|
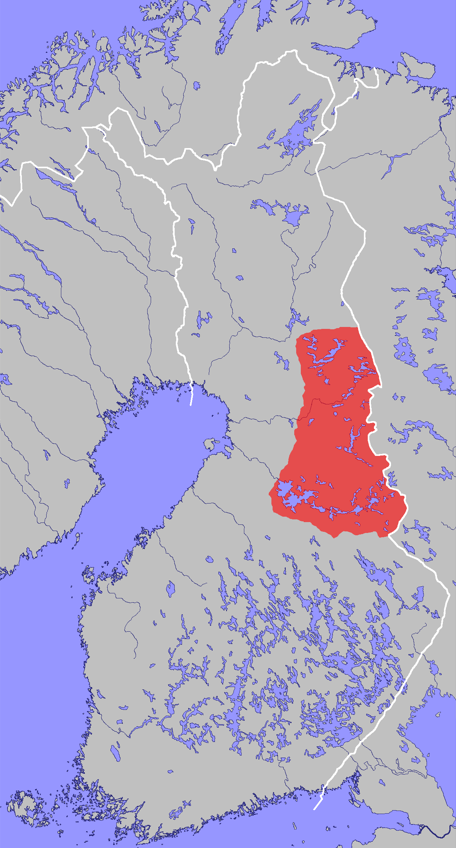
Kainuu Dialect
{{Short description, Dialect of Finnish Kainuu dialect is a dialect of Finnish spoken in Kainuu, Vaala, Koillismaa, Posio and Ranua. It belongs to the Savonian dialects, or more broadly, the eastern dialects of Finnish. Due to the region's close ties to North Ostrobothnia, the dialect has been influenced in vocabulary by Central and Northern Ostrobothnian dialects and vice versa.Puuttonen, Mikko (2018). Tutkijaryhmä selittää uudella tavalla Suomen murrealueet – Luonnonolojen synnyttämät kulttuurikuplat eriyttivät puhetavat'. hs.fi. Retrieved 2021-12-17. The Kainuu dialect can be divided into Northern, Central, and Southern groups. The Northern Kainuu dialect is spoken in Koillismaa, Posio and Ranua. The Central dialect is spoken in most of Kainuu, as well as in Vaala. The Southern dialect is spoken in Sotkamo and Kuhmo, in Southern Kainuu. Features As typical for non-standard dialects of Finnish, the /d/ sound usually occurs as other consonants in the Kainuu dialect. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotkamo
Sotkamo is a municipality of Finland, located in the Kainuu region about east of Kajaani, the capital of Kainuu. Vuokatti, in west of Sotkamo, is the most populous village in the municipality and also a popular skiing resort. Both Hiidenportti National Park and Tiilikkajärvi National Park are located in the municipality. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . In sports, Sotkamo is known for its pesäpallo team, Sotkamon Jymy. The Hiukka Stadium is the home field of Sotkamon Jymy, and its well-known competitor is Vimpelin Veto from Vimpeli, known as long-time arch-enemy of Sotkamon Jymy. - Faneille.com (in Finnish) One of the major landmarks of Sotkamo is the sandy beach of Hiukka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatalization (phonetics)
In phonetics, palatalization (, also ) or palatization is a way of pronouncing a consonant in which part of the tongue is moved close to the hard palate. Consonants pronounced this way are said to be palatalized and are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by affixing the letter ⟨ʲ⟩ to the base consonant. Palatalization cannot minimally distinguish words in most dialects of English, but it may do so in languages such as Russian, Mandarin, and Irish. Types In technical terms, palatalization refers to the secondary articulation of consonants by which the body of the tongue is raised toward the hard palate and the alveolar ridge during the articulation of the consonant. Such consonants are phonetically palatalized. "Pure" palatalization is a modification to the articulation of a consonant, where the middle of the tongue is raised, and nothing else. It may produce a laminal articulation of otherwise apical consonants such as and . Phonetically palatalized consona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortition
Fortition, also known as strengthening, is a consonantal change that increases the degree of stricture. It is the opposite of the more common lenition. For example, a fricative or an approximant may become a stop (i.e. becomes or becomes ). Although not as typical of sound change as lenition, fortition may occur in prominent positions, such as at the beginning of a word or stressed syllable; as an effect of reducing markedness; or due to morphological leveling. Examples The extremely common approximant sound is sometimes subject to fortition; since it is a semivowel, almost any change to the sound other than simple deletion would constitute fortition. It has changed into the voiced fricative in a number of indigenous languages of the Arctic, such as the Eskimo–Aleut languages and Ket, and also in some varieties of Spanish. In the Southern Ryukyuan language Yonaguni, it has changed word-initially into . Via a voiceless palatal approximant, it has turned in some Germanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epenthesis
In phonology, epenthesis (; Greek ) means the addition of one or more sounds to a word, especially in the beginning syllable ('' prothesis'') or in the ending syllable (''paragoge'') or in-between two syllabic sounds in a word. The word ''epenthesis'' comes from "in addition to" and ''en-'' "in" and ''thesis'' "putting". Epenthesis may be divided into two types: excrescence for the addition of a consonant, and for the addition of a vowel, svarabhakti (in Hindi, Bengali and other North Indian languages, stemming from Sanskrit) or alternatively anaptyxis (). The opposite process, where one or more sounds are removed, is referred to as elision. Uses Epenthesis arises for a variety of reasons. The phonotactics of a given language may discourage vowels in hiatus or consonant clusters, and a consonant or vowel may be added to make pronunciation easier. Epenthesis may be represented in writing, or it may be a feature only of the spoken language. Separating vowels A consonant may be ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphthong
A diphthong ( ; , ), also known as a gliding vowel, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech organ, speech apparatus) moves during the pronunciation of the vowel. In most International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects, varieties of English language, English, the phrase "no highway cowboy" () has five distinct diphthongs, one in every syllable. Diphthongs contrast with monophthongs, where the tongue or other speech organs do not move and the syllable contains only a single vowel sound. For instance, in English, the word ''ah'' is spoken as a monophthong (), while the word ''ow'' is spoken as a diphthong in most varieties (). Where two adjacent vowel sounds occur in different syllables (e.g. in the English word ''re-elect'') the result is described as hiatus (linguistics), hiatus, not as a diphthong. (The English word ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affricate
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pair. English has two affricate phonemes, and , often spelled ''ch'' and ''j'', respectively. Examples The English sounds spelled "ch" and "j" ( broadly transcribed as and in the IPA), German and Italian ''z'' and Italian ''z'' are typical affricates, and sounds like these are fairly common in the world's languages, as are other affricates with similar sounds, such as those in Polish and Chinese. However, voiced affricates other than are relatively uncommon. For several places of articulation they are not attested at all. Much less common are labiodental affricates, such as in German and Izi, or velar affricates, such as in Tswana (written ''kg'') or in High Alemannic Swiss German dialects. Worldwide, relatively few languages have af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuhmo
Kuhmo (known as ''Kuhmoniemi'' until 1937) is a town and a municipality in Finland and is located at the south-eastern corner of the Kainuu region. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . It has a borderline of with Russia ( Finnish-Russian border). Neighbour towns are Hyrynsalmi, Lieksa, Nurmes, Ristijärvi, Sotkamo and Suomussalmi. A neighbour city across the Russian border is Kostomuksha. Vartius, one of the border crossing points between Finland and Russia, is located in northern Kuhmo. Kuhmo´s eastern border is located at a drainage divider and town area belongs to drainage basin of Oulujärvi. The municipality is unilingually Finnish. History The first inhabitants arrived in Kuhmo after the last ice-age, around 8000 BCE. Proof of Stone Age habitation has been found around Ontojärvi and Lammasjärvi. Sami people inhabited Kuhmo area until migration from Karelia and Savonia pushed Sami people up no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
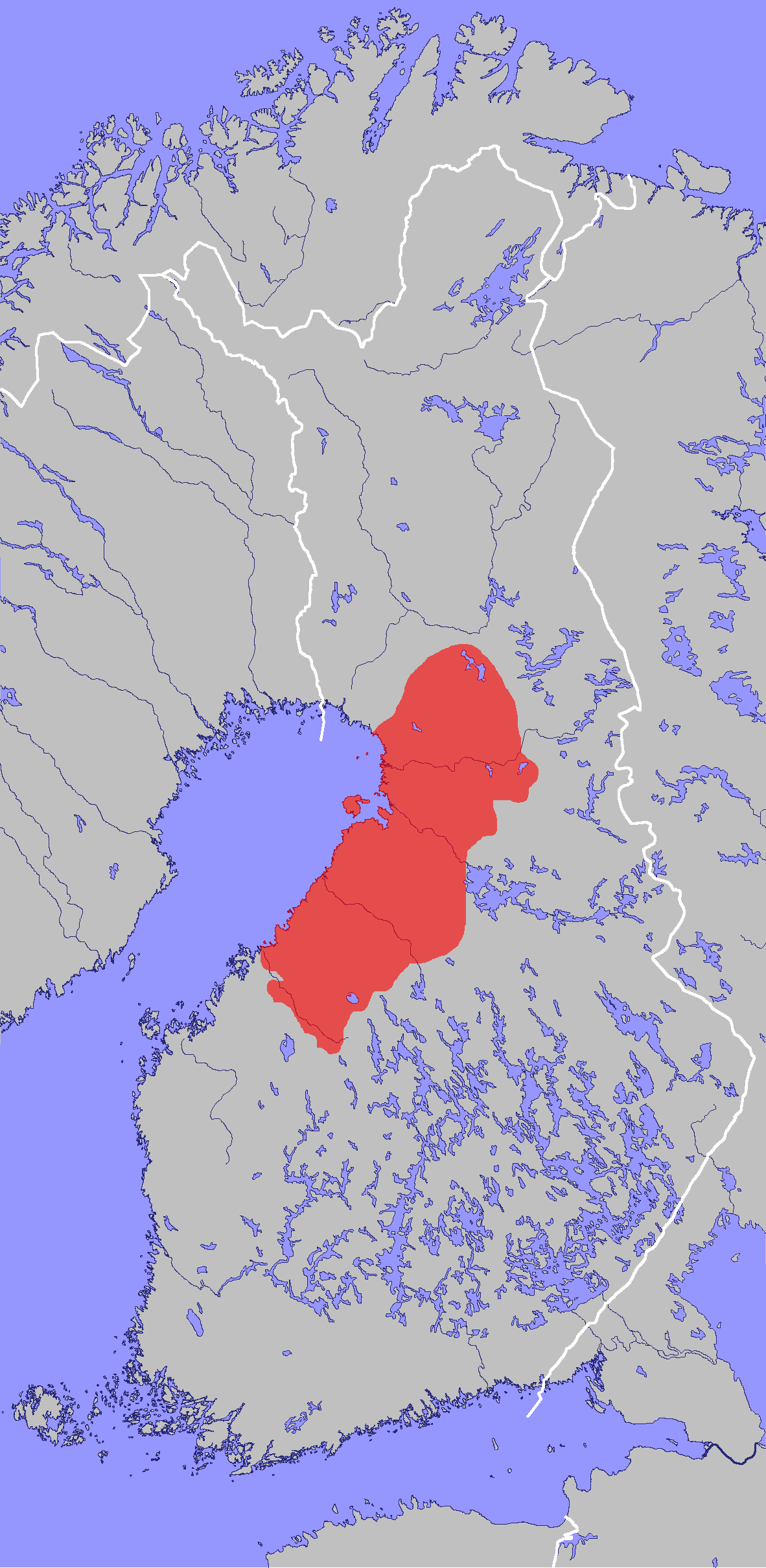
Central And Northern Ostrobothnian Dialects
Central and Northern Ostrobothnian dialects ( fi, Keski-ja Pohjois-Pohjanmaan murteet) are Western Finnish dialects spoken in Northern and Central Ostrobothnia, as well as in the Ranua municipality in Lapland. The dialects have been influenced by the Savonian dialects, the influence is weaker at the coasts and stronger in the inland areas. Features Pronunciation of standard ''D'' While the letter D in standard Finnish makes the sound , this sound is not used in most dialects of Finnish outside of loanwords. In the central and northern Ostrobothnian dialects, D is not pronounced - ''lehdet'' (leaves) is pronounced ''lehet''. In some occasions, a , or may be inserted in its place, such as ''syvän'', ''meijät'' and ''saaha'' (as opposed to standard ''sydän, meidät, saada''). The dialects of Kaustinen, Halsua and Veteli use an sound in the place of , for example ''lehdet'' is pronounced like ''lehret''. This is likely South Ostrobothnian influence, from the times befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Language
Finnish ( endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. Finnish orth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Ostrobothnia
North Ostrobothnia ( fi, Pohjois-Pohjanmaa; sv, Norra Österbotten) is a region of Finland. It borders the Finnish regions of Lapland, Kainuu, North Savo, Central Finland and Central Ostrobothnia, as well as the Russian Republic of Karelia. The easternmost corner of the region between Lapland, Kainuu and the Russian border is known as Koillismaa ("North-East Finland"). Historical provinces Municipalities The region of North Ostrobothnia is made up of 30 municipalities, of which 11 have city status (marked in bold). Koillismaa sub-region: *Kuusamo (16,177) *Taivalkoski (4,407) Nivala–Haapajärvi sub-region: *Haapajärvi (7,640) *Kärsämäki (2,758) *Nivala (11,053) *Pyhäjärvi (5,879) *Reisjärvi (2,992) Oulu sub-region: *Hailuoto (989) *Kempele (16,303) *Liminka (9,178) *Lumijoki (2,041) *Muhos (8,936) *Oulu (192,680) *Tyrnävä (6,482) Oulunkaari sub-region: * Ii (9,581) *Pudasjärvi (8,717) *Utajärvi (2,952) *Vaala (3,309) Raahe sub-region: *Pyhäjoki (3,35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savonian Dialects
The Savonian dialects (also called Savo Finnish)( fi, Savolaismurteet) are forms of the Finnish language spoken in Savonia and other parts of Eastern Finland. Finnish dialects are grouped broadly into Eastern and Western varieties; Savonian dialects are of the Eastern variety. Savonian dialects are the most widely distributed Finnish dialect group (setting aside the higher-level east/west split mentioned above). They are spoken in the Savonia region (in both North and South Savo), but also in North Karelia, parts of Päijät-Häme, Central Finland, Kainuu, Koillismaa district of Northern Ostrobothnia, the lake section between Southern and Central Ostrobothnia as far north as Evijärvi and in the municipalities of Pudasjärvi and the Southern part of Ranua in Lapland. Also the language spoken by forest settlers in Värmland and Norwegian Hedmark of Central Scandinavia belonged to the old Savonian dialects. The geographical area the Savonian dialects cover makes up one-third the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |