|
Karl Thiersch
Karl Thiersch, also spelled Carl Thiersch (20 April 1822 – 28 April 1895), was a German surgeon born in Munich. His father was educationist Friedrich Thiersch, his father-in-law was renowned chemist Justus von Liebig. One brother, Ludwig, was an influential painter, while another, Heinrich Wilhelm Josias, was a theologian. He received his doctorate from the University of Munich in 1843, where from 1848 to 1854 he served as prosector of pathological anatomy. Afterwards he became a professor of surgery at the Universities of Erlangen (from 1854) and Leipzig (from 1867). He was a medical surgeon in the First War of Schleswig under Louis Stromeyer (1804–1876), and a medical consultant during the Franco-Prussian War. In 1865 Thiersch demonstrated the epithelial origin of carcinoma, which put him in opposition to the doctrine of Rudolf Virchow in that a carcinoma could originate from connective tissue. Thiersch's findings were thus agreed upon by research done by Wilhelm v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow (; or ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder of social medicine, and to his colleagues, the "Pope of medicine". Virchow studied medicine at the Friedrich Wilhelm University under Johannes Peter Müller. While working at the Charité hospital, his investigation of the 1847–1848 typhus epidemic in Upper Silesia laid the foundation for public health in Germany, and paved his political and social careers. From it, he coined a well known aphorism: "Medicine is a social science, and politics is nothing else but medicine on a large scale". His participation in the Revolution of 1848 led to his expulsion from Charité the next year. He then published a newspaper ''Die Medizinische Reform'' (''The Medical Reform''). He took the first Chair of Pathological Anatomy at the University of Wü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Named It
''Whonamedit?'' is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliographies. The dictionary is hosted in Norway and maintained by medical historian Ole Daniel Enersen Ole Daniel Enersen (born March 14, 1943, in Oslo, Norway) is a Norwegian climber, photographer, journalist, writer, and medical historian. In 1965 he made the first ascent of the Trollveggen mountain in Romsdalen, Norway, along with Leif Norman .... References External links * Medical websites Medical dictionaries Eponyms {{online-dict-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Von Volkmann
Richard von Volkmann (17 August 1830 – 28 November 1889) was a prominent German surgeon and author of poetry and fiction. Some of his works were illustrated by his son, Hans, a well known artist. Biography He was born in Leipzig on 17 August 1830, the son of physiologist A.W. Volkmann. Richard entered medical school in Berlin and graduated in 1854. In 1867 he was appointed Professor of Surgery and Director of the Surgical Clinic at Halle where he remained until retirement. He was one of the most prominent surgeons of his day. He died in Jena. Achievements * Performed the first excision of carcinoma of the rectum in 1878. * Described Volkmann's Ischaemic Contracture in 1881. * Devised a splint and a spoon which bear his name. * His treatment of articular tuberculosis heralded attempts at preventive surgery. * In 1894 he described three patients with scrotal cancer who worked with paraffin and tar. * He was an early supporter of Joseph Lister, and helped the introduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Léopold Ollier
Louis Xavier Édouard Léopold Ollier (; 2 December 1830 – 26 November 1900) was a French surgeon, known for his pioneering work in reconstructive surgery and orthopedics. Biography Ollier was born in Les Vans, department of Ardèche. His father and grandfather were also physicians. Initially he studied natural sciences at Montpellier, and in 1851 began work as medical interne at Lyon Hospital. In 1857 he earned his medical doctorate in Paris, and in 1860 became chief-surgeon at the Hôtel-Dieu in Lyon. In 1877 he became a professor of clinical surgery. Following Ollier's death in 1900, his position at Lyon was filled by surgeon Mathieu Jaboulay (1860–1913). Ollier is famous for his work in bone and joint surgery. He became internationally known for developing techniques involving bone- resection, and is remembered for his extensive research of regeneration of bone by the periosteum following resection. He was a pioneer in the field of bone grafting, and also devised a surgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
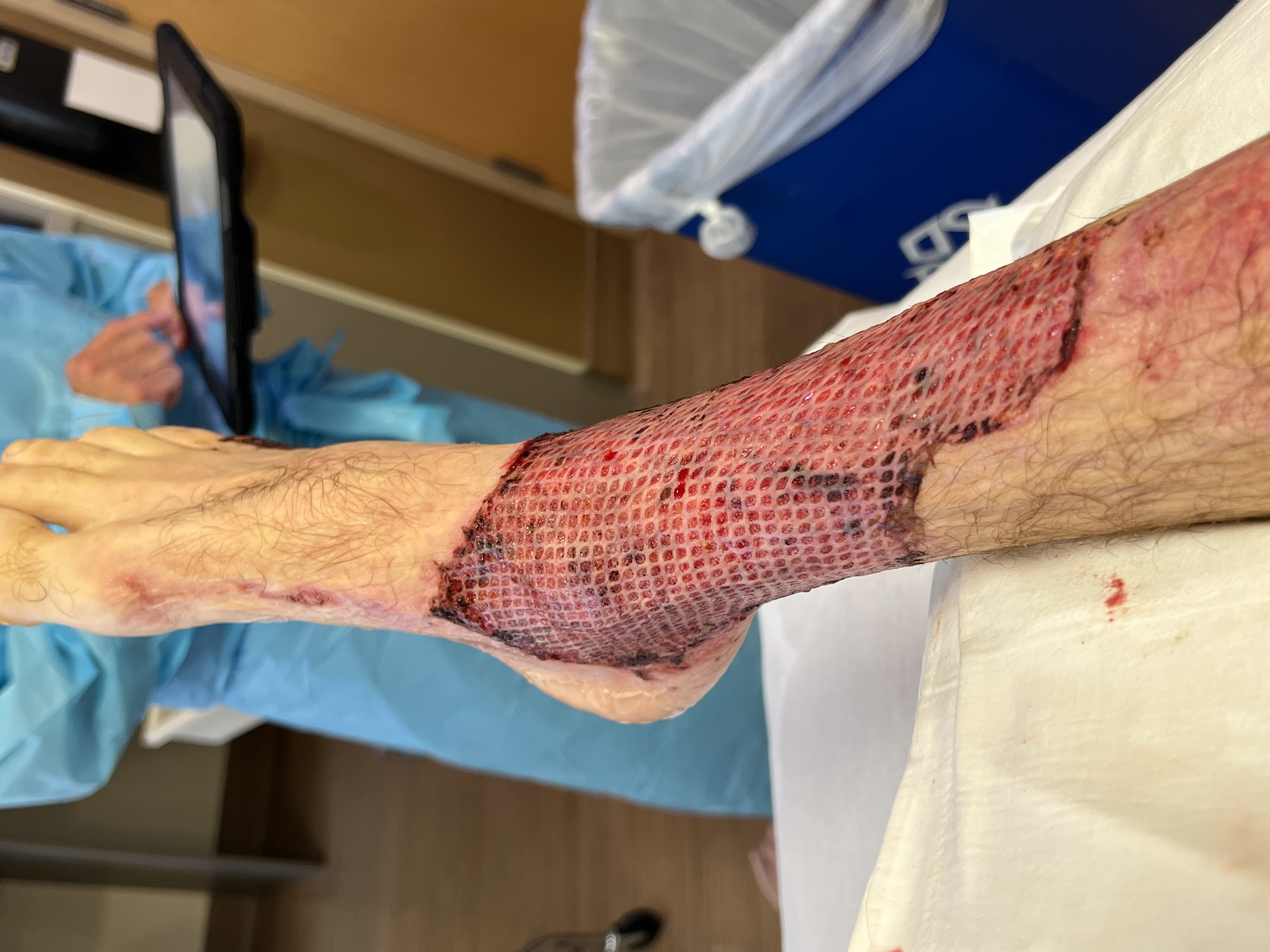
Skin Grafting
Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft. Surgeons may use skin grafting to treat: * extensive wounding or trauma * burns * areas of extensive skin loss due to infection such as necrotizing fasciitis or purpura fulminans * specific surgeries that may require skin grafts for healing to occur - most commonly removal of skin cancers Skin grafting often takes place after serious injuries when some of the body's skin is damaged. Surgical removal (excision or debridement) of the damaged skin is followed by skin grafting. The grafting serves two purposes: reducing the course of treatment needed (and time in the hospital), and improving the function and appearance of the area of the body which receives the skin graft. There are two types of skin grafts: * The more common type involves removing a thin layer of skin from a healthy part of the body (the donor section) - like peeling a potato. * A full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phossy Jaw
Phossy jaw, formally known as phosphorus necrosis of the jaw, was an occupational disease affecting those who worked with white phosphorus (also known as ''yellow phosphorus'') without proper safeguards. It was most commonly seen in workers in the matchstick industry in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It was caused by white phosphorus vapor, which destroys the bones of the jaw. Modern occupational hygiene practices have since eliminated the working conditions that caused this disease. Symptoms Those with phossy jaw would usually begin suffering painful toothaches and swelling of the gums. The pain was characterized as "persistent yet progressive ... spreading to neighboring teeth and jawbone". Over time, pus formation developed penetrating the oral mucosa with the formation of fistula, tooth loss, and recurrent abscesses. Further progression led to the formation of sequestrum (dead bone that has separated from living bone) after three months and necrosis of the jaw within six m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound Healing
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue. In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier against the external environment. When the barrier is broken, a regulated sequence of biochemical events is set into motion to repair the damage. This process is divided into predictable phases: blood clotting (hemostasis), inflammation, tissue growth ( cell proliferation), and tissue remodeling (maturation and cell differentiation). Blood clotting may be considered to be part of the inflammation stage instead of a separate stage. The wound healing process is not only complex but fragile, and it is susceptible to interruption or failure leading to the formation of non-healing chronic wounds. Factors that contribute to non-healing chronic wounds are diabetes, venous or arterial disease, infection, and metabolic deficiencies of old age.Enoch, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbolic Acid
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 billion kg/year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceutical drugs. Properties Phenol is an organic compound appreciably soluble in water, with about 84.2 g dissolving in 1000 mL (0.895 M). Homogeneous mixtures of phenol and water at phenol to wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin ''salix'' for willow tree. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. Uses Medicine Salicylic acid as a medication is commonly used to remove the outer layer of the skin. As such, it is used to treat warts, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, ringworm, dandruff, and ichthyosis. Similar to other hydroxy acids, salicylic acid is an ingredient in many skincare products for the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, psoriasis, calluses, corns, keratosis pilaris, acanthosis nigricans, ichthyosis, and warts. Uses in manufacturing Salicylic acid is used as a food preservative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery The widespread introduction of antiseptic surgical methods was initiated by the publishing of the paper ''Antiseptic Principle of the Practice of Surgery'' in 1867 by Joseph Lister, which was inspired by Louis Pasteur's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister
Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, (5 April 182710 February 1912) was a British surgeon, medical scientist, experimental pathologist and a pioneer of antiseptic surgery and preventative medicine. Joseph Lister revolutionised the craft of surgery in the same manner that John Hunter revolutionised the science of surgery. From a technical viewpoint, Lister was not an exceptional surgeon, but his research into bacteriology and infection in wounds raised his operative technique to a new plane where his observations, deductions and practices revolutionised surgery throughout the world. Lister's contribution to the fields of physiology, pathology and surgery were four-fold. He promoted the principle of antiseptic surgical care and wound management while working as a surgeon at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary by successfully introducing phenol (then known as carbolic acid) to sterilise surgical instruments, the patient's skin, sutures, the surgeon's hands and the ward. Secondly he r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |