|
Karma Tseten
Karma Tseten (; ) (died 1599), also known as Zhingshak Tseten Dorje () was a king of Upper Tsang in West Central Tibet. He was the founder of the Tsangpa Dynasty, that had an important role in the history of Tibet from 1565 to 1642. Karma ruled during the period 1565–1599. Rebelling against the Rinpungpa Karma Tseten, in full Karma Tseten Dorje, belonged to a clan from Nyag which claimed descent from Jñanakumara, a disciple of the eighth-century tantric master Padmasambhava. In fact he does not seem to have belonged to any noble house. At this time the Rinpungpa Dynasty held superior power in the Tsang region and was somehow related to Karma Tseten's lineage. Coming from relatively modest circumstances, Karma Tseten was used by the Tsang ruler for various tasks, such as chief groom and tax collector. In 1548 he was entrusted with the governorship of the Samdrubtse castle in Shigatse. This was a place of great strategical importance in Tsang. Some years later he began to plot aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
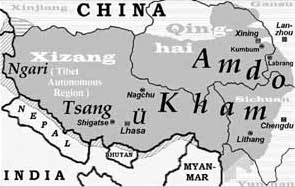
Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered the south-central of the Tibetan cultural area, including the Brahmaputra River watershed. The western districts surrounding and extending past Mount Kailash are included in Ngari, and much of the vast Changtang plateau to the north. The Himalayas defined Ü-Tsang's southern border. The present Tibet Autonomous Region corresponds approximately to what was ancient Ü-Tsang and western Kham. Ü-Tsang was formed by the merging of two earlier power centers: Ü () in central Tibet, controlled by the Gelug lineage of Tibetan Buddhism under the early Dalai Lamas, and Tsang () which extended from Gyantse to points west, controlled by the rival Sakya lineage. Military victories by the powerful Khoshut Mongol Güshi Khan that backed 5th Dalai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngawang Jigme Drakpa
Ngawang Jigme Drakpa () (died 1597) was the last ruling prince of Tsang (West Central Tibet) of the Rinpungpa Dynasty. He was also a renowned author. His increasingly chaotic reign ended in 1565, when the Tsangpa dynasty deprived the Rinpungpa of their main possessions. Early years Ngawang Jigme Drakpa was the third son of the Rinpungpa prince Ngawang Namgyal. The chronological tables of Sumpa Khanpo allege that he was born in the Water-Tiger year 1482, which is unlikely. According to his own account, his youth was not entirely happy: he grew up with great intellectual interests but was left without attention by his highly revered father, and was not entrusted with administrative responsibilities. The eldest living brother Dondup Tseten Dorje may have taken over the possessions of his father at the latter's death in 1544 (or later). The details of the succession are however obscure since another brother called Rinchen Wanggyal is said to have been entrusted with the rulership when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakya (Tibetan Buddhist School)
The ''Sakya'' (, 'pale earth') school is one of four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism, the others being the Nyingma, Kagyu, and Gelug. It is one of the Red Hat Orders along with the Nyingma and Kagyu. Origins Virūpa, 16th century. It depicts a famous episode in his hagiography when he stopped the sun in the sky. The name ''Sakya'' ("pale earth") derives from the unique grey landscape of the Ponpori Hills in southern Tibet near Shigatse, where Sakya Monastery, the first monastery of this tradition, and the seat of the Sakya School was built by Khon Konchog Gyalpo (1034–1102) in 1073. The Sakya tradition developed during the second period of translation of Buddhist scripture from Sanskrit into Tibetan in the late 11th century. It was founded by Drogmi, a famous scholar and translator who had studied at the Vikramashila directly under Naropa, Ratnākaraśānti, Vagishvakirti and other great panditas from India for twelve years. Khon Konchog Gyalpo became Drogmi's disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonang
The Jonang () is one of the schools of Tibetan Buddhism. Its origins in Tibet can be traced to early 12th century master Yumo Mikyo Dorje, but became much wider known with the help of Dolpopa Sherab Gyaltsen, a monk originally trained in the Sakya school. The Jonang school’s main practice comes from the Kalachakra cycle. The Jonang re-established their religio-political center in Golok, Nakhi and Mongol areas of Kham and Amdo with the school's seat () at Dzamtang Tsangwa () dzong and have continued practicing uninterrupted to this day. An estimated 5,000 monks and nuns of the Jonang tradition practice today in these areas. However, their teachings were limited to these regions until the Rimé movement of the 19th century encouraged the study of non-Gelug schools of thought and practice.Gruschke 2001, p.72 History The monk Künpang Tukjé Tsöndrü (, 1243–1313) established a kumbum or stupa-vihara in the Jomonang Valley about northwest of the Tashilhunpo Monastery in Ü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wangchuk Dorje
Wangchuk Dorje (1556–1603) was the ninth Gyalwa Karmapa, head of the Kagyu School of Tibetan Buddhism. Wangchuk Dorje was born in Treshod, Kham. According to legend, he said after being born: "I am Karmapa." Other sources say that soon after his birth he sat cross-legged for three days and declared he was the Karmapa. He received his education from Shamar Köncho Yenlak, the fifth Shamarpa, in a nomadic camp which traveled through Tibet but also passed through present day Mongolia and Bhutan. During his travels many monasteries were founded. Wangchuk Dorje also wrote many classic Buddhist texts, many of which are still being taught todaBiography of the 9th Karmapa Wangchuk Dorje was not only a spiritual leader, but also a mediator in conflicts. He was invited by the king of Sikkim to settle a dispute and while there he founded three monasteries one of them being in Rumtek which is currently the most important monastery of the lineage after the Chinese occupation of Tibet. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karmapa
The Karmapa (honorific title '' His Holiness the Gyalwa'' ��ྒྱལ་བ་, Victorious One''Karmapa'', more formally as ''Gyalwang'' ��ྒྱལ་དབང་ཀརྨ་པ་, King of Victorious Ones''Karmapa'', and informally as the ''Karmapa Lama'') is the head of the Karma Kagyu, the largest sub-school of the Kagyu (བཀའ་བརྒྱུད, ), itself one of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. Karmapa was Tibet's first consciously incarnating lama. The historical seat of the Karmapas is Tsurphu Monastery in the Tolung valley of Tibet. The Karmapa's principal seat in exile is the Dharma Chakra Centre at Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim, India. His regional monastic seats are Karma Triyana Dharmachakra in New York and Dhagpo Kagyu Ling in Dordogne, France. Due to a controversy within the Karma Kagyu school over the recognition process, the identity of the current 17th Karmapa is disputed by some. See Karmapa controversy for details. Origin of the lineage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karma Kagyu
Karma Kagyu (), or Kamtsang Kagyu (), is a widely practiced and probably the second-largest lineage within the Kagyu school, one of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. The lineage has long-standing monasteries in Tibet, China, Russia, Mongolia, India, Nepal and Bhutan, with current centres in over 60 countries. The spiritual head of the Karma Kagyu is the ''Gyalwa Karmapa''; the 2nd through 10th Karmapas were principal spiritual advisors to successive emperors of China. The Karma Kagyu are sometimes called the "Black Hat" lamas, in reference to the Black Crown worn by the Karmapa. The Kagyu lineage claims a continuity of oral instructions transmitted from master to disciple.La Lignée du Rosaire d’Or' (“The golden rosary lineage”). This emphasis is reflected in the literal meaning of ''Kagyu''. The first syllable, ''ka,'' is said to refer to the texts of Buddha's teachings and to the master's verbal instructions. ''Ka'' has the double meaning of the enlightened meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelugpa
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodhgaya (India). The Gelug (, also Geluk; "virtuous")Kay, David N. (2007). ''Tibetan and Zen Buddhism in Britain: Transplantation, Development and Adaptation,'' p. 39. Routledge. is the newest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. It was founded by Je Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), a Tibetan philosopher, tantric yogi and lama and further expanded and developed by his disciples (such as Khedrup Je, Gyaltsap Je and Gendün Drubpa). The Gelug school is alternatively known as New Kadam (''bKa’-gdams gsar-pa''), since it sees itself as a continuation of the Kadam tradition of Atisha (c. 11th century). Furthermore, it is also called the Ganden school, after the first monastery established by Tsongkhapa. The Ganden Tripa ("Ganden Throne Holder") is the official head of the school, though its most influential figure is the Dalai Lama ("Ocean Teacher"). Allying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Kingdom
While the Tibetan plateau has been inhabited since pre-historic times, most of Tibet's history went unrecorded until the introduction of Tibetan Buddhism around the 6th century. Tibetan texts refer to the kingdom of Zhangzhung (c. 500 BCE – 625 CE) as the precursor of later Tibetan kingdoms and the originators of the Bon religion. While mythical accounts of early rulers of the Yarlung Dynasty exist, historical accounts begin with the introduction of Buddhism from India in the 6th century and the appearance of envoys from the unified Tibetan Empire in the 7th century. Following the dissolution of the empire and a period of fragmentation in the 9th-10th centuries, a Buddhist revival in the 10th–12th centuries saw the development of three of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. After a period of control by the Mongol Empire and Yuan dynasty, Tibet became effectively independent in the 14th century and was ruled by a succession of noble houses for the next 300 years. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarat Chandra Das
Sarat Chandra Dash ( bn, শরৎচন্দ্র দাশ) (18 July 1849 – 5 January 1917) was an Indian scholar of Tibetan language and culture most noted for his two journeys to Tibet in 1879 and in 1881–1882. Biography Born in Chittagong, eastern Bengal to a Bengali Hindu Vaidya-Brahmin family, Sarat Chandra Dash attended Presidency College, as a student of the University of Calcutta. In 1874 he was appointed headmaster of the Bhutia Boarding School at Darjeeling. In 1878, a Tibetan teacher, Lama Ugyen Gyatso arranged a passport for Sarat Chandra to go the monastery at Tashilhunpo. In June 1879, Das and Ugyen-gyatso left Darjeeling for the first of two journeys to Tibet. They remained in Tibet for six months, returning to Darjeeling with a large collection of Tibetan and Sanskrit texts which would become the basis for his later scholarship. Sarat Chandra spent 1880 in Darjeeling poring over the information he had obtained. In November 1881, Sarat Chandra and Ugye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bainang County
Bainang County (; ) is a county of Xigazê in the Tibet Autonomous Region The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a Provinces of China, province-level Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China in Southwest China. I .... Towns and townships * Norbu Khyungtse Town (, ) * Gadong Town (, ) * Pältsel Township (, ) * Mak Township (, ) * Wangden Township (, ) * Qunub Township (, ) * Düjung Township (, ) * Jangtö Township (, ) * Gabug Township (, ) * Tashar Township (, ) * Tongshé Township (, ) Counties of Tibet Shigatse {{Shigatse-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)