as the F6F Hellcat, F4U Corsair, and P-51 M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aru Islands
Aru or ARU may refer to: Education * Alpha Rho Upsilon, a defunct fraternity in the United States * Anglia Ruskin University, a university in England * Ardhi University, a Tanzanian public university Places * Aru Islands Regency, a group of islands and the regency in the Moluccas * Aru, Democratic Republic of Congo, a town in Ituri province * Aru, Harju County, village in Kuusalu Parish, Harju County, Estonia * Aru, Saare County, village in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County, Estonia * Aru, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, village in Gachsaran County, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Iran * Aru, Basht, village in Basht County, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province, Iran * Aru, Damavand, village in Damavand County, Tehran Province, Iran * Aru, Firuzkuh, village in Firuzkuh County, Tehran Province, Iran * Aru, Jammu and Kashmir, village in India * Aruba, IOC and UNDP country code ARU Sports * Fabio Aru, Italian cyclist * Army Rugby Union, organizational body for rugby union i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its Urbanization by country, highly urbanized population is concentrated. The combined Free area of the Republic of China, territories under ROC control consist of list of islands of Taiwan, 168 islands in total covering . The Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area, largest metropolitan area is formed by Taipei (the capital), New Taipei City, and Keelung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries. Tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saburō Sakai
was a Japanese naval aviator and flying ace (''"Gekitsui-O"'', ) of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. Sakai had 28 aerial victories, including shared ones, according to official Japanese records, though he and his ghostwriter Martin Caidin claimed much higher numbers. Early life Saburō Sakai was born on 25 August 1916 in Saga Prefecture, Japan. He was born into a family with an immediate affiliation to the samurai and their warrior legacies. Their ancestors were themselves samurai and had taken part in the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–1598) but were later forced to take up a livelihood of farming after '' haihan-chiken'' in 1871. He was the third-born of four sons (his given name literally means "third son") and had three sisters. Sakai was 11 when his father died, which left his mother alone to raise seven children. With limited resources, Sakai was adopted by his maternal uncle, who financed his education in a Tokyo high school. However, Sakai failed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kaneyoshi Muto
was a Japanese naval aviator and flying ace known for his great skill in fighter aircraft. Fellow ace Saburō Sakai called him "a genius in the air." Second Sino-Japanese War Kaneyoshi Muto was born to a humble farming family in June 1916 in Aichi Prefecture. Muto grew to a height of —short in stature—and enlisted in the Imperial Japanese Navy in June 1935 when he was 19. After serving for a brief period aboard the destroyer ''Uranami'' he applied for flight training to advance his career. In July 1936 he graduated as a naval aviator and was assigned to the Omura Air Group. Muto went to war in China flying with the 12th Air Group. He earned his first air victory on 4 December 1937 during the Battle of Nanking when he shot down a Soviet-made Polikarpov I-16. Muto continued fighting in China, flying many sorties over Hankou to become an ace with five victories. For his distinguished service, he was honored with an official commendation on 30 April 1938. Among his fellow pil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kawanishi N1K Shiden
Kawanishi may refer to: Places * Kawanishi, Hyōgo * Kawanishi, Nara * Kawanishi, Yamagata * Kawanishi, Niigata – now merged into Tōkamachi People with the surname *, Japanese painter *, Japanese swimmer *, Japanese idol Other uses * Kawanishi Aircraft Company The was a Japanese aircraft manufacturer active during World War II. History The company was founded as Kawanishi Engineering Works in 1920 in Hyōgo Prefecture as an outgrowth of the Kawanishi conglomerate, which had been funding the Nakajima ..., a former Japanese aircraft manufacturer {{Disambig, geo, surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mitsubishi J2M
The Mitsubishi J2M ''Raiden'' (雷電, "Lightning Bolt") is a single-engined, land-based fighter aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service in World War II. Its Allied reporting name was Jack. Design and development The J2M was designed by Jiro Horikoshi, creator of the Mitsubishi A6M Zero, to meet the 14-''Shi'' (14th year of the Showa reign, or 1939 in the Western calendar) official specification. It was to be a strictly local-defense interceptor, intended to counter the threat of high-altitude bomber raids, and thus relied on speed, climb performance, and armament at the expense of manoeuvrability. The J2M was a sleek, but stubby craft with its oversized Mitsubishi Kasei engine buried behind a long cowling, cooled by an intake fan and connected to the propeller with an extension shaft. Teething development problems stemming from the engine cooling system, and the main undercarriage members led to a slowdown in production. A continual set of modifications resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flap (aircraft)
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the stall (flight), stalling speed of an aircraft wing at a given weight. Flaps are usually mounted on the wing trailing edges of a fixed-wing aircraft. Flaps are used to reduce the take-off distance and the landing distance. Flaps also cause an increase in Drag (physics), drag so they are retracted when not needed. The flaps installed on most aircraft are partial-span flaps; spanwise from near the wing root to the inboard end of the ailerons. When partial-span flaps are extended they alter the spanwise lift distribution on the wing by causing the inboard half of the wing to supply an increased proportion of the lift, and the outboard half to supply a reduced proportion of the lift. Reducing the proportion of the lift supplied by the outboard half of the wing is accompanied by a reduction in the angle of attack on the outboard half. This is beneficial because it increases the margin above the Stall (fluid dynamics), stall of the outbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Landing Gear
Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for taxiing, takeoff or landing. For aircraft, it is generally needed for all three of these. It was also formerly called ''alighting gear'' by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction ''undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US)''. For aircraft, the landing gear supports the craft when it is not flying, allowing it to take off, land, and taxi without damage. Wheeled landing gear is the most common, with skis or Seaplane, floats needed to operate from snow/ice/water and skids for vertical operation on land. Retractable undercarriages fold away during flight, which reduces drag (physics), drag, allowing for faster airspeeds. Landing gear must be strong enough to support the aircraft and its design affects the weight, balance and performance. It often comprises three wheels, or wheel-sets, giving a tripod effect. Some unusual land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating engine, reciprocating type internal combustion engine, internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinder (engine), cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized Star polygon, star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nakajima Homare
The Nakajima Homare (誉, "praise" or, more usually, "honour") was an air-cooled twin-row 18 cylinder radial Japanese aircraft engine manufactured during World War II. Producing almost 2,000 horsepower, it was used widely by both the Imperial Japanese Army The Imperial Japanese Army (IJA; , ''Dai-Nippon Teikoku Rikugun'', "Army of the Greater Japanese Empire") was the principal ground force of the Empire of Japan from 1871 to 1945. It played a central role in Japan’s rapid modernization during th ... and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Given the Navy service designation NK9, the "Homare" was also given the company designation NBA, Army experimental designation Ha-45 (ハ45) or, Army long designation Nakajima Army Type 4 1,900 hp Air-Cooled Radial and, (coincidentally) unified designation code of Ha-45. Design and development Development of the Homare started in 1940, and certification was completed in 1941. It succeeded Nakajima's previous 14 cylinder Sakae (Ha-25) engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mitsubishi Kasei
The was a two-row, 14-cylinder air-cooled radial engine built by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and used in a variety of World War II Japanese aircraft, such as Mitsubishi J2M and Mitsubishi G4M. The Mitsubishi model designation for this engine was A10 while it was an experimental project, in service it was known as the MK4, and known as the Ha101 & Ha111 by the Army and Kasei by the Navy. According to unified designation code it was Ha-32 of the variants from 11 to 27. Design and development Although originally ordered by the Imperial Japanese Navy, the ''Kasei'' was based on the earlier Mitsubishi Shinten engine, itself based originally on the Mitsubishi Kinsei. Produced in a wide variety of models, the ''Kasei'' began with a rated power of , with a gradual evolution to in later wartime versions. Three variants were developed for the Japanese Navy starting in 1939. It was also later adopted by the Imperial Japanese Army as the ''Ha-101'' engine. Unified code was Ha-32. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |