Flap (aircraft) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the
 Extending the flaps also increases the drag coefficient of the aircraft. Therefore, for any given weight and airspeed, flaps increase the
Extending the flaps also increases the drag coefficient of the aircraft. Therefore, for any given weight and airspeed, flaps increase the

 Flaps may be fully extended for
Flaps may be fully extended for
File:ILA 2008 PD 750.JPG, Plain flap at full deflection.
File:Avro Lancaster flap Flickr 4841178432.jpg, Split flap on a World War II bomber
File:A fully extended flap.jpg, Double slotted Fowler flaps extended for landing
File:Undercarriage.b747.arp.jpg, Krueger flaps and triple-slotted trailing-edge flaps of a
 A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the stalling speed
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack increases.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 486. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. This occurs when t ...
of an aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. ...
wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is exp ...
at a given weight. Flaps are usually mounted on the wing trailing edges of a fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air Aircraft, flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate Lift (force), lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the wing configuration, shape of ...
. Flaps are used to reduce the take-off distance and the landing distance. Flaps also cause an increase in drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
so they are retracted when not needed.
The flaps installed on most aircraft are partial-span flaps; spanwise from near the wing root to the inboard end of the aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement arou ...
s. When partial-span flaps are extended they alter the spanwise lift distribution on the wing by causing the inboard half of the wing to supply an increased proportion of the lift, and the outboard half to supply a reduced proportion of the lift. Reducing the proportion of the lift supplied by the outboard half of the wing is accompanied by a reduction in the angle of attack on the outboard half. This is beneficial because it increases the margin above the stall of the outboard half, maintaining aileron effectiveness and reducing the likelihood of asymmetric stall, and spinning.
Extending the wing flaps increases the camber or curvature of the wing, raising the maximum lift coefficient
In fluid dynamics, the lift coefficient () is a dimensionless quantity that relates the lift generated by a lifting body to the fluid density around the body, the fluid velocity and an associated reference area. A lifting body is a foil or a ...
or the upper limit to the lift a wing can generate. This allows the aircraft to generate the required lift at a lower speed, reducing the minimum speed (known as stall speed) at which the aircraft will safely maintain flight. The increase in camber also increases the wing drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
, which can be beneficial during approach and landing, because it allows the aircraft to descend at a steeper angle. For most aircraft configurations, a useful side effect of flap deployment is a decrease in aircraft pitch angle which lowers the nose thereby improving the pilot's view of the runway over the nose of the aircraft during landing. Another side effect however, depending on the type of flap, location on the wing and deployment speed during their extension, is that the flaps will cause the indicated (or relative to the unchanged airfoil) angle of attack to lower within a short time due to an increase in nose-down pitching moment which is characteristic to all trailing-edge flaps, as well as leading-edge flaps, then followed by a nose rise ( pitch-up) due to the increase in lift, thus obscuring the pilot's view of the runway if no action is taken over the pitch inputs.
There are many different designs of flaps, with the specific choice depending on the size, speed and complexity of the aircraft on which they are to be used, as well as the era in which the aircraft was designed. Plain flaps, slotted flaps, and Fowler flaps are the most common. Krueger flaps are positioned on the leading edge of the wings and are used on many jet airliners.
The Fowler, Fairey-Youngman and Gouge types of flap increase the wing area in addition to changing the camber. The larger lifting surface reduces wing loading, hence further reducing the stalling speed.
Some flaps are fitted elsewhere. Leading-edge flaps form the wing leading edge and when deployed they rotate down to increase the wing camber. The de Havilland DH.88 Comet racer had flaps running beneath the fuselage and forward of the wing trailing edge. Many of the Waco Custom Cabin series biplanes have the flaps at mid-chord
Chord may refer to:
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve
* Chord ( ...
on the underside of the top wing.
Principles of operation
The general airplane lift equation demonstrates these relationships:Perkins, Courtland; Hage, Robert (1949). ''Airplane performance, stability and control'', Chapter 2, John Wiley and Sons. . : where: * ''L'' is the amount of ''Lift'' produced, * '''' is the air density, * ''V'' is the true airspeed of the airplane or the ''Velocity'' of the airplane, relative to the air * S is the area of the wing * is the ''lift coefficient
In fluid dynamics, the lift coefficient () is a dimensionless quantity that relates the lift generated by a lifting body to the fluid density around the body, the fluid velocity and an associated reference area. A lifting body is a foil or a ...
'', which is determined by the shape of the airfoil used and the angle at which the wing meets the air (or angle of attack).
Here, it can be seen that increasing the area (S) and lift coefficient () allow a similar amount of lift to be generated at a lower airspeed (V).
 Extending the flaps also increases the drag coefficient of the aircraft. Therefore, for any given weight and airspeed, flaps increase the
Extending the flaps also increases the drag coefficient of the aircraft. Therefore, for any given weight and airspeed, flaps increase the drag
Drag or The Drag may refer to:
Places
* Drag, Norway, a village in Tysfjord municipality, Nordland, Norway
* ''Drág'', the Hungarian name for Dragu Commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Drag (Austin, Texas), the portion of Guadalupe Street adj ...
force. Flaps increase the drag coefficient of an aircraft due to higher induced drag caused by the distorted spanwise lift distribution on the wing with flaps extended. Some flaps increase the wing area and, for any given speed, this also increases the parasitic drag component of total drag.
Thus, flaps are extensively in use for short takeoffs and landings (STOL
A short takeoff and landing (STOL) aircraft is a conventional fixed-wing aircraft that has short runway requirements for takeoff and landing. Many STOL-designed aircraft also feature various arrangements for use on airstrips with harsh conditio ...
).
Flaps during takeoff
Depending on the aircraft type, flaps may be partially extended fortakeoff
Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle leaves the ground and becomes airborne. For aircraft traveling vertically, this is known as liftoff.
For aircraft that take off horizontally, this usually involves starting with a ...
. When used during takeoff, flaps trade runway distance for climb rate: using flaps reduces ground roll but also reduces the climb rate. The amount of flap used on takeoff is specific to each type of aircraft, and the manufacturer will suggest limits and may indicate the reduction in climb rate to be expected. The '' Cessna 172S Pilot Operating Handbook'' generally recommends 10° of flaps on takeoff, especially when the ground is rough or soft.Cessna Aircraft Company. ''Cessna Model 172S Nav III''. Revision 3-12, 2006, pp. 4–19 to 4–47.
Flaps during landing

landing
Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or ...
to give the aircraft a lower stall speed so the approach to landing can be flown more slowly, which also allows the aircraft to land in a shorter distance. The higher lift and drag associated with fully extended flaps allows a steeper and slower approach to the landing site, but imposes handling difficulties in aircraft with very low wing loading (i.e. having little weight and a large wing area). Winds across the line of flight, known as ''crosswinds'', cause the windward side of the aircraft to generate more lift and drag, causing the aircraft to roll, yaw and pitch off its intended flight path, and as a result many light aircraft land with reduced flap settings in crosswinds. Furthermore, once the aircraft is on the ground, the flaps may decrease the effectiveness of the brakes since the wing is still generating lift and preventing the entire weight of the aircraft from resting on the tires, thus increasing stopping distance, particularly in wet or icy conditions. Usually, the pilot will raise the flaps as soon as possible to prevent this from occurring.
Maneuvering flaps
Some gliders not only use flaps when landing, but also in flight to optimize the camber of the wing for the chosen speed. Whilethermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
ling, flaps may be partially extended to reduce the stall speed so that the glider can be flown more slowly and thereby reduce the rate of sink, which lets the glider use the rising air of the thermal more efficiently, and to turn in a smaller circle to make best use of the core of the thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
. At higher speeds a negative flap setting is used to reduce the nose-down pitching moment. This reduces the balancing load required on the horizontal stabilizer, which in turn reduces the trim drag associated with keeping the glider in longitudinal trim. Negative flap may also be used during the initial stage of an aerotow launch and at the end of the landing run in order to maintain better control by the aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement arou ...
s.
Like gliders, some fighters such as the Nakajima Ki-43
The Nakajima Ki-43 ''Hayabusa'' (, " Peregrine falcon", "Army Type 1 Fighter" ) is a single-engine land-based tactical fighter used by the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service in World War II.
The Allied reporting name was "Oscar", but it wa ...
also use special flaps to improve maneuverability during air combat, allowing the fighter to create more lift at a given speed, allowing for much tighter turns. The flaps used for this must be designed specifically to handle the greater stresses and most flaps have a maximum speed
In aviation, V-speeds are standard terms used to define airspeeds important or useful to the operation of all aircraft. These speeds are derived from data obtained by aircraft designers and manufacturers during flight testing for aircraft Type c ...
at which they can be deployed. Control line model aircraft built for precision aerobatics competition usually have a type of maneuvering flap system that moves them in an opposing direction to the elevators, to assist in tightening the radius of a maneuver.
Flap tracks
Manufactured most often from PH steels and titanium, flap tracks control the flaps located on the trailing edge of an aircraft’s wings. Extending flaps often run on guide tracks. Where these run outside the wing structure they may be faired in to streamline them and protect them from damage. Some flap track fairings are designed to act as anti-shock bodies, which reduce drag caused by local sonic shock waves where the airflow becomes transonic at high speeds.Thrust gates
Thrust gates, or gaps, in the trailing edge flaps may be required to minimise interference between the engine flow and deployed flaps. In the absence of an inboard aileron, which provides a gap in many flap installations, a modified flap section may be needed. The thrust gate on the Boeing 757 was provided by a single-slotted flap in between the inboard and outboard double-slotted flaps. The A320, A330, A340 andA380
The Airbus A380 is a large wide-body airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and only full-length double-deck jet airliner.
Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was ann ...
have no inboard aileron. No thrust gate is required in the continuous, single-slotted flap. Interference in the go-around case while the flaps are still fully deployed can cause increased drag which must not compromise the climb gradient.
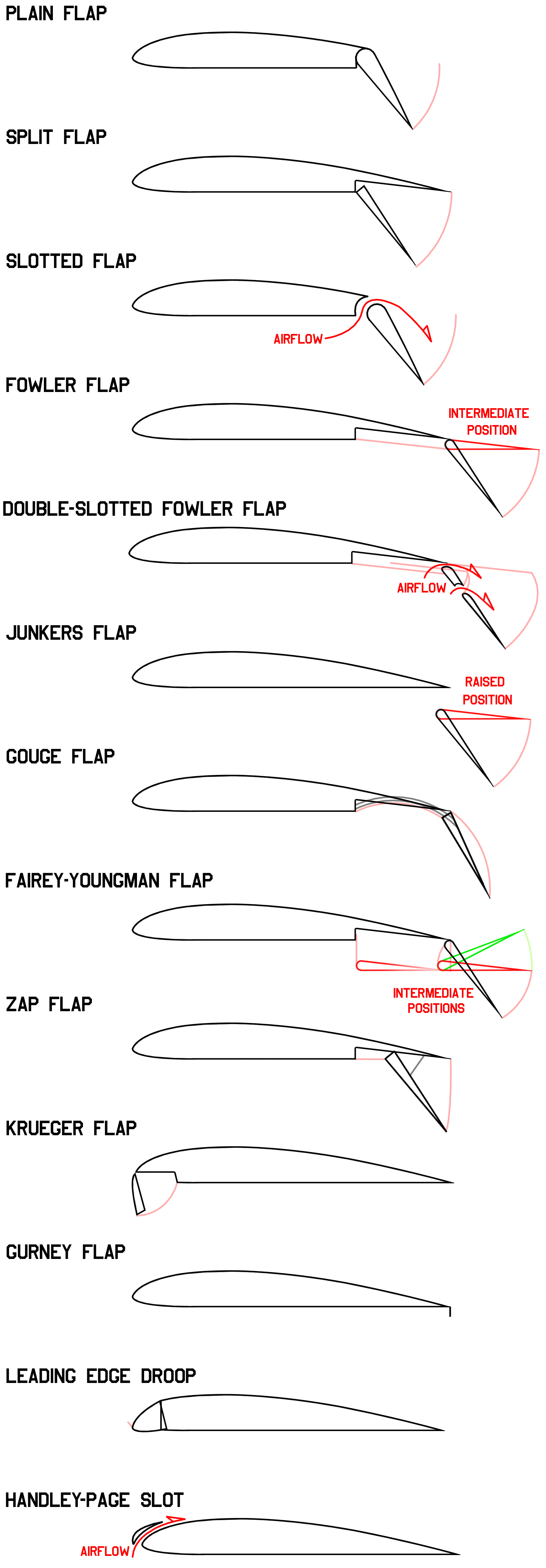
Types of flap

Plain flap
The rear portion of airfoil rotates downwards on a simple hinge mounted at the front of the flap. TheRoyal Aircraft Factory
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a ...
and National Physical Laboratory in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
tested flaps in 1913 and 1914, but these were never installed in an actual aircraft.Taylor 1974, pp. 8–9. In 1916, the Fairey Aviation Company made a number of improvements to a Sopwith Baby they were rebuilding, including their Patent Camber Changing Gear, making the Fairey Hamble Baby as they renamed it, the first aircraft to fly with flaps. These were full span plain flaps which incorporated ailerons, making it also the first instance of flaperons. Fairey were not alone however, as Breguet soon incorporated automatic flaps into the lower wing of their Breguet 14 reconnaissance/bomber in 1917. Owing to the greater efficiency of other flap types, the plain flap is normally only used where simplicity is required.
Split flap
The rear portion of the lower surface of the airfoil hinges downwards from the leading edge of the flap, while the upper surface stays immobile. This can cause large changes in longitudinal trim, pitching the nose either down or up. At full deflection, a split flaps acts much like a spoiler, adding significantly to drag coefficient. It also adds a little to lift coefficient. It was invented by Orville Wright and James M. H. Jacobs in 1920, but only became common in the 1930s and was then quickly superseded. The Douglas DC-1 (progenitor to the DC-3 and C-47) was one of the first of many aircraft types to use split flaps.Slotted flap
A gap between the flap and the wing forces high pressure air from below the wing over the flap helping the airflow remain attached to the flap, increasing lift compared to a split flap. Additionally, lift across the entire chord of the primary airfoil is greatly increased as the velocity of air leaving its trailing edge is raised, from the typical non-flap 80% of freestream, to that of the higher-speed, lower-pressure air flowing around the leading edge of the slotted flap. Any flap that allows air to pass between the wing and the flap is considered a slotted flap. The slotted flap was a result of research at Handley-Page, a variant of the slot that dates from the 1920s, but was not widely used until much later. Some flaps use multiple slots to further boost the effect.Fowler flap
A split flap that slides backwards, before hinging downward, thereby increasing first chord, then camber. The flap may form part of the upper surface of the wing, like a plain flap, or it may not, like a split flap, but it must slide rearward before lowering. As a defining feature – distinguishing it from the Gouge Flap – it always provides a slot effect. Invented byHarlan D. Fowler
Harlan D. Fowler (1895-1982) was an American inventor, writer, and airplane engineer who invented the variable wing area Fowler flap used on many commercial aircraft today.
Fowler flap
The Fowler flap combines a translation and a rotation. T ...
in 1924, and tested by Fred Weick
Fred Ernest Weick (1899–1993) was an airmail pilot, research engineer, and aircraft designer. Working at the NACA, he won the 1929 Collier Trophy for his design of the NACA cowling for radial air-cooled engines. Weick's aircraft designs inc ...
at NACA in 1932. They were first used on the Martin 146 prototype in 1935, and in production on the 1937 Lockheed Super Electra, and are still in widespread use on modern aircraft, often with multiple slots.
Junkers flap
A slotted plain flap fixed below the trailing edge of the wing, and rotating about its forward edge. When not in use, it has more drag than other types, but is more effective at creating additional lift than a plain or split flap, while retaining their mechanical simplicity. Invented by Otto Mader at Junkers in the late 1920s, they were most often seen on theJunkers Ju 52
The Junkers Ju 52/3m (nicknamed ''Tante Ju'' ("Aunt Ju") and ''Iron Annie'') is a transport aircraft that was designed and manufactured by German aviation company Junkers.
Development of the Ju 52 commenced during 1930, headed by German aeron ...
and the Junkers Ju 87 ''Stuka'', though the same basic design can also be found on many modern ultralights, like the Denney Kitfox. This type of flap is sometimes referred to as an external-airfoil flap.
Gouge flap
A type of split flap that slides backward along curved tracks that force the trailing edge downward, increasing chord and camber without affecting trim or requiring any additional mechanisms. It was invented by Arthur Gouge for Short Brothers in 1936 and used on the Short Empire andSunderland
Sunderland () is a port city in Tyne and Wear, England. It is the City of Sunderland's administrative centre and in the Historic counties of England, historic county of County of Durham, Durham. The city is from Newcastle-upon-Tyne and is on t ...
flying boats, which used the very thick Shorts A.D.5 airfoil. Short Brothers may have been the only company to use this type.
Fairey-Youngman flap
Drops down (becoming a Junkers Flap) before sliding aft and then rotating up or down. Fairey was one of the few exponents of this design, which was used on the Fairey Firefly and Fairey Barracuda. When in the extended position, it could be angled up (to a negative angle of incidence) so that the aircraft could be dived vertically without needing excessive trim changes.Zap flap
Commonly, but incorrectly, called the Zapp flap, it was invented by Edward F. Zaparka while he was with Berliner/Joyce and tested on a General Airplanes Corporation Aristocrat in 1932 and on other types periodically thereafter, but it saw little use on production aircraft other than on the Northrop P-61 Black Widow. The leading edge of the flap is mounted on a track, while a point at mid chord on the flap is connected via an arm to a pivot just above the track. When the flap's leading edge moves aft along the track, the triangle formed by the track, the shaft and the surface of the flap (fixed at the pivot) gets narrower and deeper, forcing the flap down.Krueger flap
A hinged flap which folds out from under the wing's leading edge while not forming a part of the leading edge of the wing when retracted. This increases the camber and thickness of the wing, which in turn increases lift and drag. This is not the same as a leading edge droop flap, as that is formed from the entire leading edge. Invented by Werner Krüger in 1943 and evaluated in Goettingen, Krueger flaps are found on many modern swept wing airliners.Gurney flap
A small fixed perpendicular tab of between 1 and 2% of the wing chord, mounted on the high pressure side of the trailing edge of an airfoil. It was named for racing car driver Dan Gurney who rediscovered it in 1971, and has since been used on some helicopters such as theSikorsky S-76B
The Sikorsky S-76 is a medium-size commercial utility helicopter designed and produced by the American helicopter manufacturer Sikorsky Aircraft. It is the company's first helicopter specifically developed for the civilian market.
The S-76 w ...
to correct control problems without having to resort to a major redesign. It boosts the efficiency of even basic theoretical airfoils (made up of a triangle and a circle overlapped) to the equivalent of a conventional airfoil. The principle was discovered in the 1930s, but was rarely used and was then forgotten. Late marks of the Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft used by the Royal Air Force and other Allies of World War II, Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. Many variants of the Spitfire were built, from the Mk 1 ...
used a bead on the trailing edge of the elevators, which functioned in a similar manner.
Leading edge flap
The entire leading edge of the wing rotates downward, effectively increasing camber and also slightly reducing chord. Most commonly found on fighters with very thin wings unsuited to other leading edge high lift devices.Blown flap
A type of Boundary Layer Control System, blown flaps pass engine-generated air or exhaust over the flaps to increase lift beyond that attainable with mechanical flaps. Types include the original (internally blown flap) which blows compressed air from the engine over the top of the flap, the externally blown flap, which blows engine exhaust over the upper and lower surfaces of the flap, and upper surface blowing which blows engine exhaust over the top of the wing and flap. While testing was done in Britain and Germany before theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, and flight trials started, the first production aircraft with blown flaps wasn't until the 1957 Lockheed T2V SeaStar
The Lockheed T2V SeaStar, later called the T-1 SeaStar, is a carrier-capable jet trainer for the United States Navy that entered service in May 1957. Developed from the Lockheed T-33 (itself derived from the Lockheed P-80 Shooting Star), ...
. Upper Surface Blowing was used on the Boeing YC-14 in 1976.
Flexible flap
Also known as the FlexFoil. A modern interpretation of wing warping, internal mechanical actuators bend a lattice that changes the airfoil shape. It may have a flexible gap seal at the transition between fixed and flexible airfoils.Flaperon
A type of aircraft control surface that combines the functions of both flaps andaileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement arou ...
s.
Continuous trailing-edge flap
As of 2014, U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) researchers at NASA's Langley Research Center developed an active-flap design for helicopter rotor blades. The Continuous Trailing-Edge Flap (CTEF) uses components to change blade camber during flight, eliminating mechanical hinges in order to improve system reliability. Prototypes were constructed for wind-tunnel testing. A team from ARL completed a live-fire test of a rotor blade with individual blade control technology in January 2016. The live fire experiments explored the ballistic vulnerability of blade control technologies. Researchers fired three shots representative of typical ground fire on a 7-foot-span, 10-inch-chord rotor blade section with a 4-foot-long CTEF at ARL's Airbase Experimental Facility.Related devices
* Leading edge slats andslot
Slot, the slot or Slots may refer to:
People
* Arne Slot (born 1978), Dutch footballer
* Gerrie Slot (born 1954), Dutch cyclist
* Hanke Bruins Slot (born 1977), Dutch politician
* Tonny Bruins Slot (born 1947), Dutch association football coac ...
s are mounted on the top of the wings' leading edge and while they may be either fixed or retractable, when deployed they provide a slot or gap under the slat to force air against the top of the wing, which is absent on a Krueger flap. They offer excellent lift and enhance controllability at low speeds. Leading edge slats allow the wing to fly at a higher angle of attack which decrease takeoff and landing distances. Other types of flaps may be equipped with one or more slots to increase their effectiveness, a typical setup on many modern airliners. These are known as slotted flaps as described above. Frederick Handley Page experimented with fore and aft slot designs in the 20s and 30s.
* Spoilers are intended to create drag and reduce lift by "spoiling" the airflow over the wing. A spoiler is much larger than a Gurney flap, and can be retracted. Spoilers are usually installed mid chord on the upper surface of the wing, but may also be installed on the lower surface of the wing as well.
* Air brakes are used to increase drag, allowing the aircraft to decelerate rapidly. When installed on the wings they differ from flaps and spoilers in that they are not intended to modify the lift and are built strongly enough to be deployed at much higher speeds.
* Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement arou ...
s are similar to flaps (and work the same way), but are intended to provide lateral control, rather than to change the lifting characteristics of both wings together, and so operate differentially – when an aileron on one wing increases the lift, the opposite aileron does not, and will often work to decrease lift. When ailerons are designed to lower in conjunction with flaps, they are usually called flaperons, while those that spoil lift (typically placed on the upper surface before the trailing edge) they are called spoilerons.
Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the 707 in October 1958, Pan Am wanted a jet times its size, ...
extended for landing
File:Kitfox Lite.jpg, Junkers flaps, doubling as ailerons.
See also
* Air brake (aeronautics) *Aircraft flight control system
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft flight control system consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction in flight. Aircraf ...
*Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement arou ...
*Body flaps
Starship is a fully reusable, super heavy-lift launch vehicle under development by SpaceX, an American aerospace company. With more than twice the thrust of the Saturn V, it is designed to be the most powerful launch vehicle ever built and the ...
, a type of high-drag set of aerosurfaces designed for very high angle-of-attack descent of rocket-powered vehicles, particularly used during atmospheric entry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the ...
of space vehicles. Body flaps are being designed to bleed off as much kinetic and potential energy as possible during a near-vertical descent through the atmosphere.
* Circulation control wing
* High-lift device
* Leading-edge slat
References
Bibliography
* * Gunston, Bill, The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary Cambridge, Cambridge University Press 2004, / * Windrow, Martin C. and René J. Francillon. ''The Nakajima Ki-43 Hayabusa''. Leatherhead, Surrey, UK: Profile Publications, 1965. {{DEFAULTSORT:Flap (Aircraft) Aircraft controls Aircraft wing components