|
Kamruddin Ahmed
Kamruddin Ahmed (1912-1982) was a Bangladeshi diplomat, lawyer and politician. Early life Ahmed was born on 8 September 1912 in Sholaghar, Sreenagar Upazila, Munshiganj District, Bengal Presidency, British India. He graduated from Barisal Zilla School in 1929 and from B. M. College in 1931. He completed his B.A. in 1934 and M.A. in 1935 from the University of Dhaka in English. Career Ahmed after finishing his studies joined Armanitola Government High School in Dhaka as a teacher. He was a supporter of All India Muslim League which he left after the Partition of India in 1947. In East Pakistan he joined the Sarba-daliya Rastrabhasa Sangram Parishad (All Party State Language Movement) which campaigned for Bengali language to be made a state language of Pakistan. In 1954 he joined the Awami Muslim League and was elected to the Central Committee of the Awami Muslim league in 1955. He then left politics to join the Pakistan diplomatic service. He was appointed Deputy High Commission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sreenagar Upazila
Sreenagar ( bn, শ্রীনগর) is an upazila of Munshiganj District in the Division of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Division of Dhaka Geography Sreenagar is located at . It has 36344 households and total area 202.98 km2. Demographics As of the 1991 Bangladesh census, Sreenagar has a population of 205797. Males constitute 49.88% of the population, and females 50.12%. This Upazila's eighteen up population is 99514. Sreenagar has an average literacy rate of 39.1% (7+ years), and the national average of 32.4% literate. Administration Sreenagar Upazila is divided into 14 Union Parishads: Atpara, Baghra, Baraikhali, Bhagyakul, Birtara, Hasara, Kolapara, Kukutia, Patabhog, Rarikhal, Sholaghar, Shyamsiddhi, Sreenagar, and Tantar. The union parishads are subdivided into 102 mauzas and 147 villages. See also *Upazilas of Bangladesh An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Banglad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munshiganj District
Munshiganj ( bn, মুন্সীগঞ্জ), also historically known as Bikrampur, is a district in central Bangladesh. It is a part of the Dhaka Division and borders Dhaka District. Geography Total land area is 235974 acres (954 km2), out of which 138472 acres (560 km2) are cultivable and 5609 acres (23 km2) are fallow land. It has no forest area. 40277 acres (163 km2) of land is irrigated while 26242 acres (106 km2) of land is under river. It has 14 rivers of 155 km passing through. Administration The district consists of 6 upazilas: ref name=Banglapedia #Lohajang Upazila # Sreenagar Upazila # Munshiganj Sadar Upazila # Sirajdikhan Upazila # Tongibari Upazila #Gazaria Upazila Demographics According to the 2011 Bangladesh census, Munshiganj District had a population of 1,445,660, of which 721,552 were males and 724,108 were females. Rural population was 1,259,554 (87.13%) while urban population was 186,106 (12.87%). Munshiganj had a litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
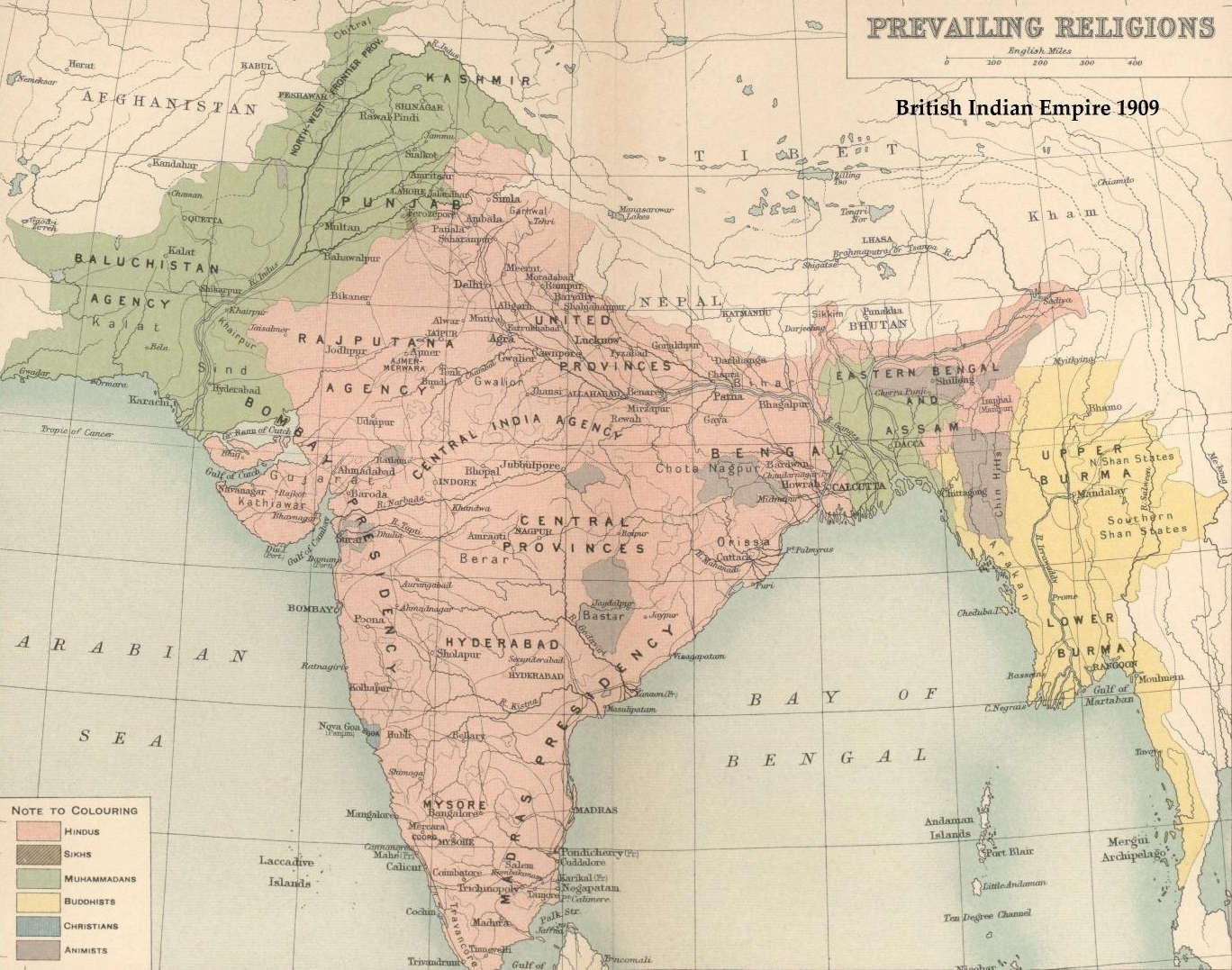
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911. The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in Mughal Bengal during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (HEIC), a British monopoly with a Royal Charter, competed with other European companies to gain influence in Bengal. After the decisive overthrow of the Nawab of Bengal in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the HEIC expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barisal Zilla School
Barishal Zilla School (), popularly known as BZS, is a public educational institution for boys, located in Barisal, Bangladesh. It was the first high school established in Barisal Division. It was founded as Barisal English School on 23 December 1829 by W. N. Garrett. It began with 27 students. In 1853, it was renamed Barisal Zilla School. Notable alumni * A. K. Fazlul Huq, Prime Minister of Bengal (1937–1943) * Khan Bahadur Hasem Ali Khan, Bengali nationalist and former minister of United Bengal * Abdul Jabbar Khan, Speaker of the National Assembly of Pakistan (1965-1969) * Abdur Rahman Biswas, President of Bangladesh (1991-1996) * Altaf Mahmud, music composer * Sardar Fazlul Karim, philosopher * Buddhadeb Guha, writer * Golam Mustafa, Ekushey Padak and National Film Award winning actor * Manzoor Alam Beg, father of the fine art photography movement in Bangladesh, Alokchitracharya (the great teacher of photography), Ekushey Padak awardee * Lieutenant General Hasan Mashhu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Dhaka
The University of Dhaka (also known as Dhaka University, or DU) is a public research university located in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is the oldest university in Bangladesh. The university opened its doors to students on July 1st 1921. Currently it is the largest public research university in Bangladesh, with a student body of 46,150 and a faculty of 1,992. Nawab Bahadur Sir Khwaja Salimullah, who played a pioneering role in establishing the university in Dhaka, donated 600 acres of land from his estate for this purpose. It has made significant contributions to the modern history of Bangladesh. After the Partition of India, it became the focal point of progressive and democratic movements in Pakistan. Its students and teachers played a central role in the rise of Bengali nationalism and the independence of Bangladesh in 1971. Notable alumni include Muhammad Yunus (winner 2006 Nobel Peace Prize, pioneer of microcredit), Natyaguru Nurul Momen (pioneer literature, theatre & cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armanitola Government High School
Armanitola Government High School is a secondary school for boys in Armanitola, in the old part of Dhaka, Bangladesh. It celebrated its centenary in 2004. History This school was established in 1904 by the British government, as an experimental school of the only teacher training college of East Bengal at that time. The school started at a vast campus with red brick buildings constructed in the British style at a location in front of the Tara Masjid ( Star Mosque), a famous monument of Muslim architecture. Within a few years after its establishment, it drew attention of the city dwellers for its performance in education, sports and culture. The school, however, could not sustain its name and fame during later years, particularly during the Pakistan period. Only by turning it into a government school in 1960 could it be saved from chronic financial crisis. Even after the independence of Bangladesh, it took a long time for the school to recover. Only since 1992 has it started to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastrabhasa Sangram Parishad
The Rashtrabhasha Sangram Parishad (''National Language Action Committee'') was an organisation founded by Bengali politicians and intellectuals to agitate for the recognition of the Bengali language by the Government of Pakistan. It was established on 1 October 1948 by Nurul Bhuiyan.It became one of the most influential groups during the Bengali Language Movement. Tamaddun Majlish catalyzed the foundation of the first Rashtrabhasha Sangram Parishad. It was founded at the end of December in 1947. Founding convener of the committee was Nurul Huq Bhuiyan. Other founding members were Shamsul Alam, Abul Khaer, Abdul Wahed Choudhury and Oli Ahad. Later the committee was expanded as Mohammad Toaha and Syed Nazrul Islam Syed Nazrul Islam ( bn, সৈয়দ নজরুল ইসলাম, Soiyod Nozrul Islam; 1925 – 3 November 1975) was a Bangladeshi politician and a senior leader of the Awami League. During the Bangladesh Liberation War, he was declared a ... joined in. Accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Pakistan Awami Muslim League
Awami League ( ur, ; bn, আওয়ামী লীগ) was a Pakistani political party founded by Huseyn Shaheed Suhrawardy in February 1950. Pir of Manki Sharif and Khan Ghulam Mohammad Khan from the North-West Frontier Province (NWFP) joined it soon afterwards. History In East Pakistan, East Pakistan Awami Muslim League ( bn, পূর্ব পাকিস্তান আওয়ামী মুসলিম লীগ) was founded by Abdul Hamid Khan Bhashani and Yar Mohammad Khan in June 1949. It was established as the Bengali alternative to the Urdu dominated Muslim League in Pakistan and over centralization of the government. The party quickly gained massive popular support in East Bengal. In the 1954 provincial election in Bengal, the party won 143 seats. The United Front of East Pakistan led by Haq, Bhasani and Surahwardhy the party won a total of 223 seats, soundly defeating the Muslim League with 10 seats. In 1950, Iftikhar Mamdot, who was dismissed from the premi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Society Of Bangladesh
The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh is a non political and non profit research organisation registered under both Society Act of 1864 and NGO Bureau, Government of Bangladesh. The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh was established as the Asiatic Society of East Pakistan in Dhaka in 1952 by a number of Muslim leaders, and renamed in 1972. Ahmed Hasan Dani, a noted Muslim historian and archaeologist of Pakistan played an important role in founding this society. He was assisted by Muhammad Shahidullah, a Bengali linguist. The society is housed in Nimtali, walking distance from the Curzon Hall of Dhaka University, locality of Old Dhaka. Publications The society's publications include: * ''Banglapedia, the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh'' (edition 2, 2012) * ''Encyclopedia of Flora and Fauna of Bangladesh'' (2010, 28 volumes) * ''Cultural Survey of Bangladesh, a documentation of the country's cultural history, tradition and heritage'' (2008, 12 volumes) * ''Children’s Banglapedia'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalism, Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani Military dictatorship, military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the 1971 Bangladesh genocide, Bangladesh genocide. In response to the violence, members of the Mukti Bahini—a guerrilla resistance movement formed by Bengali military, paramilitary and civilians—launched a mass Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against the Pakistani military, liberating numerous towns and cities in the initial months of the conflict. At first, the Pakis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukti Bahini
The Mukti Bahini ( bn, মুক্তিবাহিনী, translates as 'freedom fighters', or liberation army), also known as the Bangladesh Forces, was the guerrilla resistance movement consisting of the Bangladeshi military, paramilitary and civilians during the Bangladesh Liberation War, War of Liberation that transformed East Pakistan into Bangladesh in 1971. They were initially called the Mukti Fauj. On 7 March 1971 Sheikh Mujibur Rahman issued a call to the people of East Pakistan to prepare themselves for an all-out struggle. Later that evening resistance demonstrations began, and the military began a full-scale retaliation with Operation Searchlight, which continued through May 1971. A formal military leadership of the resistance was created in April 1971 under the Provisional Government of Bangladesh. The military council was headed by General M. A. G. Osmani''Unconventional Warfare in South Asia: Shadow Warriors and Counterinsurgency'', Gates and Roy, Routledge, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |