|
Arthur Gouge
Sir Arthur Gouge (3 July 1890 – 14 October 1962) was a British engineer and aircraft designer from Kent, who worked notably for Short Brothers where he designed the "C-class" Empire and Sunderland flying boats. Early life He was born in Northfleet, Kent to Elizabeth (née Wickham) and George Gouge. His father George (who was born about 1862 in Sittingbourne, Kent) was a Methodist preacher. He had an older brother George (born 1889), a younger sister Grace (born 1896) and two younger brothers Hubert (born 1893) and Walter (born 1899). He attended Gravesend Technical School (now Gravesend Grammar School) then Woolwich Polytechnic. Career As he did not like school he left it at the age of 13 and took up a carpentry apprenticeship with a firm of builders. Once working he however soon developed a desire for learning and began studying engineering and mathematics at night school. This was eventually to lead to him obtaining a B.Sc. degree. Shorts He joined Short brothers in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces the French department of Pas-de-Calais across the Strait of Dover. The county town is Maidstone. It is the fifth most populous county in England, the most populous non-Metropolitan county and the most populous of the home counties. Kent was one of the first British territories to be settled by Germanic tribes, most notably the Jutes, following the withdrawal of the Romans. Canterbury Cathedral in Kent, the oldest cathedral in England, has been the seat of the Archbishops of Canterbury since the conversion of England to Christianity that began in the 6th century with Saint Augustine. Rochester Cathedral in Medway is England's second-oldest cathedral. Located between London and the Strait of Dover, which separates England from mainla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Sunderland
The Short S.25 Sunderland is a British flying boat patrol bomber, developed and constructed by Short Brothers for the Royal Air Force (RAF). The aircraft took its service name from the town (latterly, city) and port of Sunderland in North East England. Developed in parallel with the civilian S.23 ''Empire'' flying boat, the flagship of Imperial Airways, the Sunderland was developed specifically to conform to the requirements of British Air Ministry Specification R.2/33 for a long-range patrol/reconnaissance flying boat to serve with the Royal Air Force (RAF). As designed, it served as a successor to the earlier Short Sarafand flying boat. Sharing several similarities with the S.23, it featured a more advanced aerodynamic hull and was outfitted with various offensive and defensive armaments, including machine gun turrets, bombs, aerial mines, and depth charges. The Sunderland was powered by four Bristol Pegasus XVIII radial engines and was outfitted with various detection equi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Fedden
Sir Alfred Hubert Roy Fedden MBE, FRAeS (6 June 1885 – 21 November 1973) was an engineer who designed most of Bristol Engine Company's successful piston aircraft engine designs. Early life Fedden was born in the Bristol area to fairly wealthy and influential parents. His older brother was the artist Romilly Fedden. Fedden's family was the first in the area to own a car, an interesting parallel with fellow engine designer, Harry Ricardo. This early influence almost certainly led to his future career. Fedden attended Clifton College, but did not do well scholastically and was known primarily for sports. After leaving, he declined to enter the Army, and announced he would apprentice as an engineer. Apprenticeship His apprenticeship was completed in 1906, and he immediately designed a complete car. He managed to convince the local firm of Brazil Straker to hire him, and the design was produced as the successful Shamrock. He remained at Brazil Straker over the following years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Aeronautical Society
The Royal Aeronautical Society, also known as the RAeS, is a British multi-disciplinary professional institution dedicated to the global aerospace community. Founded in 1866, it is the oldest aeronautical society in the world. Members, Fellows, and Companions of the society can use the post-nominal letters MRAeS, FRAeS, or CRAeS, respectively. Function The objectives of The Royal Aeronautical Society include: to support and maintain high professional standards in aerospace disciplines; to provide a unique source of specialist information and a local forum for the exchange of ideas; and to exert influence in the interests of aerospace in the public and industrial arenas, including universities. The Royal Aeronautical Society is a worldwide society with an international network of 67 branches. Many practitioners of aerospace disciplines use the Society's designatory post-nominals such aFRAeS CRAeS, MRAeS, AMRAeS, and ARAeS (incorporating the former graduate grade, GradRAeS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffith Brewer
Griffith Brewer (23 July 1867–1 March 1948)Penrose 1967, p.575 was an English balloonist, aviator and patent agent. He was also a founding member of the Royal Aero Club. He became a friend of the Wright Brothers, and was one of their main supporters."Grace's Guide To British Industrial History: Biographies: Griffith Brewer." Retrieved 24 July 2018. On 8 October 1908 at Camp d'Auvours, France, 11 Kilometers east of Le Mans, Griffith flew as a passenger with Wilbur Wright. The flight lasted for 4 minutes and 22 seconds. In doing so, he became the first Englishman to go up in an aeroplane.Dr. Richard Stimso [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Lipscomb
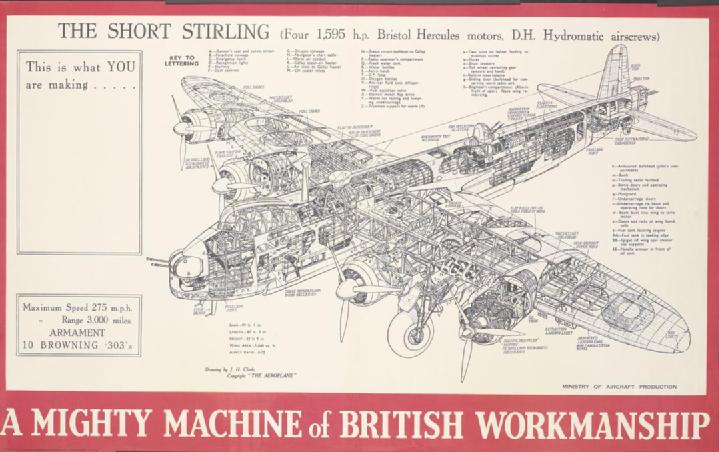
Claude Percival Thomas Lipscomb (1887- 11 April 1974) FRAeS was a British engineer and aircraft designer, who designed the RAF Bomber Command's first four-engined heavy bomber, the Short Stirling (S.29). Early life C.P.T. Lipscomb was born on Portsea Island. Career Shorts He joined Short Brothers in 1914 in Kent, then he later designed airships at Bedford from 1916 to 1921. By the late 1930s he was assistant chief designer. He became chief designer in 1943. Short Stirling The Short Stirling, which he designed with Arthur Gouge, first flew, as ''L7600'', on 14 May 1939 with John Lankester Parker, the Short Chief Test Pilot. The aircraft was designed in response to the Air Ministry Directive B.12/36. It had Bristol Hercules I radial engines. The second prototype, ''L7605'', flew on 3 December 1939. The Stirling Mk 1 entered service in August 1940, with 756 being made. 1,047 were made of the Stirling Mk II, which entered service in 1942. He later designed a possible transatlantic fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Birthday Honours
The 1948 Birthday Honours were appointments by King George VI to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by citizens of the Commonwealth Realms. The appointments were made to celebrate the official birthday of the King, and were published in ''The London Gazette'' on 4 June.Mine and Bomb Disposal list: The recipients of honours are displayed here as they were styled before their new honour, and arranged by honour, with classes (Knight, Knight Grand Cross, ''etc.'') and then divisions (Military, Civil, ''etc.'') as appropriate. United Kingdom and British Empire Baron *Colonel Sir Alfred Edward Webb-Johnson , President of the Royal College of Surgeons of England since 1941, ''by the name, style and title of Baron Webb-Johnson, of Stoke-on-Kent in the County of Stafford''. *Sir William Francis Kyffin Taylor , Presiding Judge of the Liverpool Court of Passage, 1931—April, 1948; railway and Canal Commissioner since 1930, ''by the name, style and title of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westland Aircraft
Westland Aircraft was a British aircraft manufacturer located in Yeovil, Somerset. Formed as a separate company by separation from Petters Limited just before the start of the Second World War, Westland had been building aircraft since 1915. During the war the company produced a number of generally unsuccessful designs, but their Lysander would serve as an important liaison aircraft with the Royal Air Force. After the war the company focused on helicopters, and was merged with several other British firms to create Westland Helicopters in 1961. History Foundation In 1915 the Westland Aircraft Works was founded as a division of Petters in response to government orders for the construction under licence of initially 12 Short Type 184 seaplanes, followed by 20 Short Admiralty Type 166. Orders for other aircraft followed during First World War, including the Sopwith 1½ Strutter, the de Havilland designed Airco DH.4, Airco DH.9 and Airco DH.9A and the Vickers Vimy. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1941 Committee
{{Use British English, date=January 2013 The 1941 Committee was a group of British politicians, writers and other people of influence who got together in 1940. Its members comprised liberals, and those further left, who were not generally involved with a political party. Its immediate purpose was to press for more efficient production in order to enhance the war effort. This swiftly developed into discussion of the methods and mores by which the United Kingdom would be governed after World War II. The members met at the home of Edward Hulton, the publisher of ''Picture Post''. Members The committee's members included: *Richard Acland *David Astor * Thomas Balogh *Vernon Bartlett *Violet Bonham Carter *Tom Driberg *Michael Foot *Raymond Gauntlett, Secretary *Victor Gollancz *Eva Hubback *Edward Hulton *Julian Huxley * Margaret Storm Jameson *Douglas Jay * David Low *Kingsley Martin *Christopher Mayhew * J. B. Priestley, chairman *Ritchie Calder *Peter Thorneycroft * Richard Titmuss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
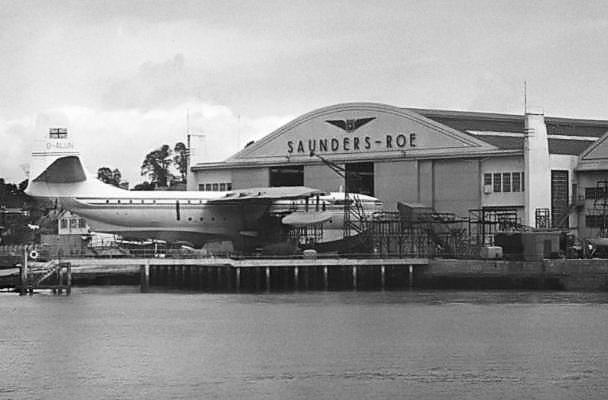
Saunders-Roe Princess
The Saunders-Roe SR.45 Princess was a British flying boat aircraft developed and built by Saunders-Roe at their Cowes facility on the Isle of Wight. It has the distinction of being the largest all-metal flying boat to have ever been constructed. The Princess had been developed to serve as a larger and more luxurious successor to the pre-war commercial flying boats, such as the Short Empire. It was intended to serve the transatlantic route, carrying up to 100 passengers between Southampton, United Kingdom and New York City, United States in spacious and comfortable conditions. To achieve this, it was decided early on to make use of newly developed turboprop technology, opting for the Bristol Proteus engine still in development to power the aircraft. The project suffered delays due to difficulties encountered in the development of the Proteus engine. On 22 August 1952, the first prototype Princess, ''G-ALUN'', conducted its maiden flight. Between 1952 and 1954, the first prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saunders-Roe
Saunders-Roe Limited, also known as Saro, was a British aero- and marine-engineering company based at Columbine Works, East Cowes, Isle of Wight. History The name was adopted in 1929 after Alliott Verdon Roe (see Avro) and John Lord took a controlling interest in the aircraft and boat-builders S. E. Saunders. Prior to this (excepting for the Sopwith/Saunders Bat Boat) the products were Saunders, the A4 Medina for example dating from 1926. Sam Saunders the founder developed the Consuta material used in marine and aviation craft. The Saunders-Roe interest in aviation didn’t prevent the firm from continuing with the boatbuilding activities associated with S. E. Saunders Ltd Saunders Roe concentrated on producing flying-boats, but none were produced in very large quantities – the longest run being 31 Londons. They also produced hulls for the Blackburn Bluebird. During the Second World War Saro manufactured Supermarine Walrus and Supermarine Sea Otters. Their w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gouge Flap
The Gouge flap, invented by Arthur Gouge of Short Brothers in 1936, allowed the pilot to increase both the wing area and the chord of an aircraft's wing, thereby reducing the stalling speed at a given weight. This provided the benefit of a shorter takeoff distance for a given load, a shorter distance to achieve a given height and a lower takeoff speed. This type of flap, in spite of its use on successful aircraft such as the Short Sunderland and the Short Stirling, was limited to use on aircraft produced by Short Brothers. __TOC__ Development The Gouge flap was patented in 1936, British Patent no. 443,516 being awarded jointly to Short Bros. Ltd. and Arthur Gouge for "Improvements in or connected with Wings for Aircraft, (controller flaps)". The Gouge flap "consists of a sharp nosed aerofoil, which in the closed position, forms part of the wing profile . The flap tapers with the wing, i.e. the width of the flap at any point is a constant proportion of the wing chord at that point; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |