|
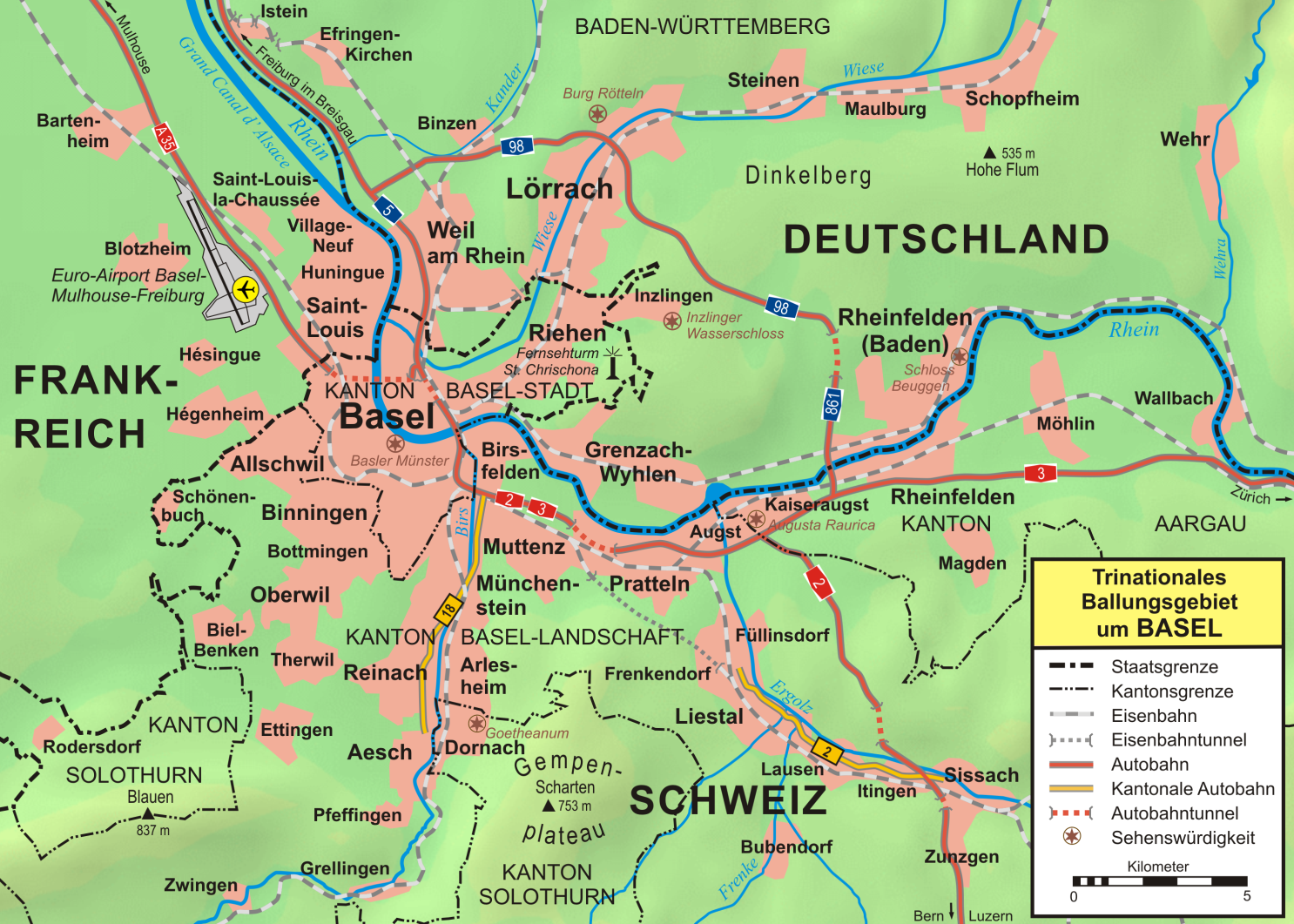
Kaiseraugst
Kaiseraugst (Swiss German: ''Chäiseraugscht'') is a municipality within the district of Rheinfelden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It is named after the Ancient Roman city of Augusta Raurica whose ruins are situated nearby. The prefix ''Kaiser-'' ("imperial") refers to the fact that from medieval times this town formed part of the Habsburg territory of Further Austria, as opposed to neighbouring village of Augst, part of the then Canton of Basel in the Old Swiss Confederacy. History About AD 300, following the loss of the Limes Germanicus and the right bank of the Rhine, the Roman army built a fort near the city of Augusta Raurica. The fort, which was named ''Castrum Rauracense'' was intended to serve as the headquarters of the '' legio I Martia'' and to protect a ford over the Rhine. During the 4th century, the fort grew in importance because it commanded a bridge that lay along the road from Gaul to the Danube, and sometime around 337 and 341 AD, an amphitheatre, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta Raurica
Augusta Raurica is a Roman archaeological site and an open-air museum in Switzerland located on the south bank of the Rhine river about 20 km east of Basel near the villages of Augst and Kaiseraugst. It is the site of the oldest known Roman colony on the Rhine. Founding Augusta Raurica, or ''Colonia Augusta Rauracorum'', was founded by Lucius Munatius Plancus around 44 BC in the vicinity of a local Gallic tribe, the Rauraci, relatives of the Helvetii. No archaeological evidence from this period has yet been found, leading to the conclusion that, either the settlement of the colony was disturbed by the civil war following the death of Julius Caesar, or that Plancus' colony was actually in the area of modern Basel, not Augst. Successful colonization of the site had to wait for Augustus' conquest of the central Alps around 15 BC. The oldest find to date at Augusta Raurica has been dated to 6 BC by dendrochronology. Name The inscription on Munatius Plancus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
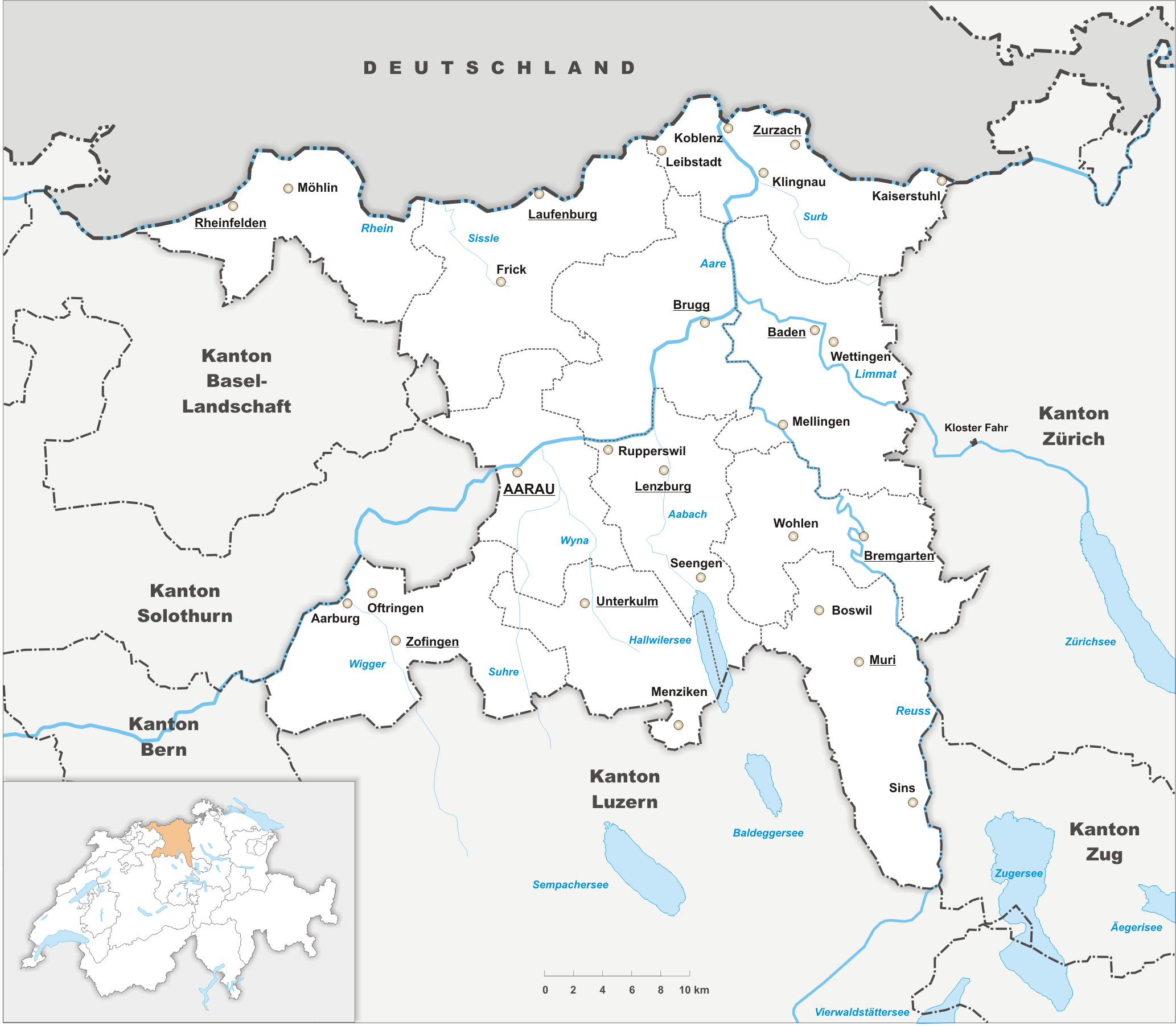
Rheinfelden, Switzerland
Rheinfelden ( gsw, Rhyfälde, ) is a municipality in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland, seat of the district of Rheinfelden. It is located 15 kilometres east of Basel. The name means the fields of the Rhine, as the town is located on the High Rhine. It is home to Feldschlösschen, the most popular beer in Switzerland. The city is across the river from Rheinfelden in Baden-Württemberg; the two cities were joined until Napoleon Bonaparte fixed the Germany–Switzerland border on the Rhine in 1802 and are still socially and economically tied. Geography The old town of Rheinfelden lies on the left bank of the Rhine, where the river is divided into two arms by the "Inseli", a roughly long island. Downstream of the Inseli and the ''Rheinbrücke'', the river bottoms drops to about deep, creating a huge and deadly vortex, known as the ''St-Anna-Loch. Nearly east is the '' Magdenerbach''. The wooded, gently-rising foothills of the '' Tafeljura'' lie south of the town. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinfelden (district)
Rheinfelden District lies in the northwest of the canton of Aargau in Switzerland, in the Fricktal region. Its capital is Rheinfelden. Around 88% of the population live in the conurbation of Basel. There are 14 municipalities, with a population of (as of ) living in an area of 112.09 km2. The population density is around 355 persons per square kilometre. Geography The Rheinfelden district has an area, , of . Of this area, or 44.0% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 39.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 13.4% is settled (buildings or roads). Demographics Rheinfelden district has a population () of . , 21.3% of the population are foreign nationals.Statistical Department of Canton Aargau -Bereich 01 -Bevölkerung accessed 20 January 2010 Economy there we ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augst
Augst ( Swiss German: ''Augscht'') is a municipality in the district of Liestal in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland. It was known as Augusta Raurica in Roman times. History Augst is first mentioned in 615 as ''Augustodunensem praesulem''. In 752 it was mentioned as ''Augusta'' and in 1288 as ''Augst''. Geography Augst has an area, , of . Of this area, or 34.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 6.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 40.2% is settled (buildings or roads), or 17.1% is either rivers or lakes.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 6.1% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 11.0% and transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenzach-Wyhlen
Grenzach-Wyhlen is a municipality in the district of Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated on the right bank of the Rhine, 7 km east of Basel, and 8 km south of Lörrach. It has borders to Inzlingen and Rheinfelden (Baden) in Germany, and Riehen (BS), Birsfelden (BL) and Kaiseraugst (AG) in Switzerland. History Grenzach-Wyhlen was established on January 1, 1975 from the two independent municipalities Grenzach and Wyhlen in the course of the Baden-Württemberg reform of the local governments. First settlements in today's municipality area are of Celtic origin, belonging to the Hallstatt culture in the early 1st millennium BC. The Celtic settlement was followed by Roman settlements and from the 3rd century on by Alemannic ones. The name "Wyhlen" originates in Alemannic "ze wilon", meaning "at the farmstead". The Roman settlement was called Carantiacum (well of Carantius). From this name today's name Grenzach emerged. In 1982 remains of a Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olsberg, Switzerland
