|
Louis Léopold Ollier
Louis Xavier Édouard Léopold Ollier (; 2 December 1830 – 26 November 1900) was a French surgeon, known for his pioneering work in reconstructive surgery and orthopedics. Biography Ollier was born in Les Vans, department of Ardèche. His father and grandfather were also physicians. Initially he studied natural sciences at Montpellier, and in 1851 began work as medical interne at Lyon Hospital. In 1857 he earned his medical doctorate in Paris, and in 1860 became chief-surgeon at the Hôtel-Dieu in Lyon. In 1877 he became a professor of clinical surgery. Following Ollier's death in 1900, his position at Lyon was filled by surgeon Mathieu Jaboulay (1860–1913). Ollier is famous for his work in bone and joint surgery. He became internationally known for developing techniques involving bone- resection, and is remembered for his extensive research of regeneration of bone by the periosteum following resection. He was a pioneer in the field of bone grafting, and also devised a surgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Vans
Les Vans (; oc, Los Vans) is a commune in the Ardèche department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of southern France. Geography The village of Les Vans, the principal settlement of the canton of the same name in the south of the Ardèche, lies at the centre of a basin near the Chassezac river. Dominant to the south is the Serre de Barre, the last western summit of the Cévennes du Bas-Vivarais range. In 2001, Les Vans became the "gateway town" of the Monts d'Ardèche Natural Regional Park. The village is a tourist haven in summer; a traditional market is held every Saturday morning. A night-time craft market is held on summer Tuesdays at the Place de la Fontaine. Many activities are available in the vicinity of Les Vans: walking, climbing, caving, horse riding, canyoning, swimming, fishing and kayaking in the Chassezac gorges. History Les Vans was a dependency of the Abbey of Saint-Gilles. The town became Protestant in the 16th century; in 1629 it returned to Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
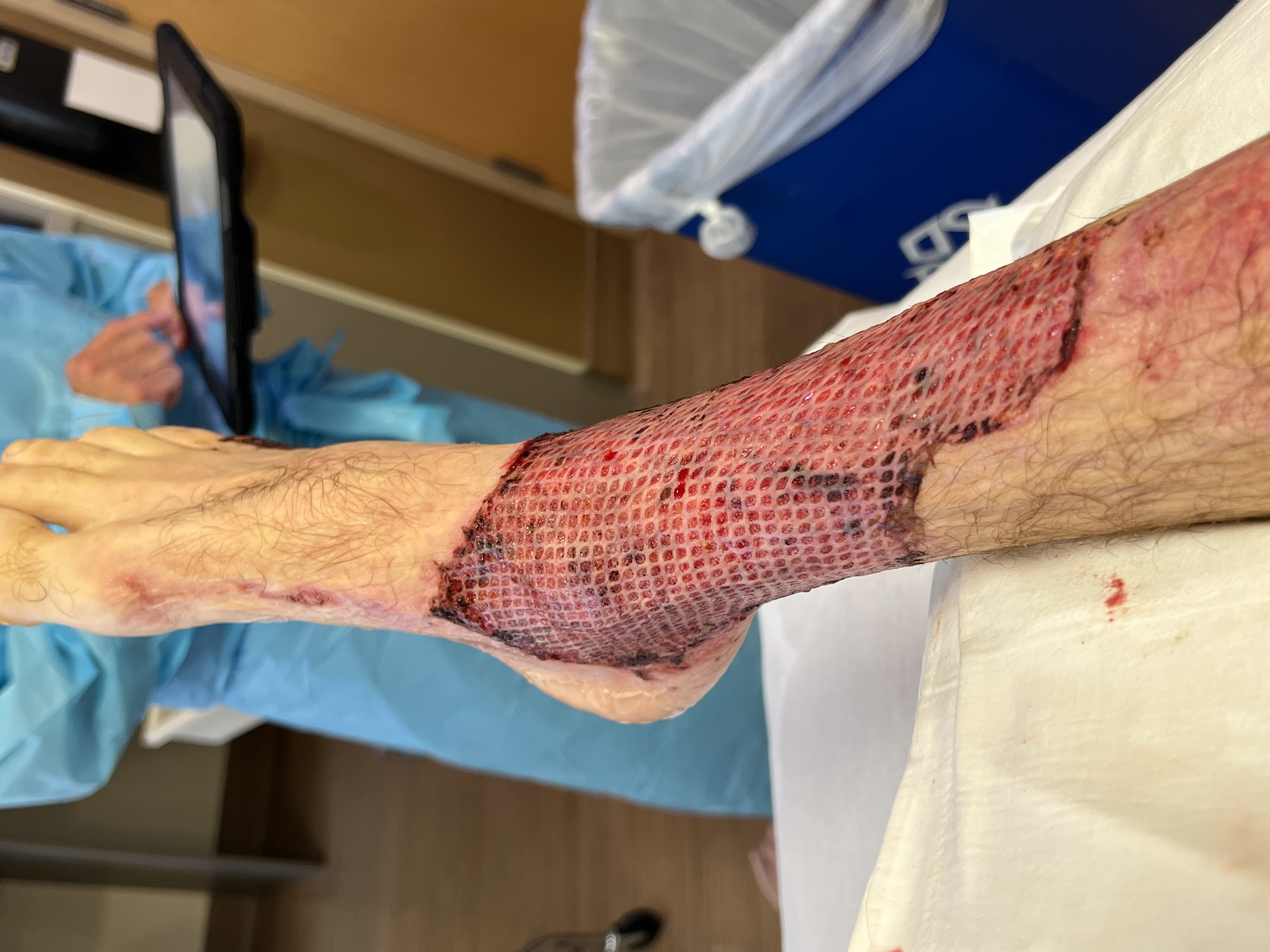
Skin Grafting
Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft. Surgeons may use skin grafting to treat: * extensive wounding or trauma * burns * areas of extensive skin loss due to infection such as necrotizing fasciitis or purpura fulminans * specific surgeries that may require skin grafts for healing to occur - most commonly removal of skin cancers Skin grafting often takes place after serious injuries when some of the body's skin is damaged. Surgical removal (excision or debridement) of the damaged skin is followed by skin grafting. The grafting serves two purposes: reducing the course of treatment needed (and time in the hospital), and improving the function and appearance of the area of the body which receives the skin graft. There are two types of skin grafts: * The more common type involves removing a thin layer of skin from a healthy part of the body (the donor section) - like peeling a potato. * A full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Les Vans
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1900 Deaths
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album '' Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slipk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1830 Births
Year 183 ( CLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 936 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 183 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * An assassination attempt on Emperor Commodus by members of the Senate fails. Births * January 26 – Lady Zhen, wife of the Cao Wei state Emperor Cao Pi (d. 221) * Hu Zong, Chinese general, official and poet of the Eastern Wu state (d. 242) * Liu Zan (Zhengming), Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 255) * Lu Xun Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary critic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Named It
''Whonamedit?'' is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliographies. The dictionary is hosted in Norway and maintained by medical historian Ole Daniel Enersen Ole Daniel Enersen (born March 14, 1943, in Oslo, Norway) is a Norwegian climber, photographer, journalist, writer, and medical historian. In 1965 he made the first ascent of the Trollveggen mountain in Romsdalen, Norway, along with Leif Norman .... References External links * Medical websites Medical dictionaries Eponyms {{online-dict-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Académie De Médecine
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Lyon
The University of Lyon (french: Université de Lyon), located in Lyon and Saint-Étienne, France, is a center for higher education and research comprising 11 members and 24 associated institutions. The three main universities in this center are: Claude Bernard University Lyon 1, which focuses upon health and science studies and has approximately 27,000 students; Lumière University Lyon 2, which focuses upon the social sciences and arts, and has about 30,000 students; Jean Moulin University Lyon 3, which focuses upon the law and humanities with about 20,000 students. Members *Claude Bernard University Lyon 1 *Lumière University Lyon 2 *Jean Moulin University Lyon 3 *Jean Monnet University *École Normale Supérieure de Lyon *École centrale de Lyon * École nationale des travaux publics de l'État (ENTPE) *INSA Lyon *Institut d'études politiques de Lyon * VetAgro Sup (previously École Nationale Vétérinaire de Lyon) *École nationale d'ingénieurs de Saint-Étienne, ( ENIS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathological Anatomy
Anatomical pathology (''Commonwealth'') or Anatomic pathology (''U.S.'') is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination of organs and tissues. Over the last century, surgical pathology has evolved tremendously: from historical examination of whole bodies (autopsy) to a more modernized practice, centered on the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer to guide treatment decision-making in oncology. Its modern founder was the Italian scientist Giovan Battista Morgagni from Forlì. Anatomical pathology is one of two branches of pathology, the other being clinical pathology, the diagnosis of disease through the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids or tissues. Often, pathologists practice both anatomical and clinical pathology, a combination known as general pathology. Similar specialties exist in veterinary pathology. Differences with clinical pathology Anatomic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie-François-Sadi Carnot
Marie François Sadi Carnot (; 11 August 1837 – 25 June 1894) was a French statesman, who served as the President of France from 1887 until his assassination in 1894. Early life Marie François Sadi Carnot was the son of the statesman Hippolyte Carnot and was born in Limoges, Haute-Vienne. His third given name Sadi was in honour of his uncle Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, the engineer who formulated the second law of thermodynamics and is generally regarded as the founder of the subject, named after the famed Persian poet Sadi of Shiraz. Like his uncle, Marie François too came to be known as Sadi Carnot. In his scientific-mindedness and Republican leanings, he resembled his grandfather, Lazare Carnot, the military modernizer and member of the Directory of the French Revolution. He was educated as a civil engineer and was a highly distinguished student at both the École Polytechnique and the École des Ponts et Chaussées. After his academic course, he obtained an appointme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Légion D'Honneur
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon Bonaparte, it has been retained (with occasional slight alterations) by all later French governments and regimes. The order's motto is ' ("Honour and Fatherland"); its seat is the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur next to the Musée d'Orsay, on the left bank of the Seine in Paris. The order is divided into five degrees of increasing distinction: ' (Knight), ' (Officer), ' (Commander), ' (Grand Officer) and ' (Grand Cross). History Consulate During the French Revolution, all of the French orders of chivalry were abolished and replaced with Weapons of Honour. It was the wish of Napoleon Bonaparte, the First Consul, to create a reward to commend civilians and soldiers. From this wish was instituted a , a body of men that was not an order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts function in groups of connected cells. Individual cells cannot make bone. A group of organized osteoblasts together with the bone made by a unit of cells is usually called the osteon. Osteoblasts are specialized, terminally differentiated products of mesenchymal stem cells. They synthesize dense, crosslinked collagen and specialized proteins in much smaller quantities, including osteocalcin and osteopontin, which compose the organic matrix of bone. In organized groups of disconnected cells, osteoblasts produce hydroxylapatite, the bone mineral, that is deposited in a highly regulated manner, into the organic matrix forming a strong and dense mineralized tissues, mineralized tissue, the mineralized mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1938.jpg)