Olsberg (Swiss German: ''Olschprg'') is a municipality in the district of Rheinfelden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. History During the neolithic era there was a small settlement near Olsberg. There was also a Roman farm in the area during the 1st Century AD. The modern village of Olsberg is first mentioned in 1236 as ''Olsperg''. The original settlement grew out from the courtyard of the convent. Until 1790, the convent held the low justice rights as well as the ownership of the land. With some interruptions, the part of Olsberg to the right of the ''Violenbach'' stream belonged to the Austrian district of Rheinfelden from 1330 until 1797. After 1797 it was a French protectorate and then went with the rest of the Fricktal to the newly formed Canton of Aargau in 1803. The left hand side of the stream belonged to the city of Basel from 1461 and later to Canton of Basel-Country (and now forms part of the municipality of Arisdorf). The Abbey Church was renovated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why the canton is called ''Aar- gau'' (meaning "Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a member of the Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitheatre Of Castrum Rauracense
The Amphitheatre of Catrum Rauracense is the youngest known surviving Roman amphitheatre across the entire Roman Empire. It is located in the ancient Roman fort of ''Castrum Rauracense'', near Kaiseraugst, Switzerland and only ruins survive today. It is the eighth Roman amphitheatre discovered in Switzerland to date. The fort was built around 300 AD, and the amphitheatre also dates to the fourth century, shortly before the collapse of the Roman Empire and local Germanic tribes moved into the area; the amphitheatre was extant by around 337 to 341 AD based on coins found at the site. It was built on the site of a Roman quarry and is roughly long and wide. A boathouse was planned to be built on the site, and the ruins of a Roman quarry were expected to be found. Excavations by the Aargau Canton Archaeology Department, led by Jakob Baerlocher, began on the site in December 2021 and the amphitheatre was discovered instead, with parts of the gates and side entrances complete with pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian The Apostate
Julian ( la, Flavius Claudius Julianus; grc-gre, Ἰουλιανός ; 331 – 26 June 363) was Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplatonic Hellenism in its place, caused him to be remembered as Julian the Apostate in Christian tradition. A nephew of Constantine, Julian was one of few in the imperial family to survive the purges and civil wars during the reign of Constantius II, his cousin. Julian became an orphan as a child after his father was executed in 337, and spent much of his life under Constantius's close supervision.''Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity'', "Julian the Apostate", p. 839 However, the emperor allowed Julian to freely pursue an education in the Greek-speaking east, with the result that Julian became unusually cultured for an emperor of his time. In 355, Constantius II summoned Julian to court and appointed him to rule Gaul. Despite his inexperience, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giebenach
Giebenach is a municipality in the district of Liestal in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland. History Giebenach is first mentioned in 1246 as ''in villa Gibenacho''. Geography Giebenach has an area, , of . Of this area, or 57.5% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 17.9% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 24.6% is settled (buildings or roads).Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 14.9% and transportation infrastructure made up 7.5%. Out of the forested land, 16.4% of the total land area is heavily forested and 1.5% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 44.8% is used for growing crops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Legions
This is a list of Roman legions, including key facts about each legion, primarily focusing on the Principate (early Empire, 27 BC – 284 AD) legions, for which there exists substantial literary, epigraphic and archaeological evidence. When Augustus became sole ruler in 31 BC, he disbanded about half of the over 50 legions then in existence. The remaining 28 legions became the core of the early Imperial army of the Principate (27 BC – AD 284), most lasting over three centuries. Augustus and his immediate successors transformed legions into permanent units, staffed by entirely career soldiers on standard 25-year terms. During the Dominate period (near the end of the Empire, 284–476), legions were also professional, but are little understood due to scarcity of evidence compared to the Principate. What is clear is that late legions were radically different in size, structure, and tactical role from their predecessors, despite several retaining early period names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval continuation, the Eastern Roman Empire. It is thus a term that may span approximately 2,205 years (753 BC–1453 AD), during which the Roman armed forces underwent numerous permutations in size, composition, organisation, equipment and tactics, while conserving a core of lasting traditions. Historical overview Early Roman army (c. 500 BC to c. 300 BC) The early Roman army was the armed forces of the Roman Kingdom and of the early Roman Republic. During this period, when warfare chiefly consisted of small-scale plundering raids, it has been suggested that the army followed Etruscan or Greek models of organisation and equipment. The early Roman army was based on an annual levy. The army consisted of 3,000 infantrymen and 300 cavalrymen, all of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |